Articles
A comparison of two aluminizing methods for corrosion protection in the wet seal of molten carbonate fuel cells
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1834-1839
-
- Article
- Export citation
Polycarbodiimide and polyimide/cyanate thermoset in situ molecular composites
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1840-1847
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compositional and physical changes on perovskite crystal surfaces
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1848-1852
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microstructural development of SCS-6 SiC fibers during high temperature creep
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1853-1860
-
- Article
- Export citation
Photoluminescence in PbMg1/3Nb2/3O3–PbIn1/2Nb1/2O3 systems
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1861-1864
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interactions between bismuth oxide and ceramic substrates for thick film technology
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1865-1874
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fabrication of dense nanocrystalline ZrO2−3 wt. % Y2O3 by hot-isostatic pressing
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1875-1880
-
- Article
- Export citation
Binder surface segregation during spray drying of ceramic slurry
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1881-1887
-
- Article
- Export citation
Early age microstructure of the paste-aggregate interface and its evolution
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1888-1898
-
- Article
- Export citation
Detection of contact damage in ceramics by an ultrasonic method
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1899-1904
-
- Article
- Export citation
System Bi–Sr–O: Synergistic measurements of thermodynamic properties using oxide and fluoride solid electrolytes
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1905-1918
-
- Article
- Export citation
Analytic embedded atom method potentials for face-centered cubic metals
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1919-1927
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stress evolution in passivated thin films of Cu on silica substrates
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1928-1937
-
- Article
- Export citation
Atomic force microscope investigation of the thermal stability of thin TiSi2 films
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1938-1949
-
- Article
- Export citation
Solid-phase reactions in Ir/(111)Si systems studied by means of x-ray emission spectroscopy
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1950-1955
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evolution of stresses in passivated and unpassivated metal interconnects
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1956-1966
-
- Article
- Export citation
Appropriate passivation structure in dynamic random access memory devices to improve stress-related reliability performance after plastic packaging
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1967-1973
-
- Article
- Export citation
Downshift of Raman peak in diamond powders
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1974-1976
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthesis of a Mo/Nb mixed carbide
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1977-1988
-
- Article
- Export citation
Large Faraday effect and local structure of alkali silicate glasses containing divalent europium ions
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 1989-1995
-
- Article
- Export citation


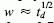 , where
, where  of component binary oxides. The results are discussed in the light of the phase diagram and compared with calorimetric and chemical potential measurements reported in the literature. The combined use of emf data from cells incorporating fluoride and oxide electrolytes enhances the reliability of derived data.
of component binary oxides. The results are discussed in the light of the phase diagram and compared with calorimetric and chemical potential measurements reported in the literature. The combined use of emf data from cells incorporating fluoride and oxide electrolytes enhances the reliability of derived data.