Despite substantial improvements in food security over the last few decades, undernutrition remains a global burden. Approximately 800 million people are chronically hungry, most of them living in developing countries( 1 ). An estimated two billion people suffer from deficiencies in particular micronutrients, such as iron, zinc or vitamin A( 2 ). Nutritional deficiencies harm physical and mental human development, increase the susceptibility to infectious diseases and contribute to premature deaths. Women and children pay the heaviest toll. Forty-five per cent of all deaths of children under 5 years of age are linked to undernutrition( 2 ). Overall, undernutrition is the cause of 3·1 million child deaths annually( Reference Black, Victora and Walker 3 ). Childhood undernutrition also decreases adult productivity and entails substantial economic losses in many developing countries( 2 ).
Nutrition is closely linked to agriculture, not only because agriculture is the sector that produces food, but also because many of the undernourished people worldwide are smallholder farmers( Reference Frelat, Lopez-Ridaura and Giller 4 , Reference Pinstrup-Andersen 5 ). For a long time, the main agricultural policy response to undernutrition was to strengthen staple food production through price incentives and promoting improved farm technologies. The focus was primarily on a narrow range of cereal crops, especially wheat, rice and maize( Reference Pingali 6 ). While this strategy has clearly helped to reduce hunger, it has also contributed to lower levels of crop species diversity( Reference Khoury, Bjorkman and Dempewolf 7 ). More homogeneous global food supplies may have decreased dietary diversity( Reference Graham, Welch and Saunders 8 , Reference Frison, Smith and Johns 9 ). And low levels of dietary diversity are associated with higher rates of micronutrient deficiencies, child stunting, child deaths and other negative health consequences( Reference M’Kaibi, Steyn and Ochola 10 – Reference Steyn, Nel and Nantel 13 ).
More diversified agricultural and food systems may help to improve dietary quality and nutrition( Reference Pingali 6 , Reference Berry, Dernini and Burlingame 14 – Reference Bowman and Zilberman 16 ), but empirical evidence on the effects of diversification strategies on dietary improvement in smallholder households is scarce( Reference Webb and Kennedy 17 ). Appropriate levels of diversification are a question of scale. Food systems diversity does not necessarily imply that every single farm has to be extremely diverse. On the one hand, diverse farm production may promote diverse food consumption in the farm household. This is especially true in sub-Saharan Africa, where smallholder farms are often subsistence-oriented( 18 ). On the other hand, typical farms in Africa are already quite diverse. Further diversification might prevent gains from specialization on the farm and could thus result in income losses, with potential negative nutritional effects( Reference Sibhatu, Krishna and Qaim 19 ). In spite of their subsistence orientation, smallholder farm households are engaged in market transactions. A substantial share of the food consumed in farm households is purchased from the market( Reference Luckett, DeClerck and Fanzo 20 – Reference Barrett 23 ). In addition, foods obtained through hunting, fishing or collection from the natural environment can play a significant role for dietary diversity in rural areas( Reference Johns, Powell and Maundu 24 – Reference Bharucha and Pretty 26 ).
Recent studies have empirically analysed the link between farm species diversity and dietary diversity in a number of developing countries( Reference Sibhatu, Krishna and Qaim 19 , Reference Sibhatu and Qaim 27 – Reference Jones, Shrinivas and Bezner Kerr 29 ). While the exact estimates differ, a significant but relatively small positive relationship was generally found. Yet, the same studies also pointed out that market access may be a more important factor influencing dietary diversity in smallholder farm households. These results have stirred an interesting debate( Reference Berti 30 – Reference Sibhatu, Krishna and Qaim 32 ). In particular, questions about the indicators used to measure production and consumption diversity were raised.
We contribute to this emerging literature on the link between farm production diversity and dietary diversity by using alternative indicators and comparing results. Previous studies used food consumption data to construct dietary diversity scores at the household level( Reference Sibhatu, Krishna and Qaim 19 , Reference Sibhatu and Qaim 27 – Reference Jones, Shrinivas and Bezner Kerr 29 ). The use of household-level consumption data is convenient, because such data are often available from nationally representative living standard measurement surveys. Living standard surveys often include a 7d or 30d consumption recall that can be used to construct dietary indicators. However, from a nutritional perspective, shorter recall periods are generally preferred( Reference de Haen, Klasen and Qaim 33 ). Moreover, household-level data do not account for issues of intra-household distribution and therefore cannot be used for statements concerning particular population groups, such as children. Herein, we use data from a 24 h dietary recall carried out at household and individual levels to analyse and compare the relationship between farm production diversity and dietary diversity. Furthermore, beyond measuring farm diversity in terms of a simple count of the species produced, we construct production diversity scores that better account for nutritional functions( Reference Sibhatu and Qaim 27 , Reference Berti 30 ). Finally, in comparison to previous studies we use a larger set of variables to estimate the role of market access and agricultural technology.
For the empirical analysis, we use data from a recent survey of farm households in Malawi, covering household- and individual-level information. Malawi is an interesting study country for several reasons. First, Malawi is poor with high rates of undernutrition( Reference Ecker and Qaim 34 ). Second, farm households in Malawi are primarily subsistence-oriented. Third, several previous studies on the link between farm production and dietary diversity used household-level data from Malawi’s Living Standards Measurement Survey( Reference Sibhatu, Krishna and Qaim 19 , Reference Snapp and Fisher 28 , Reference Jones, Shrinivas and Bezner Kerr 29 ). Focusing on the same setting with individual-level data and alternative indicators has advantages in terms of comparability.
Materials and methods
Data
Data for the present study come from a farm household survey that we conducted in cooperation with the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and the Malawian Department of Agricultural Research Services in January and February 2014. The survey covered sixteen districts and 165 villages throughout the country’s central and southern regions. Household selection was based on a multistage proportionate random sampling procedure. Interviews captured a wide array of information, including details on household demographics, household socio-economic status, agricultural production and marketing and consumption of food and non-food products. A special section with a 24 h food consumption recall captured dietary patterns of all household members combined, as well as individually for children below the age of 5 years and their mothers.
The survey team included experienced local enumerators who had been selected and trained intensively. Sensitive sections, such as the 24 h consumption recall, were especially emphasized during the training and the pre-testing of the questionnaire. Enumerators were carefully trained to not only focus on the main meals consumed in the household, but to also elicit details on snacks and minor dietary components. Overall, 1482 farm households were surveyed. Out of the sampled households, only 408 had children below 5 years of age. We want to compare dietary diversity at household level and individual level for children and mothers, which is most meaningful when focusing on the same households. Hence, the current analysis builds on the 408 households with small children and their mothers. The sample is representative of farm households with small children in central and southern Malawi.
Analytical approach
To analyse the relationship between farm production diversity and dietary diversity, we use the following regression model:
where DD i is dietary diversity and PD i is production diversity in farm household i. ε i is a random error term, and α 0 and α 1 are coefficients to be estimated. We are particularly interested in the estimate for α 1. We estimate different versions of this model, changing the measures of DD and PD, as is further explained below. In one set of models, DD is measured at the household level. In alternative specifications, DD is measured for individual j living in household i. In particular, we consider children below 5 years of age and their mothers.
The model in equation (1) includes only production diversity as explanatory variable. Yet, there may also be other factors that could influence dietary diversity, such as market access and other socio-economic and demographic characteristics. To better understand the role of such other factors, we extend the regression model as follows:
where M i is a vector of variables capturing market access and H i is a vector of other socio-economic and demographic variables, including farm size, household size, off-farm income, as well as age, education and gender of the household head. We use different indicators to capture market access and market use for agricultural sales and food purchases of household i.
To analyse the role of agricultural technology, we further extend this model as follows:
where AT i represents a vector of dummy variables indicating the use of different types of agricultural technology. Further details of how variables are defined and measured are provided below.
Measurement of dietary diversity
We measure dietary diversity in terms of dietary diversity scores (DDS), a common indicator that counts the number of food groups consumed over a certain period of time( Reference Headey and Ecker 35 – Reference Ruel 37 ). Most previous studies that analysed the relationship between farm production diversity and dietary diversity calculated DDS at the household level, using data from 7 d food consumption recalls( Reference Sibhatu, Krishna and Qaim 19 , Reference Sibhatu and Qaim 27 – Reference Jones, Shrinivas and Bezner Kerr 29 ). We use 24 h recall data collected for the household as a whole and for children below 5 years of age and their mothers to calculate and compare DDS at household and individual levels. Only very few previous studies have examined the relationship between production and consumption diversity using individual-level DDS( Reference Hirvonen and Hoddinott 22 , Reference Herforth 38 , Reference Olney, Talukder and Iannotti 39 ).
Our data in Malawi were collected in one single round. Single-round 24 h food consumption recalls have clear limitations, as they are unable to capture day-to-day variation in dietary intakes. While such variation is often relatively low among poor rural households, it cannot be ignored when making nutritional assessments at individual or household level. In such cases, repeated 24 h recalls are required( Reference Gibson 40 ). In our study, we do not make nutritional assessments for individuals or households but focus on the analysis of population-level associations, for which the general drawbacks of single-round recalls are less problematic.
Another important aspect when analysing dietary patterns is the question of seasonality. In poor rural households, the types and sources of foods consumed can vary significantly over the year, usually following the cycles of crop harvests( Reference Hirvonen, Taffesse and Hassen 21 , Reference Luckett, DeClerck and Fanzo 20 ). Our survey was conducted during the months of January and February, before the main maize harvest. This is considered the lean season in Malawi, when the role of purchased foods tends to be more important than during harvest and post-harvest periods( Reference Ellis and Manda 41 ). In addition, fishing and the collection of wild fruits are more important for household diets during the lean season( Reference Johnson, Jacob and Brown 42 – Reference Akinnifesi, Kwesiga and Mhango 44 ). In the 24 h recall, foods from all sources were captured, including any snacks consumed outside the home. However, for result interpretation it needs to be kept in mind that the concrete findings refer to one particular season and cannot be extrapolated to the rest of the year.
For the calculation of DDS, individual food items consumed were clubbed into broader food groups. Many studies consider twelve different food groups, but there is no international consensus on the best number to use( Reference Ruel, Harris and Cunningham 45 ). Sometimes, food groups with low micronutrient densities are excluded to reflect more healthy diets( Reference Kennedy, Ballard and Dop 46 ). Other studies consider a larger number of food groups to analyse dietary patterns in particular situations( Reference Keding, Msuya and Maass 47 ). Here, we use the following twelve food groups to calculate DDS at household and individual levels: (i) cereals; (ii) tubers and roots; (iii) vegetables; (iv) fruits; (v) meat and poultry; (vi) eggs; (vii) fish; (viii) pulses, legumes and nuts; (ix) milk and milk products; (x) oils and fats; (xi) sugar and honey; and (xii) miscellaneous, including spices, condiments and beverages( Reference Kennedy, Ballard and Dop 46 , Reference Swindale and Bilinsky 48 ).
Measurement of farm production diversity
During the survey, farmers were asked to report details of their farm production for the last 12 months. Almost all farm households in the sample produce maize as the main staple food. In addition, many households also grow other cereals (e.g. sorghum, millet), legumes (e.g. groundnut, beans, cowpeas), roots and tubers (e.g. cassava, sweet potato), several fruits and vegetables (including from household gardens) as well as cash crops such as tobacco and cotton. Small-scale livestock keeping is also common.
Based on the agricultural data, production diversity indicators were calculated. Several recent studies measured production diversity in terms of a simple count of the number of crop species produced on a farm, or a combination of crop and livestock species( Reference Sibhatu, Krishna and Qaim 19 , Reference Jones, Shrinivas and Bezner Kerr 29 , Reference Herforth 38 ). However, a simple species count does not necessarily reflect diversity from a dietary point of view. To better account for the dietary perspective, we use a production diversity score defined as the number of food groups produced( Reference Hirvonen and Hoddinott 22 , Reference Sibhatu and Qaim 27 , Reference Malapit, Kadiyala and Quisumbing 49 ). To construct the production diversity score, we considered the same twelve food groups that were already explained above. Hence, if a farm produces several species that belong to the same food groups, the production diversity score will be smaller than the simple species count. For comparison, we also show results of models estimated with a simple crop species count as the indicator of farm production diversity.
Measurement of market access
Markets can play an important role for farm households who act as both sellers and buyers of food and other agricultural commodities. We capture access to two different types of market, namely small local village markets and larger district markets. Local markets are relevant for sales and purchases of smaller quantities, in order to satisfy immediate needs. Local markets also play an important role for fresh fruits, vegetables and dairy products that cannot be stored for longer periods of time. As local markets are not available in every village in Malawi, we construct a dummy variable that takes a value of 1 if such a market exists in the village where a household resides and 0 otherwise. Larger markets are available in every district, usually in the district capital. Farm households use these district markets to sell farm produce and to buy food and non-food items. Reaching district markets usually involves walking a longer distance; hence most households do this only occasionally. We capture access to district markets through distance expressed in walking hours, which is a continuous variable.
These two market access variables describe the market infrastructure conditions a household faces, but there may also be other factors that influence actual market participation. To gain further insights into the role of markets, we define three market participation variables that we use in alternative model specifications. First is the share of maize sold. Maize is the most important staple food in Malawi that almost all farm households produce, often primarily for subsistence purposes. Yet, even subsistence-oriented households often sell some of their maize to buy other goods needed. Second is the share of other food crops sold, such as legumes, fruits, vegetables, etc. Third is the farm area share grown with non-food cash crops, such as tobacco or cotton. Non-food cash crops are entirely sold. In principle, agricultural sales can influence household nutrition in positive and negative ways. Positive effects on dietary diversity could occur when the cash revenues are used to buy food groups that are not produced by the households themselves. Negative effects could occur when less food is produced at home and the cash revenues are not spent on improving nutrition and health.
Measurement of agricultural technologies
There is a relatively large body of literature that has analysed effects of agricultural technology adoption on farm incomes, but only a few studies have looked more specifically at the link between technology adoption and household food security or nutrition( Reference Snapp and Fisher 28 , Reference Shiferaw, Kassie and Jaleta 50 , Reference Qaim and Kouser 51 ). In Malawi, the government has recently promoted different technologies to sustainably increase agricultural productivity and reduce poverty. On the one hand, this includes modern inputs such as improved crop varieties and chemical fertilizers, which have been promoted through a targeted input subsidy scheme for several years( Reference Chirwa and Dorward 52 ). On the other hand, there are also efforts to preserve soil fertility through crop diversification and intercropping with legumes( Reference Mhango, Snapp and Phiri 53 , Reference Bezner Kerr, Snapp and Chirwa 54 ). To analyse the role of these technologies for dietary diversity, we construct four technology variables: (i) improved maize varieties; (ii) improved legume varieties; (iii) chemical fertilizers; and (iv) maize–legume intercropping (i.e. growing maize and legumes simultaneously on the same plot of land). These variables are defined as dummies taking a value of 1 when the particular technology was adopted and 0 otherwise.
Regression estimators
The regression models described in equations (1) to (3) above have dietary diversity as the dependent variable. Dietary diversity is a count variable that is not normally distributed. A common approach for count data models is to use a Poisson estimator( Reference Greene 55 ). The Poisson estimator assumes equidispersion; that is, the mean and variance of the dependent variable are assumed to be equal. This assumption is often violated and can lead to incorrect standard errors. Overdispersion, where the conditional variance exceeds the conditional mean, is a common phenomenon in many practical applications( Reference Cameron and Trivedi 56 ). Similarly, underdispersion can also occur in certain situations( Reference Harris, Yang and Hardin 57 ). For each model that we estimate, we use an auxiliary regression test( Reference Cameron and Trivedi 56 ). The test results are reported below. When the null hypothesis of equidispersion (α=0) cannot be rejected, we use the standard Poisson estimator. However, for several models the test results suggest underdispersion (α<0). In those cases, we use a generalized Poisson estimator that is suitable for modelling count data with underdispersion( Reference Harris, Yang and Hardin 57 ).
In Poisson models, the estimated coefficients can be interpreted as semi-elasticities. For more convenient interpretation, instead of the coefficients we report marginal effects for all explanatory variables. In our models, marginal effects describe how the number of food groups consumed changes when the explanatory variables change by one unit. All models are estimated with standard errors corrected for village clusters. Cluster correction controls for possible error term correlation within villages that can result from similarities in environmental or other conditions( Reference Cameron and Miller 58 ).
Results
Descriptive statistics
Descriptive statistics for the variables used in the present study are shown in Table 1. The top part of Table 1 shows DDS at the household level, and individually for children and mothers. At the household level, mean DDS is 4·17; that is, the average household has consumed 4·17 food groups during the reference day. Forty per cent of the households have consumed fewer than four food groups; only 10 % have consumed more than six food groups. The most frequently consumed food groups were cereals and vegetables (see Table S1 in the online supplementary material). Fish was consumed by 20 %, meat by 6 %, and eggs and milk or milk products by less than 5 % of the sample households. These patterns point to relatively low levels of dietary diversity among rural households in Malawi during the lean season, when the data were collected.
Table 1 Description of variables (408 farm household observations); smallholder farm households, rural central and southern Malawi, 2014

† The total number of children (below 5 years of age) in the 408 households is 519.
Individual-level DDS are somewhat lower than those measured at the household level. This is expected because at household level all household members’ consumption is covered, including children above the age of 5 years, adolescents, male adults, etc. However, the differences between household- and individual-level DDS are relatively small, and the different measures are strongly correlated. The correlation coefficient between child and household DDS and between mother and household DDS is 0·78 and 0·90, respectively. Within the group of children, we examined whether age and gender have a systematic influence on DDS, but found no significant effects.
The lower part of Table 1 shows the variables that we use as covariates in the different specifications of the regression models. The average farm produces 4·88 different food groups and 5·79 different crop species. In terms of market access, 56 % of the sample households live in villages that have a local market. The average walking distance to the larger district market is 1·34 h. Less than 8 % of the maize produced is sold in the market, underlining that the sample farms are fairly subsistence-oriented. On the other hand, about one-third of the harvest from other food crops is sold on average and about 11 % of the area is cultivated with non-food cash crops. These numbers reveal that – in spite of their subsistence orientation – farm households in Malawi participate in market transactions and depend on agricultural cash incomes to buy goods and services that they do not produce themselves. Farm-gate sales, village markets and district markets all play important roles for smallholder crop marketing (see Table S2 in the online supplementary material).
In terms of agricultural technologies, improved maize and legume varieties are used by 81 and 62 % of the farm households, respectively. Over 90 % of the households use chemical fertilizers for crop production. Maize–legume intercropping is practised by about half of the farm households. Hence, it seems that modern inputs and improved agricultural practices have been adopted relatively widely by smallholder farmers in Malawi. This may be the result of special support and dissemination programmes run by governmental and non-governmental organizations during the last 10 years.
Association between farm production diversity and dietary diversity
We now look at results from the regression models explained in equation (1) with dietary diversity as dependent and farm production diversity as independent variables. In Table 2, the production diversity score is used as indicator of production diversity. The production diversity score is positively associated with dietary diversity. This should not surprise in subsistence-oriented households, where a large part of what is produced on the farm is consumed in the farm household. Yet the marginal effects are relatively small. Increasing farm production diversity by one food group is associated with only a 0·12 increase in the number of food groups consumed by the farm household. For children, the marginal effect is somewhat larger (0·17), for mothers it is somewhat smaller (0·11).
Table 2 Association between production diversity score and dietary diversity in smallholder farm households, rural central and southern Malawi, 2014
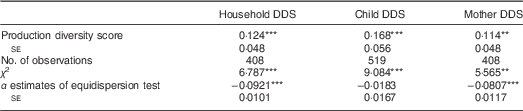
DDS, dietary diversity score.
Marginal effects are shown with their village cluster-corrected standard errors. Based on equidispersion test results, the models for household and mother DDS were estimated with a generalized Poisson estimator; the model for child DDS was estimated with a standard Poisson estimator.
**P<0·05, ***P<0·01.
In Table 3, results from the same type of regression models are shown, but now using the crop species count instead of the production diversity score as independent variable. The estimated marginal effects are also positive, but smaller than those in Table 2. For the household-level model, the effect is not statistically significant. Comparison between Tables 2 and 3 suggests that the number of crop species grown has a lesser influence on dietary diversity than the number of food groups produced. But regardless of the indicator used, substantial improvement in dietary diversity would require very high levels of farm production diversity if this were the only strategy pursued.
Table 3 Association between crop species count and dietary diversity in smallholder farm households, rural central and southern Malawi, 2014
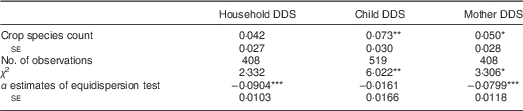
DDS, dietary diversity score.
Marginal effects are shown with their village cluster-corrected standard errors. Based on equidispersion test results, the models for household and mother DDS were estimated with a generalized Poisson estimator; the model for child DDS was estimated with a standard Poisson estimator.
*P<0·1, **P<0·05, ***P<0·01.
The role of markets
We now analyse the role of markets for dietary diversity by estimating the regression models explained in equation (2). In one set of models, we use the market access variables as covariates. In another set of models, we use the market participation variables instead. Due to the correlation between market access and market participation, including both types of variables in the same models would lead to problems of collinearity. In addition to the market variables, we include a vector of other socio-economic and demographic covariates. Results are shown in Table 4.
Table 4 Associations between farm production diversity, market access and dietary diversity in smallholder farm households, rural central and southern Malawi, 2014

DDS, dietary diversity score
Marginal effects are shown with their village cluster-corrected standard errors. Based on equidispersion test results, all models were estimated with a generalized Poisson estimator.
**P<0·05, ***P<0·01.
While the village market dummy is positively associated with dietary diversity, the marginal effects are not statistically significant. Distance to the district market, however, is statistically significant in all three models (household, child and mother). The negative marginal effects imply that longer walking times to the district market are associated with lower dietary diversity. At the same time, the effects of farm production diversity on dietary diversity remain robust. Comparing the estimates suggests that reducing the walking time to the district market by 1 h would have a larger positive effect on dietary diversity than producing one additional food group on the farm. While the exact magnitude of the point estimates should not be over-interpreted, these results clearly confirm that market access matters for the dietary quality of farm households and individual household members.
Another interesting question is whether the effect of farm production diversity on dietary diversity differs by market access. A plausible hypothesis would be that production diversity matters more in remote settings and loses importance with better market access. To test this hypothesis, we split the sample at the mean value of the variable ‘time to district market’ and re-estimated the models for the two sub-samples. The results, which are summarized in Fig. 1, confirm this hypothesis. For households closer to the district market, the effect of farm production diversity is smaller and even turns statistically insignificant in the individual-level models.

Fig. 1 Marginal effect of production diversity score on household (n 408) and individual (children below 5 years, n 519; mothers, n 408) dietary diversity scores (DDS) by distance to district market (![]() , far from district market;
, far from district market; ![]() , close to district market; based on mean value of the variable ‘time to district market’); smallholder farm households, rural central and southern Malawi, 2014. **P<0·05
, close to district market; based on mean value of the variable ‘time to district market’); smallholder farm households, rural central and southern Malawi, 2014. **P<0·05
The role of actual market participation is analysed in the models shown on the right-hand side of Table 4. The share of maize and other food crops sold is positively associated with household and individual dietary diversity. The marginal effects imply that a 10 percentage point increase in the share of maize sold is associated with a 0·14 higher household DDS, almost identical in magnitude across the three models. It seems that the cash incomes generated from maize sales are used to buy more food diversity in the market. The effects for the sale of other food crops are smaller, but also positive and significant in the models for households and mothers.
Table 4 also shows estimates for the role of other socio-economic and demographic factors. Household size is negatively associated with dietary diversity in all models. Education of the household head plays a positive role for household and mothers’ dietary diversity. Interesting to observe are also the effects of off-farm income, which are positive and highly significant in all models. This is another signal of the important role of markets for purchasing food diversity.
To test the robustness of the results, we re-estimated all models in Table 4 using the crop species count instead of production diversity scores as explanatory variable (see Table S3 in the online supplementary material). The effects of production diversity are smaller when the crop species count is used as the indicator. The other estimates in these alternative model specifications largely confirm the findings already discussed.
The role of agricultural technologies
A final set of regression models examines the role of agricultural technology for dietary diversity, as described in equation (3). As explained, we look at four concrete technologies that are included into the models as dummy variables. Results are shown in Table 5. The estimated coefficients for the four technologies are predominantly positive, but many of these coefficients are not statistically significant. One exception is the use of chemical fertilizer, with positive and significant coefficients in the household models and the individual models for mothers. Using chemical fertilizer in crop production is associated with a 0·57 higher household DDS. This effect is larger than that of any other single factor included in the models and points at the important role of crop productivity for farm household diets. At the same time, the fertilizer effect further stresses the important role of markets. Access to input and output markets facilitates farmers’ adoption of fertilizers and other productivity-enhancing inputs.
Table 5 Associations between farm production diversity, market access, agricultural technology and dietary diversity in smallholder farm households, rural central and southern Malawi, 2014

DDS, dietary diversity score.
Marginal effects are shown with their village cluster-corrected standard errors. Based on equidispersion test results, all models were estimated with a generalized Poisson estimator.
*P<0·1, **P<0·05, ***P<0·01.
Fertilizer adoption is positively correlated with the adoption of improved seeds. This correlation and the resulting inflation of the standard errors may explain why the effects for improved maize varieties are not statistically significant, in spite of the relatively large point estimates.
Again as a robustness check, we re-estimated all models in Table 5 using the crop species count instead of production diversity scores as explanatory variable (see Table S4 in the online supplementary material). Except for the smaller effects of the crop species count, the other estimates are similar. Furthermore, as the adoption of agricultural technologies may influence farm production diversity and vice versa, we also re-estimated the same models but excluding farm production diversity (see Table S5 in the online supplementary material). The estimates for the remaining variables do not change much, meaning that the main results are fairly robust to changes in model specification.
Discussion
We have analysed the role of farm production diversity, market access and technology adoption for dietary diversity in smallholder farm households in Malawi. Even though we used different data and indicators of dietary diversity, our results are in line with those from previous studies( Reference Sibhatu, Krishna and Qaim 19 , Reference Sibhatu and Qaim 27 – Reference Jones, Shrinivas and Bezner Kerr 29 ). Yet the analysis also offers a few new insights.
Our results confirm that production diversity is positively associated with dietary diversity. But the effect is relatively small. Previous studies measured production diversity in terms of a simple species count, which we also did in some of the model specifications. However, in the main specifications we used production diversity scores, defined as the number of food groups produced. When using production diversity scores instead of a species count, the effect on dietary diversity is larger. This is plausible in a subsistence-oriented setting like rural Malawi, where a significant share of what is produced on the farm is consumed in the farm household. Interestingly, the opposite was found in a previous study that had used data from more commercially oriented farms in Indonesia, Kenya and Uganda( Reference Sibhatu and Qaim 27 ). In more commercialized settings with better market access, increasing the number of food groups produced on a farm may entail lower cash revenues and foregone benefits from specialization( Reference Sibhatu, Krishna and Qaim 32 ).
But even in a more subsistence-oriented setting like rural Malawi we found an important role of markets for dietary diversity. Closer proximity to markets does not only contribute to higher dietary diversity, but also tends to reduce the effect of farm production diversity. Farm households use markets to sell agricultural produce and to buy foods that they do not or cannot produce themselves. Even foods that are produced on the farm may not always be stored for the entire year; issues of seasonality are particularly important for fresh fruits and vegetables( Reference Hirvonen, Taffesse and Hassen 21 ). Previous studies have shown that foods purchased from the market contribute considerably to farm household diets also in subsistence-oriented settings( Reference Sibhatu, Krishna and Qaim 19 , Reference Luckett, DeClerck and Fanzo 20 ). We also found that sales of maize and other crops have positive effects, because the cash income thus generated can be used to purchase diverse foods in the market. Finally, the analysis has shown that the adoption of modern agricultural technologies is positively associated with dietary diversity. These results clearly suggest that commercial orientation and productivity-enhancing innovation are conducive for better nutrition in smallholder farm households.
Most previous studies that had analysed the role of farm production diversity and other factors for dietary diversity used food consumption data collected at the household level. In the present study, we have used 24 h recall data collected at household and individual levels for young children and mothers. The estimation results for the household- and individual-level models were surprisingly similar. Hence, results do not seem to be driven by the method of measurement of dietary intakes. This is good news for researchers wishing to use secondary data sources. Many nationally representative living standard measurement survey nowadays contain food consumption recalls at the household level, whereas individual-level recall data are available only from more specialized surveys that have a particular nutrition focus.
However, it should be stressed that cross-sectional data collected in a single round have limitations when they are used to assess diets. This applies to secondary data as well as to the primary data collected and used in the present study. In particular, single-round data do not reflect seasonal variation in dietary patterns that can be very important in rural areas. Our data were collected during the lean season prior to the main agricultural harvest. This means that the role of own farm production for dietary diversity may be smaller than during harvest or post-harvest periods. To capture seasonality effects, repeated surveys carried out during different times of the year would be required.
Conclusion
Farm production diversity is positively associated with dietary diversity in Malawi. Hence, on-farm crop diversification may help to improve household diets to some extent. However, the magnitude of the estimates suggests that the positive dietary effects of further diversifying on-farm production will be relatively small. Access to markets for buying food and for selling farm produce, as well as the adoption of modern agricultural technology, were shown to be more important for dietary quality. Hence, improving access to markets through better infrastructure and institutions and promoting the spread of productivity-enhancing technologies seem to be more promising approaches to improve farm household diets. If diversification is pursued, it should not obstruct smallholder market integration and commercialization.
Different models were used, comparing effects on DDS at household and individual levels. Overall, the results were similar across the different models. This similarity suggests that household-level food consumption data, which are more often available from secondary statistics than individual-level data, can be used for broader questions of dietary quality without introducing a significant bias. Of course, for planning interventions that focus on particular target groups, more detailed individual-level data will be required.
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgements: The authors thank the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and the MAIZE Consortium Research Program for hosting the original research, organizing the survey and for useful discussions at all stages of this research. M.K. was affiliated with CIMMYT, Kenya during study implementation. Financial support: This work was supported by a grant from the CGIAR Standing Panel on Impact Assessment (SPIA) provided to CIMMYT. The funder had no role in the design, analysis or writing of this article. Conflict of interest: The authors do not report any conflicts of interest. Authorship: All authors contributed to the design of the research. S.K. and M.K. collected the data. S.K. analysed the data. S.K. and M.Q. wrote the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the paper. Ethics of human subject participation: No ethical approval was required. Participation in the socio-economic survey was not associated with any risk. Verbal informed consent was obtained from all survey respondents. Verbal consent was witnessed and formally recorded.
Supplementary Material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S1368980016002135









