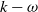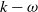In order to improve the performance of 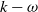 $k - \omega $ SST model in turbomachinery, previous studies have used the machine-learning (ML) technique to obtain turbulence models (for example, the ML-RANS EQ model). However, these models do not lead to satisfactory results in complex flows in turbomachinery. In this study, we use non-equilibrium training dataset to obtain a new turbulence model (i.e., the ML-RANS TR-NE-EQ model). Calculations in various cases of turbine cascade flows show that ML-RANS TR-NE-EQ model performs obviously better than ML-RANS EQ model as well as
$k - \omega $ SST model in turbomachinery, previous studies have used the machine-learning (ML) technique to obtain turbulence models (for example, the ML-RANS EQ model). However, these models do not lead to satisfactory results in complex flows in turbomachinery. In this study, we use non-equilibrium training dataset to obtain a new turbulence model (i.e., the ML-RANS TR-NE-EQ model). Calculations in various cases of turbine cascade flows show that ML-RANS TR-NE-EQ model performs obviously better than ML-RANS EQ model as well as 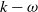 $k - \omega $ SST model.
$k - \omega $ SST model.