1 results
Middle-school students’ school lunch consumption does not meet the new Institute of Medicine's National School Lunch Program recommendations
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 14 / Issue 10 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2011, pp. 1876-1881
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation

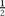 serving of fruit,
serving of fruit, 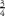 serving of vegetables, 8 oz of milk and
serving of vegetables, 8 oz of milk and 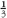 serving of whole grains at lunch. Non-NSLP consumers reported almost no intake of fruit, vegetables or milk, and consumed
serving of whole grains at lunch. Non-NSLP consumers reported almost no intake of fruit, vegetables or milk, and consumed 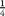 serving of whole grains at lunch. Among NSLP consumers, about 40 % selected and consumed a fruit serving. About two-thirds of students selected a vegetable, consuming about 67 %. Less than 4 % selected a dark green or orange vegetable.
serving of whole grains at lunch. Among NSLP consumers, about 40 % selected and consumed a fruit serving. About two-thirds of students selected a vegetable, consuming about 67 %. Less than 4 % selected a dark green or orange vegetable.