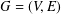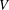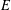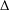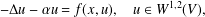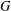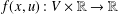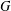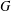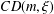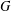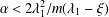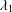Suppose that 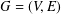 $G=(V,E)$ is a finite graph with the vertex set
$G=(V,E)$ is a finite graph with the vertex set 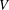 $V$ and the edge set
$V$ and the edge set 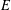 $E$. Let
$E$. Let 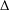 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E5}$ be the usual graph Laplacian. Consider the nonlinear Schrödinger equation of the form
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E5}$ be the usual graph Laplacian. Consider the nonlinear Schrödinger equation of the form 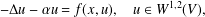 $$\begin{eqnarray}-\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E5}u-\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}u=f(x,u),\quad u\in W^{1,2}(V),\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}-\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E5}u-\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}u=f(x,u),\quad u\in W^{1,2}(V),\end{eqnarray}$$ $G$, where
$G$, where 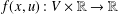 $f(x,u):V\times \mathbb{R}\rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ is a nonlinear real-valued function and
$f(x,u):V\times \mathbb{R}\rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ is a nonlinear real-valued function and  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$ is a parameter. We prove an integral inequality on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$ is a parameter. We prove an integral inequality on 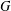 $G$ under the assumption that
$G$ under the assumption that 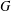 $G$ satisfies the curvature-dimension type inequality
$G$ satisfies the curvature-dimension type inequality 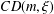 $CD(m,\unicode[STIX]{x1D709})$. Then by using the Poincaré–Sobolev inequality, the Trudinger–Moser inequality and the integral inequality on
$CD(m,\unicode[STIX]{x1D709})$. Then by using the Poincaré–Sobolev inequality, the Trudinger–Moser inequality and the integral inequality on 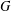 $G$, we prove that there is a nontrivial solution to the nonlinear Schrödinger equation if
$G$, we prove that there is a nontrivial solution to the nonlinear Schrödinger equation if 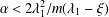 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}<2\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{1}^{2}/m(\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{1}-\unicode[STIX]{x1D709})$, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}<2\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{1}^{2}/m(\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{1}-\unicode[STIX]{x1D709})$, where 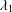 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{1}$ is the first positive eigenvalue of the graph Laplacian.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{1}$ is the first positive eigenvalue of the graph Laplacian.