22 results in African Archaeology
Do cultural and biological variation correspond in the Middle Nile Valley Neolithic? Some insights from dental morphology
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2024, pp. 32-47
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Faith embodied: a tattooed individual from medieval Ghazali
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, e7
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Oued Beht, Morocco: a complex early farming society in north-west Africa and its implications for western Mediterranean interaction during later prehistory
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 July 2024, pp. 1199-1218
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Raw-material exploitation in the Earlier and Middle Stone Age in the Eastern Desert of Egypt: evidence from Wadi Abu Subeira
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, e13
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inequality or insecurity? The case of pre-colonial farming communities in southern Africa
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 135-154
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
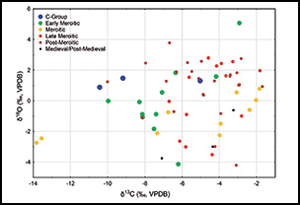
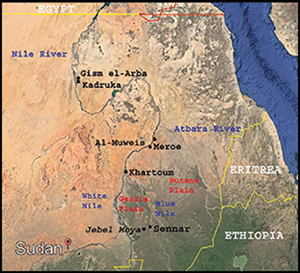
Isotopic evidence of an environmental shift at the fall of the Kushite kingdom of Meroë, Sudan
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2023, pp. 1501-1515
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Kanyimangin: the Early to Middle Pleistocene Transition in the south-west of the Turkana Basin
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2023, e25
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Social networks as risk-mitigation strategies in south-west Madagascar
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, pp. 1296-1312
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bitter legacy: archaeology of early sugar plantation and slavery in São Tomé
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, e30
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Real but unrealised: object transformations and political economy in East and southern Africa, AD 750–1250
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2023, pp. 975-990
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Jarigole mortuary tradition reconsidered
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 December 2022, pp. 1460-1477
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An archaeology of conversion? Evidence from Adulis for early Christianity and religious transition in the Horn of Africa
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 December 2022, pp. 1555-1573
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
A story of abandonment: settlements and landscape in the Niokolo-Koba National Park, Senegal
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2022, pp. 1330-1336
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
New radiocarbon dates from Jebel Moya (Sudan): 2500 years of burial activity
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2022, pp. 1015-1020
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
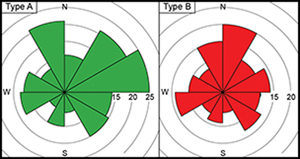
Hunting in the desert: assessing the form and use of kite-like structures in the western Sahara
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2022, pp. 719-726
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Detecting and mapping the ‘ephemeral’: magnetometric survey of a Pastoral Neolithic settlement at Luxmanda, Tanzania
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2022, pp. 298-318
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Masters and apprentices at the Chapel of Hatshepsut: towards an archaeology of ancient Egyptian reliefs
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2021, pp. 85-102
- Print publication:
- February 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The spatial organisation of Soba: a medieval capital on the Blue Nile
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2021, pp. 213-220
- Print publication:
- February 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Zimbabwe Culture and the development of the Nambya state in north-western Zimbabwe
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2021, e34
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The archaeology of complexity and cosmopolitanism in medieval Ethiopia: an introduction
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2021, pp. 450-466
- Print publication:
- April 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation