Consuming the soluble dietary fibre (1 → 3)(1 → 4)-β- d-glucan has been shown to provide multiple health benefits and has thus garnered attention as a functional food ingredient. Health Canada and the United States Food and Drug Administration have issued health claims which state that 3 g of β-glucan fibre per d from oat sources may help to reduce the risk of CHD(1, 2). Furthermore, β-glucan has been shown to lower postprandial glycaemic responses, which may reduce the risk of developing diabetes and assists individuals with glycaemic control(Reference Barclay, Petocz and McMillan-Price3).
The ability of β-glucan to lower postprandial glycaemic responses has been attributed to the viscosity of the solution in which the fibre is solubilised. It has been demonstrated that the viscosity of a β-glucan solution increases with the molecular weight (MW) of β-glucan polymers, as well as the dose or concentration (C) of those polymers in solution. In accordance with polymer solution theory, Wood et al. (Reference Wood, Beer and Butler4, Reference Wood, Braaten and Scott5) showed that the log of the viscosity of a β-glucan solution is directly proportional to the log of the product of β-glucan C and MW. Thus, increasing the β-glucan C or MW leads to an exponential increase in solution viscosity, which then leads to a greater reduction in glycaemic response.
Numerous studies have shown that glycaemic response lowering is strengthened when the C of a β-glucan solution of fixed liquid volume is increased by increasing the β-glucan dose. However, since the C of a β-glucan solution depends on solution volume as well as on the amount of fibre present, further investigation was needed to determine whether the effect of β-glucan solutions on glycaemic response was due to the viscosity per se or dependent on the β-glucan dose. Therefore, we tested the effects of altering β-glucan solution viscosity by altering solution volume at a fixed amount of β-glucan fibre. Knowing how to incorporate β-glucan into the solution so that its physiological benefits are preserved will assist in the development of β-glucan-containing functional foods.
Experimental methods
Subjects
A total of fifteen healthy subjects (seven males, eight females) were recruited to determine the glycaemic response elicited by six test beverages prepared for the present study. Subjects were excluded if they were under 18 or over 75 years of age, had a BMI equal to or above 35 kg/m2, or were known to have diabetes, HIV, AIDS, hepatitis or a heart condition. Exclusion criteria also included the use of medications or having a condition which may harm the subjects or affect the study results.
Clinical trial
The present study followed a randomised, controlled block design with repeated measures. Participants visited the study site (Glycemic Index Laboratories) on mornings between 08.00 and 10.00 hours following a 10–14 h overnight fast. The height and weight of the subjects were measured. Thereafter, two fasting blood samples spaced 5 min apart ( − 5 and 0 min) were collected by finger-prick using a monoejector lancet device. Immediately following the collection of the second blood sample, subjects consumed a test beverage and 250 ml of a beverage of their choice (water, tea or coffee with milk and/or the artificial sweetener aspartame). Subjects received the same beverage and volume of that beverage for each test in the study. Additional finger-prick blood samples were taken at 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 90 and 120 min after the start of the meal. Blood samples (two to three drops from each time point) were collected in fluoro-oxalate tubes to prevent coagulation, immediately stored at − 20°C and analysed within 72 h. Subjects remained seated for the duration of the test. Glucose concentration was analysed using an automatic analyser (2300 Stat; Yellow Springs Instruments). The peak rise in blood glucose concentration (PBGR) and the incremental area under the glycaemic response curve (AUC) elicited by each test beverage were determined according to the methods by Wolever et al. (Reference Wolever, Jenkins and Jenkins6). Subjects served as their own control.
Test beverages
The test beverages were six 50 g oral glucose solutions prepared with or without the addition of 4 g purified oat β-glucan fibre (provided by Megazyme International Ireland), with a solution volume of either 250 or 600 ml. The ingredients used to make the beverages are shown in Table 1. β-Glucan was extracted from oat bran and purified to remove starch, proteins and arabinoxylan, and was subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis with lichenase to achieve β-glucan polymers of high or low viscosity.
Table 1 Composition of the test beverages varying in β-glucan dose, β-glucan molecular weight (MW) and solution volume

HMW, high molecular weight; LMW, low molecular weight; 250N, glucose control solution of 250 ml volume; 600N, glucose control solution of 600 ml volume; 250H, HMW β-glucan solution of 250 ml volume; 600H, HMW β-glucan solution of 600 ml volume; 250L, LMW β-glucan solution of 250 ml volume; 600L, LMW β-glucan solution of 600 ml volume.
* MW: HMW (580 000 g/mol) or LMW (145 000 g/mol).
† 0·05 % solution.
Beverages are named to correspond to their volume (250 or 600 ml) and to indicate the presence or absence of β-glucan fibre. Thus, beverages containing no β-glucan are designated with the letter ‘N’, while beverages containing β-glucan are designated with the letters ‘H’ or ‘L’ which describe the relative MW of β-glucan used in the present study (‘H’ for high or ‘L’ for low).
To prepare each beverage, dry ingredients were weighed in a 1-litre cylindrical Ziplock© container with a screw-on cap, shaken to mix the contents and either 250 or 600 ml of boiling 0·05 % potassium sorbate solution were added to the dry ingredients. Potassium sorbate acted as a preservative to prevent bacterial and mould growth. Immediately after the addition of liquid, the solution was thoroughly homogenised with a handheld blender until no clumps of the dry ingredients were visible. To impart an orange flavour and colour to the beverage, pure orange extract and food colouring were incorporated with further homogenisation. The beverage was left to cool and to sit overnight (between 19 and 22 h) at room temperature before being served the following day. All beverages were tested in random order, and every subject received each beverage once during the study.
Physico-chemical properties of the test beverages
The physico-chemical properties of the beverages were measured to determine whether those properties relate to the effects on glycaemic response. The MW of β-glucan was determined by high-performance size-exclusion chromatography using the methods described in the study by Ragaee et al. (Reference Ragaee, Wood and Wang7) but with modifications. Briefly, the high-performance size-exclusion chromatography system consisted of a Shodex OHpak KB-806M and Ultrahydrogel linear column with a Shimadzu SCL-10Avp pump and auto-injector (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments). Elution was with 0·1 m-NaNO3 containing 0·03 % (w/w) NaN3 at a flow rate of 0·6 ml/min. Chromatographic peaks were detected with a Viscotek TDA 305 detector, which consists of a refractive index detector, a low-angle laser light scattering detector, a right-angle laser light scattering detector and a differential pressure detector. The Viscotek DM 400 data manager and OmniSEC software were used to determine the MW distributions of β-glucan standards and β-glucan used in the test beverages. Weight average molecular weight (MW) and number average molecular weight (Mn) were calculated from the distributions. Pullulan (J.M. Science) was used to calibrate the detectors. A refractive index increment (dn/dc) of 0·146 ml/g was used(Reference Beer, Wood and Weisz8, Reference Wang, Wood and Huang9).
Apparent viscosity values for the test solutions were measured using the methods described in the study by Tosh et al. (Reference Tosh, Brummer and Wolever10). Using a controlled strain rheometer (ARES; TAInstrument) fitted with a cone and plate geometry (cone angle 0·04 radians, diameter 50 mm), apparent viscosity was measured in a shear rate range of 0·1–100 per s at 37°C. For statistical analysis, viscosities measured at the shear rate of 32 per s were used.
Statistical analysis
The means for the PBGR, incremental area under the glycaemic response curve (AUC), ignoring the area below fasting, and blood glucose concentrations at each time point were subjected to repeated measures of ANOVA. After demonstration of significant heterogeneity, the significance of difference among individual measures was determined using Tukey's test. PBGR was calculated as the difference between the fasting blood glucose value and the highest blood glucose value achieved. Linear regression analysis was used to determine the interaction between the physico-chemical properties of the test beverages, as well as between those properties and the glycaemic response elicited by the test beverages. A two-tailed P value of < 0·05 was taken as the criterion for statistical significance. Results are presented as means with their standard errors. All analyses were performed using the Microsoft Excel Data Analysis Tool Pack. The number of subjects in the present study allowed for differences in PBGR of 0·73 mmol/l between means to be detected with 80 % power at a P value of 0·05 for statistical significance.
Ethics
The present study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki, and all procedures involving human subjects were approved by the Health Sciences Research Ethics Board of the University of Toronto. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects, and participants received financial compensation for completing the study.
Results
Subjects
The fifteen subjects were seven males and eight females, aged 37·2 (sem 2·9) years with a BMI of 26·6 (sem 1·1) kg/m2. All subjects completed the series of the six glycaemic response tests.
Physico-chemical properties of the test beverages
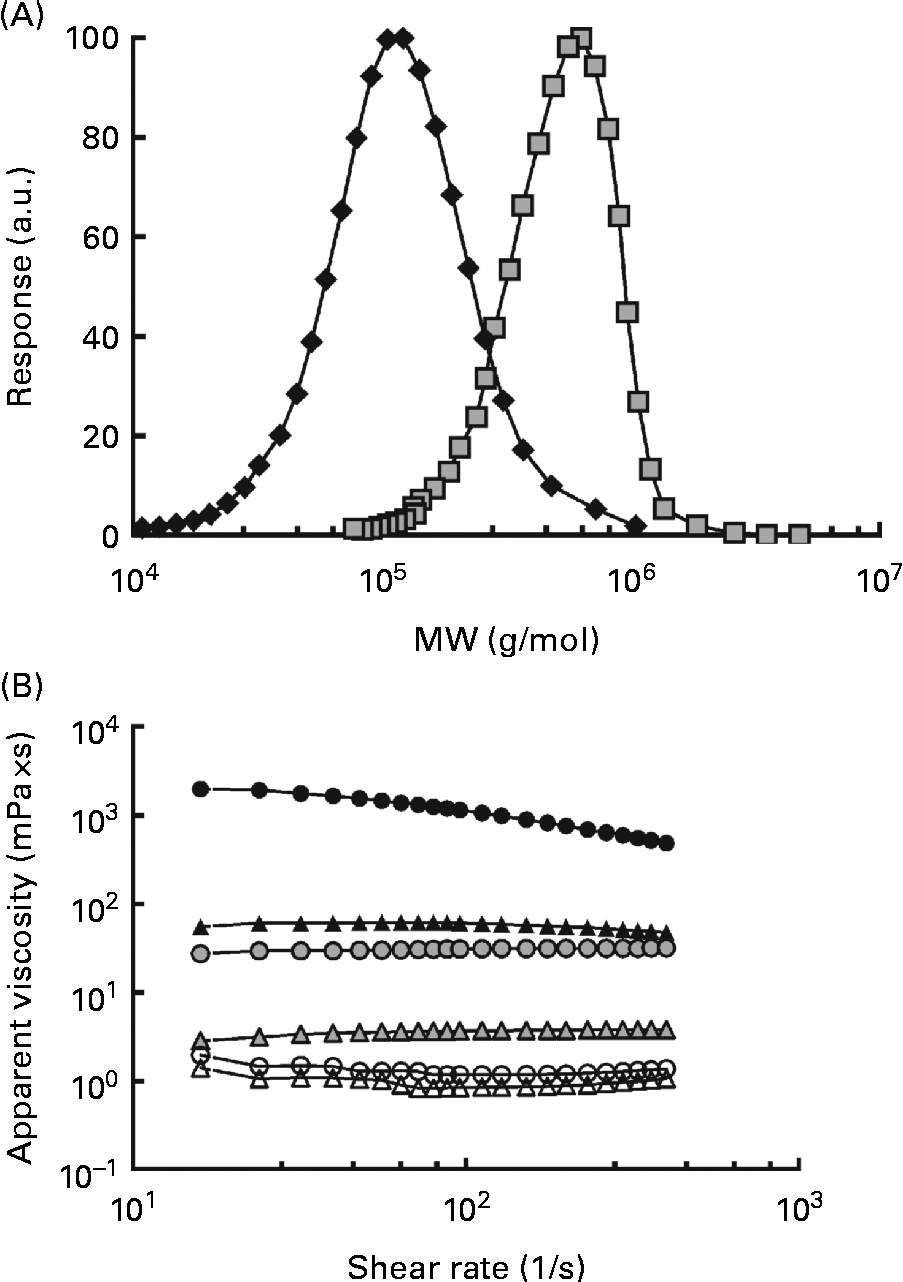
The MW of the high-MW (HMW) β-glucan was 580 000 g/mol and the Mn was 474 000 g/mol, resulting in a polydispersity value of 1·3. The MW for the low-MW (LMW) isolate was 145 000 g/mol and the Mn was 114 000 g/mol, giving a slightly higher polydispersity of 1·6. The distributions are shown in Fig. 1(A). The viscosity profiles for the drinks, as a function of the shear rate, are shown in Fig. 1(B). Shear thinning behaviour was exhibited by the 250H drink, whereas the other drinks demonstrated Newtonian behaviour. The apparent viscosities of the solutions at 32 per s containing β-glucan (250L, 600L, 250H and 600H) ranged from 4·33 (sd 0·04) to 205 000 (sd 40) mPa × s. The viscosities of the control glucose solutions containing no β-glucan (250N and 600N) were comparable with that of water (approximately 1·0 mPa × s) (Table 2).

Fig. 1 Characteristics of the oat β-glucans used. (A) Molecular weight (MW) distributions of the high-MW (HMW, 580 000 g/mol, ![]() ) and low-MW (LMW, 145 000 g/mol,
) and low-MW (LMW, 145 000 g/mol, ![]() ) β-glucans and (B) apparent viscosity of the treatments as a function of the shear rate. Test beverages: 250H (
) β-glucans and (B) apparent viscosity of the treatments as a function of the shear rate. Test beverages: 250H (![]() ), 250 ml HMW β-glucan solution; 600H (
), 250 ml HMW β-glucan solution; 600H (![]() ), 600 ml HMW β-glucan solution; 250L (
), 600 ml HMW β-glucan solution; 250L (![]() ), 250 ml LMW β-glucan solution; 600L (
), 250 ml LMW β-glucan solution; 600L (![]() ), 600 ml LMW β-glucan solution; 250N (
), 600 ml LMW β-glucan solution; 250N (![]() ), 250 ml glucose control; 600N, 600 ml glucose control (
), 250 ml glucose control; 600N, 600 ml glucose control (![]() ). a.u., Arbitrary units.
). a.u., Arbitrary units.
Table 2 Physico-chemical characteristics of the test beverages varying in β-glucan dose, β-glucan molecular weight (MW) and solution volume (Mean values and standard deviations)

C, β-glucan concentration (g/l); Pd, polydispersity (MW/Mn); 600N, glucose control solution of 600 ml volume; 250N, glucose control solution of 250 ml volume; 600L, LMW β-glucan solution of 600 ml volume; 250L, LMW β-glucan solution of 250 ml volume; 600H, HMW β-glucan solution of 600 ml volume; 250H, HMW β-glucan solution of 250 ml volume.
* Mw: high MW (580 000 g/mol) or low MW (145 000 g/mol).
† Mean of the viscosity values measured from three separate samples of a test solution each measured three times at 32 per s.
Solution viscosity varied depending on the solution volume and the MW of β-glucan if the fibre was present. At the same solution volume, solutions containing HMW β-glucan (250H and 600H) were more viscous than solutions containing LMW β-glucan (250L and 600L), and at the same MW, 250 ml β-glucan solutions were more viscous than 600 ml β-glucan solutions (Table 2). However, solutions with HMW β-glucan had the highest viscosity values of all the solutions regardless of volume. The beverage volumes were chosen so that the viscosities of 250L and 600H would be similar (Table 2).
Postprandial glycaemic response to the test beverages
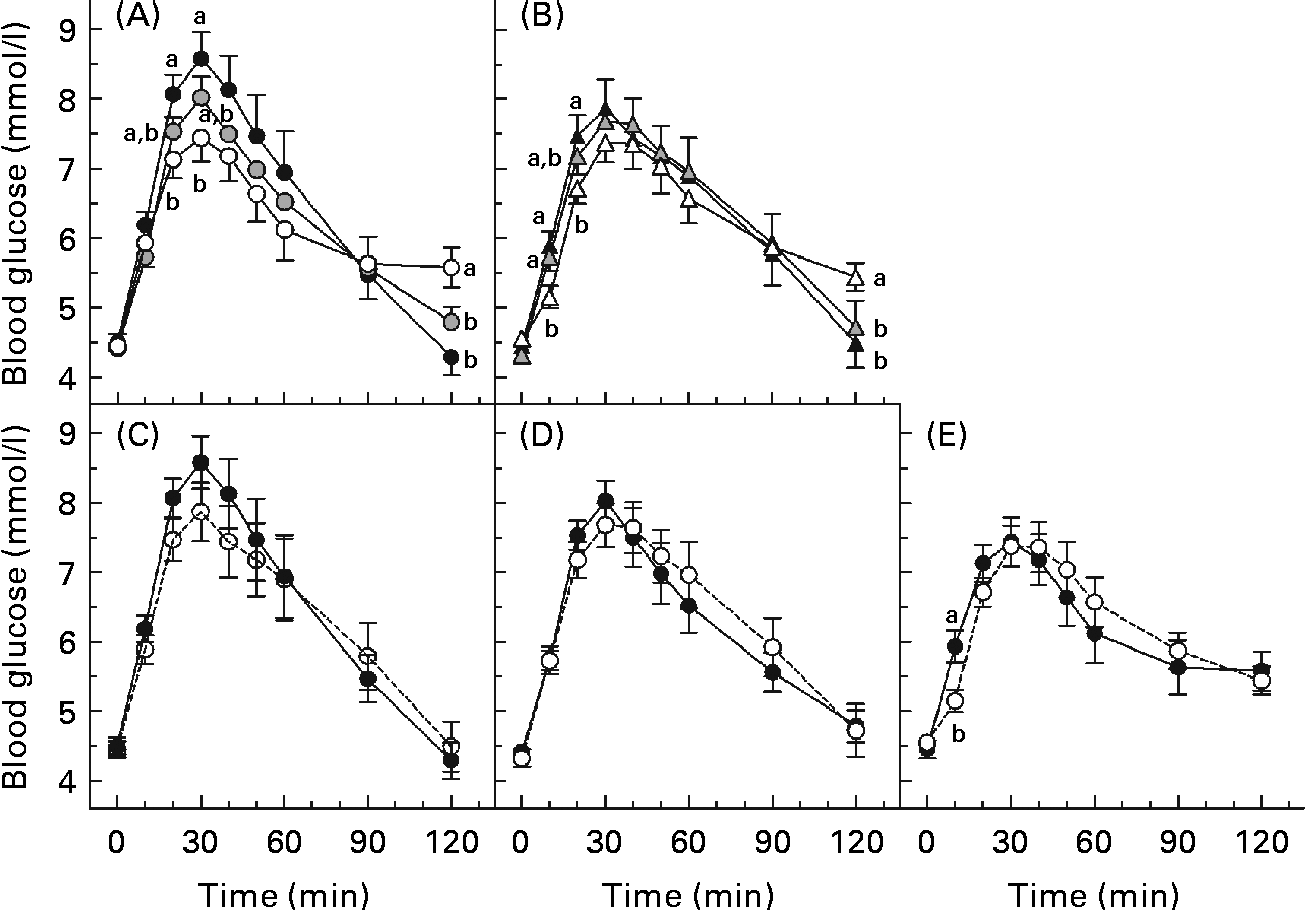
The glycaemic response curves elicited by each solution over 2 h after fasting are shown (Fig. 2(A)–(E)). Fig. 2(A) and (B) shows the curves for the beverages of 600 and 250 ml volume, respectively, and illustrates the effect of β-glucan MW on glycaemic response. At the same volume, a higher MW tended to yield lower incremental blood glucose values. This is evident at both 250 and 600 ml volumes since blood glucose concentration for the 600H drink was significantly lower than that of the 600N drink at 20 and 30 min (P< 0·05; Fig. 2(A)), and blood glucose concentration for the 250H drink was lower than that of the 250N drink at 10 and 20 min (P< 0·05; Fig. 2(B)). However, at the same volume, the HMW beverage also yielded the highest blood glucose concentration at 120 min.

Fig. 2 Mean 2 h postprandial blood glucose concentrations following various 50 g oral glucose beverages of (A) 600 ml volume with or without 4 g β-glucan, (B) 250 ml volume with or without 4 g β-glucan, containing (C) no β-glucan, (D) high-molecular-weight (HMW, 580 000 g/mol) β-glucan or (E) low-molecular-weight (LMW, 145 000 g/mol) β-glucan. Values are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars. a,bMean values with unlike letters were significantly different. (P< 0·05). 250H ((b) ![]() , (e)
, (e) ![]() ), 250 ml HMW β-glucan solution; 600H ((a)
), 250 ml HMW β-glucan solution; 600H ((a) ![]() , (e)
, (e) ![]() ), 600 ml HMW β-glucan solution; 250L ((b)
), 600 ml HMW β-glucan solution; 250L ((b) ![]() , (d)
, (d) ![]() ), 250 ml LMW β-glucan solution; 600L ((a)
), 250 ml LMW β-glucan solution; 600L ((a) ![]() , (d)
, (d) ![]() ), 600 ml LMW β-glucan solution; 250N ((b)
), 600 ml LMW β-glucan solution; 250N ((b) ![]() , (c)
, (c) ![]() ), 250 ml glucose control; 600N ((a)
), 250 ml glucose control; 600N ((a) ![]() , (c)
, (c) ![]() ), 600 ml glucose control.
), 600 ml glucose control.
Fig. 2(C)–(E) shows the curves of the 250 and 600 ml beverages containing no β-glucan, LMW β-glucan and HMW β-glucan, respectively, and illustrates the effect of β-glucan beverage volume on glycaemic response. The blood glucose concentration did not differ between the beverages of the same MW at any time point, except that glucose after the 600H drink was significantly greater than that after the 250H drink at 10 min (P< 0·05; Fig. 2(E)).
The HMW β-glucan beverages resulted in broad, flattened glycaemic response curves that had not returned to baseline 120 min after consumption. Therefore, there were no significant differences in AUC among the beverages (P= 0·147). Previous studies have shown that insulin responses after a meal including oat β-glucan parallel glycaemic responses(Reference Wood, Braaten and Scott5, Reference Tappy, Gugolz and Wursch11–Reference Kim, Stote and Behall13). Thus, the shape of the curves would suggest that the lower peak for the HMW beverages resulted in reduced insulin secretion, delaying return of the glucose concentration to baseline. However, the beverages differed in PBGR (P< 0·0001; Table 3). The PBGR for the 250N, 600N and 250L drinks were significantly greater than those for the 250H and 600H drinks, while the PBGR for the 600L drink did not differ from any of the other beverages. Although the 250L and 600H beverages were similar in viscosity (Table 2), their PBGR values were significantly different (P= 0·004).
Table 3 Incremental areas under the blood glucose response curve (AUC) and peak blood glucose rise (PBGR) elicited by the test meals (Mean values with their standard errors, n 15)

MW, molecular weight.
a,b,c,d,eMean values with unlike superscript letters were significantly different (P< 0·05).
There was a significant main effect of MW on PBGR (P= 0·00 005), with H, L and N differing significantly from each other in the order H < L < N (Table 3). There was no main effect of volume (P= 0·718) and no MW × volume interaction effect on PBGR (P= 0·487).
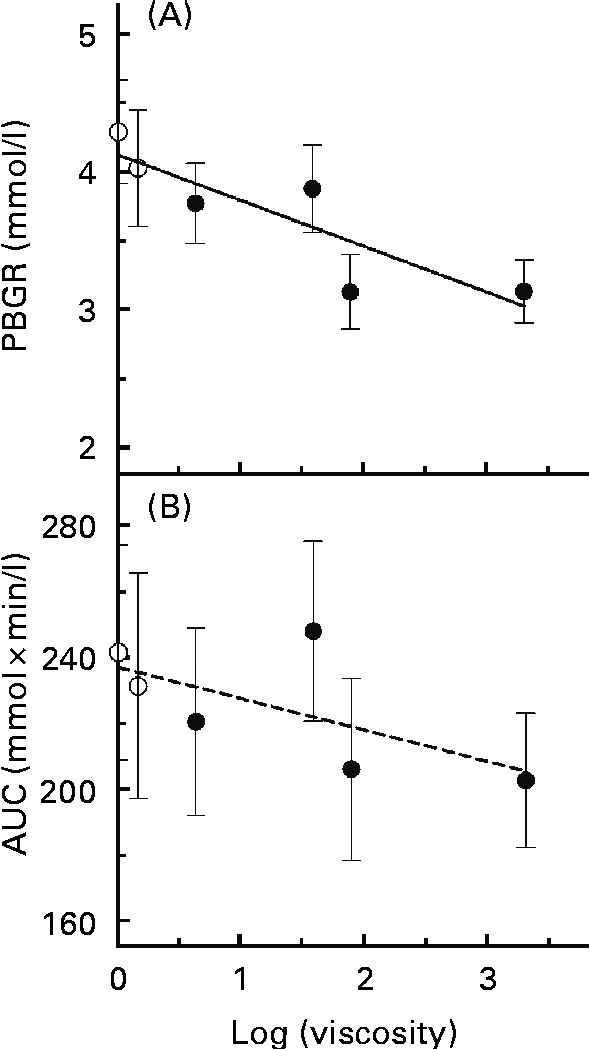
A simple linear regression model was applied to assess the associations between log(viscosity) and PBGR (Fig. 3(A)). There was a significant trend of decreasing PBGR with increasing log(viscosity) (r 2 0·759, P= 0·024). Associations between log(viscosity) and AUC were also assessed (Fig. 3(B)) and found not to be significant (r 2 0·416, P= 0·167).

Fig. 3 Regression relationships between the physico-chemical properties of glucose controls or β-glucan beverages and the peak blood glucose rise (PBGR, mmol/l) or the area under the glycaemic response curve (AUC, mmol × min/l): (A) log(viscosity) and PBGR (r 2 0·759, P= 0·024); (B) log(viscosity) and AUC (r 2 0·416, P= 0·167). Values are means, with their standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 15). ○, Glucose controls; ●, β-glucan solutions.
Discussion
In the present study, β-glucan solution viscosity was manipulated by varying the β-glucan MW and varying the solution volume. High solution viscosity was achieved with high β-glucan MW or with low solution volume. When C is held constant in a β-glucan beverage of fixed volume and dose, increasing or decreasing the MW, respectively, increases or decreases the solution viscosity. Similarly, when β-glucan MW and dose are fixed, the apparent viscosity of the solution increases with decreasing volume.
The effect of β-glucan on glycaemic response is apparent when examining the patterning of the blood glucose curves. At the beverage volume of 600 ml, the glucose curve elicited by the control beverage had a higher peak value than the curves after either HMW or LMW β-glucan, while the blood glucose concentrations for both β-glucan curves were higher than that for the control at the end of the sampling period. The observed patterning may be explained by the mechanism with which β-glucan attenuates glycaemic response. The presence of viscous β-glucan solution in the digestive environment causes a delayed release of glucose and a delayed absorption of glucose into the bloodstream. As a result, the maximum blood glucose concentration attained is lower and the decline in blood glucose levels after reaching the peak level is more gradual than when compared with the glucose control. The pattern of the glycaemic responses at 250 ml was similar to that of the 600 ml beverages, but differences among the 250 ml curves were not as evident.
There was a strong, negative correlation between PBGR and log(viscosity). On the other hand, the correlation between log(viscosity) and AUC was small and not significant. Furthermore, the AUC did not differ between the glucose control and β-glucan beverages. However, this does not necessarily suggest that β-glucan is ineffective at lowering glycaemic response, and similar results have been reported elsewhere(Reference Wood, Braaten and Scott5, Reference Tosh, Brummer and Wolever10, Reference Jenkins, Wolever and Leeds14). Rather, the HMW beverages produced flatter and broader blood glucose response curves after consumption of β-glucan beverages than after control beverages. Thus, while the shape of the β-glucan and control curves may differ, the AUC did not(Reference Tosh, Brummer and Wolever10).
At the two volumes used in the present study (250 and 600 ml), changing viscosity by changing solution volume did not affect β-glucan bioactivity. This was evident in that a main effect was detected for MW but not for volume on PBGR. The fact that changes in viscosity affected PBGR only when viscosity was altered by MW and not by volume is a novel finding. It would appear that the digestive system adjusts the volume of the meal bolus and equilibrates the viscosity. Previously, MRI showed that viscous polymer beverages increase the secretion of gastric fluids which diluted the polymer in the stomach(Reference Marciani, Gowland and Spiller15). Thus, the stomach has the ability to reduce the viscosity of a concentrated polymer solution in vivo. The similarity of responses to the two treatments with the same MW suggests that the dose rather than the concentration in the beverage consumed determined the physiological response. However, the beverages with different MW β-glucans resulted in different glycaemic responses so β-glucan did not appear to have been diluted to the same viscosity.
In a study using hydroxymethylpropyl cellulose, increasing the MW of polymers added to rat or hamster feed increased the viscosity of intestinal contents(Reference Carr, Wood and Hassel16), indicating that intestinal viscosity is not always equalised and is in part determined by meal composition. If gastric secretions are sensitive to osmotic pressure cues, then it may be that LMW β-glucan would draw more water than an equal weight of HMW β-glucan. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property and depends on the number of molecules in a solution rather than on the weight, and LMW β-glucan would require more molecules to make up the 4 g dose. If higher osmotic pressure stimulated increased gastric secretions, LMW β-glucan solutions would have a lower final in vivo viscosity than HMW solutions.
Although log(viscosity) was negatively associated with PBGR, the results of the present study suggest that the physical presence (the dose and MW level) rather than the initial viscosity of the β-glucan beverage may determine whether this viscous fibre affects glycaemic response. Previous studies have demonstrated that increasing viscosity by increasing β-glucan MW or C can enhance blood glucose lowering, but these studies increased C by increasing the β-glucan dose without changing the solution volume(Reference Wood, Braaten and Scott5, Reference Tappy, Gugolz and Wursch11–Reference Kim, Stote and Behall13). Thus, while a higher β-glucan C, and thus a higher viscosity, achieved a greater glycaemic response reduction, it is unclear whether this was due to an increase in viscosity or an effect of dose–response. The present study shows that beverages with the same β-glucan MW and dose yielded similar effects on peak rise when the viscosities of these beverages differed, demonstrating that viscosity may not play as important a role in β-glucan bioactivity as is believed. Marciani et al. (Reference Marciani, Gowland and Spiller17) showed that the viscosity of a test meal before ingestion bears no relationship with the rate of gastric emptying after consuming the meal, since the initial meal viscosity is reduced by the release of digestive fluids during consumption. This means that the viscosity of the β-glucan beverages consumed neither reflects in vivo lumenal viscosity nor predicts the magnitude of glycaemic response lowering by the β-glucan beverages. Moreover, β-glucan dose and MW may be better predictors of how the fibre affects glycaemic response. Thus, the inverse linear relationship between log(viscosity) and log(PBGR) is strongest when C is varied by dose at a constant solution volume.
Although the present results show that volume does not contribute to the effects of β-glucan on glycaemic response, this does not dictate that volume itself, irrespective of β-glucan, has no effect on blood glucose levels. Indeed, food volume has been shown to affect gastric emptying, which has implications for resulting postprandial glycaemic responses. Sievenpiper et al. (Reference Sievenpiper, Jenkins and Josse18) observed that increasing the volume of glucose solutions 3-fold leads to a faster and higher rise in glycaemic response. Young et al. (Reference Young and Wolever19) also found that a higher food volume resulted in changes to curve patterning, where peak rise increased with increasing volume up to 750 ml. The authors explained that a higher volume may initially lead to a higher rate of gastric emptying, resulting in a greater initial rise and peak in glycaemic response.
In the present study, the effects of volume are apparent in the blood glucose curves and are similar to those of the studies discussed. For the glucose beverages and β-glucan beverages of the same MW level, although differences between the 600 and 250 ml curves at each time point were mainly not significant, the larger volume of 600 ml tended to yield a steeper rise and a higher peak in blood glucose than the lower volume of 250 ml. The lack of significance may be because 250 and 600 ml are not sufficiently different volumes for significant differences in the effect on gastric emptying to be observed. Also, the lack of significance between the β-glucan beverages of the same MW level may be due to the great suppression of glycaemic response by the fibre itself, which could result in both 250 and 600 ml curves being attenuated to the point where there is little difference in blood glucose concentration at individual time points. More research is needed on how gastric emptying affects glycaemic responses.
Since the present study tested beverage volumes of 250 and 600 ml, the results may not apply to other volume levels. Future experiments should test a broader set of solution volumes to determine the range of volumes to which the present results hold true. This would help answer related questions, such as how large a volume is necessary for the effect of volume on gastric emptying to eclipse the glycaemic response-lowering effect of β-glucan, and conversely, what C would allow the effect of β-glucan to overcome the effect of volume on gastric emptying. Furthermore, the results for how β-glucan affects glycaemic response when administered as liquid beverages may differ from when it is consumed in solid foods. However, the results for β-glucan consumed as a liquid may indicate how β-glucan solutions formed during digestion affect glycaemic response.
The goal of the present study was to determine whether altering β-glucan solution viscosity by altering volume changes the effect of β-glucan on glycaemic response. We found MW and not volume to be the main contributing factor for how β-glucan affects blood glucose levels. However, volume itself affects the patterning of the glycaemic response curve through its effect on gastric emptying. The physical presence of β-glucan and the β-glucan MW remain most important for lowering glycaemic response and should be targeted for optimising the bioactivity of β-glucan solutions.
Acknowledgements
The present study was funded by Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada under the Growing Forward program. Oat β-glucan was a gift from Megazyme International Ireland. T. M. S. W. and S. M. T. designed the research project, provided the essential materials and equipment, and had primary responsibility for the final content. S. M. T. and Y. B. developed the beverage formulations. Y. B. prepared the beverages and conducted the physico-chemical analyses on the solutions. M. G. Y. K. prepared the beverages, conducted the clinical trial, analysed the data and drafted the paper. All authors contributed to the critical revisions and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.