Obesity and osteoporosis affect millions of Americans. While phenotypically, obesity is negatively correlated with fracture risk, research on a genetic basis for this relationship is lacking. We used males and females from 16 LGXSM recombinant inbred (RI) mouse strains to investigate the genetically mediated relationship between obesity and osteoporosis-related traits. First, heritabilities were estimated for (1) bone morphology properties determined by microCT (femoral and radial diaphyseal bone cross-sectional area and moments of inertia, as well as proximal tibial trabecular bone volume, connectivity density, structure model index, trabecular number, trabecular thickness and trabecular separation), (2) mechanical properties determined by bending tests (femoral and radial rigidity, yield moment, ultimate moment, fracture displacement and post-yield displacement), and (3) effective material properties (femoral and radial modulus of elasticity and ultimate tensile strength). All femoral (H2=43–74%) and tibial traits (H2=31–56%) were heritable; as were 8 of 10 radial traits (H2=21–33%). Eighteen significant genetic correlations were discovered between obesity- and osteoporosis-related phenotypes. Genetic correlations indicate that gene effects associated with increased fat mass and leptin levels are also associated with larger, stronger femora. Gene effects associated with larger, stronger radii and with denser tibiae were also associated with increased fat mass but not with leptin levels. Furthermore, quantitative trait loci (QTLs) previously reported for obesity and leptin levels also had effects on bone morphology, mechanical and material properties. Our results support the use of the LG/J-by-SM/J mouse intercross populations as models for normal, complex genetic variation in obesity, bone properties and their interrelationship.


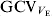 ) was estimated to be 20%, which is lower than estimates obtained for other species. A few genomic regions involved in the stability of one trait or two traits were detected, and these did not have an important influence on the mean of the trait. One region that could be associated with the environmental correlations between traits was also detected.
) was estimated to be 20%, which is lower than estimates obtained for other species. A few genomic regions involved in the stability of one trait or two traits were detected, and these did not have an important influence on the mean of the trait. One region that could be associated with the environmental correlations between traits was also detected.