The Mangalitza pig breed has suffered strong population reductions due to competition with more productive cosmopolitan breeds. In the current work, we aimed to investigate the effects of this sustained demographic recession on the genomic diversity of Mangalitza pigs. By using the Porcine Single Nucleotid Polymorphism BeadChip, we have characterized the genome-wide diversity of 350 individuals including 45 Red Mangalitza (number of samples; n=20 from Hungary and n=25 from Romania), 37 Blond Mangalitza, 26 Swallow-belly Mangalitza, 48 Blond Mangalitza × Duroc crossbreds, 5 Bazna swine, 143 pigs from the Hampshire, Duroc, Landrace, Large White and Pietrain breeds and 46 wild boars from Romania (n=18) and Hungary (n=28). Performance of a multidimensional scaling plot showed that Landrace, Large White and Pietrain pigs clustered independently from Mangalitza pigs and Romanian and Hungarian wild boars. The number and total length of ROH (runs of homozygosity), as well as FROH coefficients (proportion of the autosomal genome covered ROH) did not show major differences between Mangalitza pigs and other wild and domestic pig populations. However, Romanian and Hungarian Red Mangalitza pigs displayed an increased frequency of very long ROH (>30 Mb) when compared with other porcine breeds. These results indicate that Red Mangalitza pigs underwent recent and strong inbreeding probably as a consequence of severe reductions in census size.

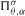 on the ordered infinite simplex. Furthermore, we prove the central limit theorem related to this distribution when both the mutation rate
on the ordered infinite simplex. Furthermore, we prove the central limit theorem related to this distribution when both the mutation rate 