We consider the following Kirchhoff-type problem in an unbounded exterior domain 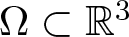 $\Omega\subset\mathbb{R}^{3}$:(*)
$\Omega\subset\mathbb{R}^{3}$:(*)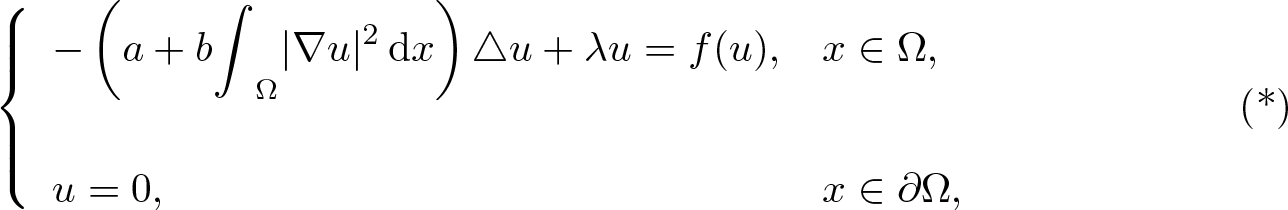 \begin{align}\left\{\begin{array}{ll}-\left(a+b\displaystyle{\int}_{\Omega}|\nabla u|^{2}\,{\rm d}x\right)\triangle u+\lambda u=f(u), & x\in\Omega,\\\\u=0, & x\in\partial \Omega,\\\end{array}\right.\end{align}
\begin{align}\left\{\begin{array}{ll}-\left(a+b\displaystyle{\int}_{\Omega}|\nabla u|^{2}\,{\rm d}x\right)\triangle u+\lambda u=f(u), & x\in\Omega,\\\\u=0, & x\in\partial \Omega,\\\end{array}\right.\end{align}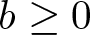 $b\geq0$, and λ > 0 are constants,
$b\geq0$, and λ > 0 are constants, 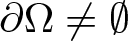 $\partial\Omega\neq\emptyset$,
$\partial\Omega\neq\emptyset$, 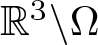 $\mathbb{R}^{3}\backslash\Omega$ is bounded,
$\mathbb{R}^{3}\backslash\Omega$ is bounded, 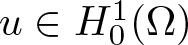 $u\in H_{0}^{1}(\Omega)$, and
$u\in H_{0}^{1}(\Omega)$, and 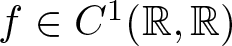 $f\in C^1(\mathbb{R},\mathbb{R})$ is subcritical and superlinear near infinity. Under some mild conditions, we prove that if
$f\in C^1(\mathbb{R},\mathbb{R})$ is subcritical and superlinear near infinity. Under some mild conditions, we prove that if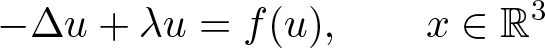 \begin{equation*}-\Delta u+\lambda u=f(u), \qquad x\in \mathbb R^3 \end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}-\Delta u+\lambda u=f(u), \qquad x\in \mathbb R^3 \end{equation*}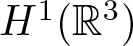 $H^1(\mathbb R^3)$ and the diameter of the hole
$H^1(\mathbb R^3)$ and the diameter of the hole 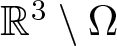 $\mathbb R^3\setminus \Omega$ is small enough, then the problem (*) admits a positive solution. Same conclusion holds true if Ω is fixed and λ > 0 is small. To our best knowledge, there is no similar result published in the literature concerning the existence of positive solutions to the above Kirchhoff equation in exterior domains.
$\mathbb R^3\setminus \Omega$ is small enough, then the problem (*) admits a positive solution. Same conclusion holds true if Ω is fixed and λ > 0 is small. To our best knowledge, there is no similar result published in the literature concerning the existence of positive solutions to the above Kirchhoff equation in exterior domains.