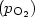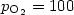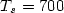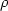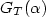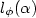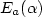Physics of Organic Materials and Devices
Research Article
Dark electrical and photovoltaic properties of Schottky device based on organic thin film of 4-tricyanovinyl-N, N-diethylaniline
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2009, 30403
-
- Article
- Export citation
Surfaces, Interfaces and Films
Research Article
Accelerated nitridation and oxidation by plasma on polyethylene
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2009, 30501
-
- Article
- Export citation
Acoustically conceal an object with hearing
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 July 2009, 20501
-
- Article
- Export citation
Phase diagrams of ferroelectric thin film with two surface layers
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 July 2009, 10503
-
- Article
- Export citation
Some aspects of pulsed laser deposition of Si nanocrystalline films
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 September 2009, 20502
-
- Article
- Export citation
Wettability and surface forces measured by atomic force microscopy: the role of roughness
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 July 2009, 10504
-
- Article
- Export citation
Efficient field emission from structured gold nanowire cathodes
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2009, 30502
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spectroscopic investigations on tetravalent doped LiCoO2 thin film cathodes
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 September 2009, 20503
-
- Article
- Export citation
Substrate temperature dependence of the structure of polythiophene thin films obtained by Matrix Assisted Pulsed Laser Evaporation (MAPLE)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2009, 10505
-
- Article
- Export citation
Electrical properties and Kerr effect study of evaporated Fe/Si and Fe/glass thin films
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2009, 30503
-
- Article
- Export citation
Electrochemical production of Fe-Cu films: determinationof the deposition potentials and their effect on microstructural and magnetic properties
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2009, 30504
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanomaterials and Nanotechnologies
Research Article
Stability, size and optical properties of colloidal silver nanoparticles prepared by electrical arc discharge in water
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 July 2009, 10601
-
- Article
- Export citation
Surfaces, Interfaces and Films
Research Article
Structure and optical constants of electron beam deposited zinc nitride films
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2009, 20504
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanomaterials and Nanotechnologies
Research Article
Layer-by-layer self assembly deposition and characterizationof TiO2 nanoparticles by using a short chain polycation
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 July 2009, 10602
-
- Article
- Export citation
The effects of nitrogen on the configurations and magnetic moments ofsmall iron, cobalt and nickel clusters
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2009, 30601
-
- Article
- Export citation
Surfaces, Interfaces and Films
Research Article
The coordinate function in the problem of the nonlinear dynamic response of an elongated printed circuit board (PCB) to a drop impactapplied to its supports
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 October 2009, 20505
-
- Article
- Export citation
Photonics
Research Article
Optimisation of a corrugation-pitch-modulated DFB laser structure with inhomogeneous coupling coefficient for stable single longitudinal mode operation
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2009, 30701
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanomaterials and Nanotechnologies
Research Article
The study of optical properties of ZnS, ZnS:Co2+ nanoparticles
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 October 2009, 20601
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structure and photoluminescence properties of SnO2nanowires synthesized from SnO powder
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2009, 10603
-
- Article
- Export citation
Conductance of disordered semiconducting nanowires and carbon nanotubes: a chain of quantum dots
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2009, 10604
-
- Article
- Export citation