Dietary guidelines recommend a diet with sufficient fruits and vegetables (F&V). F&V provide essential fibre, vitamins and minerals. Low F&V consumption is associated with overweight and chronic diseases such as CVD and cancer( 1 ).
The traditional Korean diet features kimchi (side dish of fermented and seasoned vegetables such as cabbage) and provides sufficient vegetables and fresh fruit( Reference Lee, Popkin and Kim 2 – Reference Kim, Ha and Choi 4 ). For Koreans in the USA (hereafter referred to as ‘Korean Americans’), acculturation has been associated inversely with vegetable intake. Fruit intake among Korean Americans is less clear. One study reported higher fruit intake among acculturated Koreans( Reference Lee, Sobal and Frongillo 5 ), while another study of women found higher fruit intake among Korea-born women( Reference Park, Murphy and Sharma 6 ). The proportion overweight or obese was much higher in US-born women (31 %) v. Korea-born women (9 %)( Reference Park, Murphy and Sharma 6 ).
There is a need for culturally congruent interventions for Korean Americans to address the unfavourable trends in vegetable intake and overweight, as well as access barriers. Most Korean American adults were born in Korea (90 %)( Reference Hofstetter, Ayers and Irvin 7 ), do not speak English very well (51 %), and their income and proportion with health insurance rank below the median for Asians( 8 ). Language barriers, financial barriers, deportation fears and cultural beliefs make them less accessible by mainstream health care( Reference Jo, Maxwell and Yang 9 ). Korean churches are potential forums for reaching large groups of Korean Americans. Over 70 % of Korean Americans attend church regularly( Reference Hofstetter, Ayers and Irvin 7 , Reference Hurh and Kim 10 , Reference Massey and Higgins 11 ) and most prefer the church setting for receiving health information( 8 ). F&V interventions in collaboration with Korean churches have yet to be tested. Almost a third of Korean Americans reside in California, forming a large and growing minority group( Reference Yau 12 ). The present paper describes a pilot study of a culturally acceptable, faith-based intervention in Southern California to promote F&V intake. The pilot’s aims were to test the feasibility of developing and implementing the intervention and to describe pilot results.
Methods
Study design
Feasibility was tested for a cluster randomized design, with churches randomized to the F&V group or control group. Within each church, individual study participants formed a cluster. The study was conducted during 2009–2013.
Recruitment
The bilingual (Korean/English) study church coordinator met with the pastors and other church leaders of the largest Korean churches on several occasions to discuss the study during the first year of the study. The largest eleven churches (forty to 1000+ members) were invited and participated. Seven churches were Presbyterian, two were Baptist, and the others were Nondenominational or Catholic. We grouped the two smallest Presbyterian churches and matched churches on denomination similarity before randomization to treatment group.
A two-page screening questionnaire was offered in Korean and English to adult members after church services during 2010. Of 1093 respondents, 217 met inclusion criteria (over 18 years old; Korean descent; combined daily F&V intake that is at least 1·5 cups below existing dietary guidelines( 1 , 13 ); not moving; and non-smoker reporting second-hand smoke exposure). The last criterion was applied because controls received an alternative (reducing second-hand smoke exposure) intervention. Eligible screening respondents (n 75) from each church were invited to participate from mid-2010 to 2011. Two participants refused (one in each group), leaving seventy-three (97 %) participants enrolled (thirty-six in the F&V intervention; thirty-seven controls).
Intervention
Development
Using a community-based participatory research framework, study and church teams (well-known and respected congregants) collaborated throughout the study. The intervention comprised multiple components to address individual and sociocultural factors in the behavioural ecological model( Reference Hovell, Wahlgren and Adams 14 ) and social ecological framework( 1 ), and was modelled after church-based studies( Reference Resnicow, Campbell and Carr 15 ). The intervention consisted of the following main components: educational materials; five coaching sessions; and church activities. The components were provided in English or Korean (94 % of participants in Korean, per participants’ preference) and tailored to Korean norms, such as group-mindedness and elder respect. The intervention’s goal was to improve knowledge, attitudes, behaviours and social support for F&V intake.
Intervention materials
Intervention participants’ binder provided study information, exercises to identify important values related to healthy eating, benefits of F&V, etc. Korean dishes (e.g. kimchi) and religious messages with health themes were featured. Participants received weekly diaries (to track goals, strategies and progress) and study logo items (refrigerator magnet, pen and reusable grocery bag) to provide environmental cues.
Coaching sessions
A bilingual coach of Korean descent conducted five individual motivational interviewing sessions by telephone every week. Coaches were trained in motivational interviewing, including open-ended questions, affirmation and reflective listening( 13 , Reference Rollnick and Miller 16 ). Sessions focused on improving F&V intake. The coach guided goal setting and strategies, which were discussed at subsequent sessions.
Church activities
Study participants were encouraged by their coach to attend two F&V cooking demonstrations and taste testing at churches following church services or functions. These activities were organized and led by members of their church teams and were open to all church members, which provided social support.
Controls
Control participants received a similar intervention (e.g. materials, coaching and church activities) but on reducing second-hand smoke exposure. An alternative intervention was provided to boost controls’ participation and comparability between treatment conditions(8).
Interview data
Two trained non-coaching staff conducted baseline and follow-up interviews by telephone in English/Korean. Participants reported their demographic and other characteristics shown in Table 1. Questions about knowledge, attitudes and diet were asked at both interviews. Participants were called within a week after completing their coaching sessions to conduct their follow-up interview.
Table 1 Participants’ baseline characteristics, by experimental group, in the feasibility pilot of a faith-based intervention to increase fruit and vegetable intake among Korean Americans, Southern California, 2009–2013
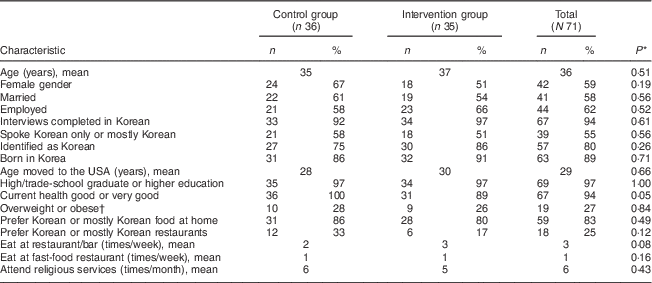
* P value from independent t tests for continuous variables; Pearson or Fisher’s exact χ 2 tests for categorical variables.
† Overweight or obese=BMI of 23·0 kg/m2 or above, per WHO definition.
Knowledge
Participants indicated: (i) whether Koreans eat less vegetables the longer they live in the USA; (ii) whether animal products such as chicken contain fibre; (iii) whether most fresh F&V contain almost no sodium; (iv) whether adults should eat the same amount of F&V regardless of their physical activity levels; and (v) how many cups of F&V they should eat daily according to existing guidelines (MyPyramid) about recommended daily intake (RDI)( 13 ). Responses were scored as accurate or inaccurate.
Attitudes
Participants reported which factor (price, taste, nutrition or convenience) was most important in selecting food.
Dietary intake
Past month consumption frequency and quantity of green salad, other vegetables, fruit juice and fruit were adapted from the National Institutes of Health all-day screener( 17 ). Frequency was converted to daily units following the National Cancer Institute’s scoring( 18 ). Daily frequency was multiplied by daily quantity to estimate daily intake. In addition, participants reported kimchi consumption and meals (breakfast, lunch, dinner and snack) at which they consumed F&V during the past week.
Participants’ feedback
Feedback from participants was obtained at the follow-up interview.
Church activities
Participants reported whether: their pastor mentioned F&V in sermons; church members discussed F&V; they attended church activities; and activities were helpful.
Coaching sessions
Participants rated: how easy it was to find time (very, somewhat or not very); the number of sessions (too many, too few or just right); session length (too short, too long or just right); whether the coach listened (definitely, probably or not); and whether goal setting was helpful (very, somewhat or not very).
Educational materials. Participants reported if they read their binder and used their pen, magnet or bag.
Perceived effectiveness
Participants indicated: what made it easy or hard to achieve their goals; their confidence level (very, somewhat or not very) to maintain any results achieved; and whether they would recommend the study to someone else.
Analysis
Feasibility
To assess feasibility, process measures included: receptivity by churches; feasibility of screening at churches; church activities to promote the intervention; participant recruitment and retention rates; average time to complete interviews; treatment fidelity (number of coaching calls completed); and study participants’ appraisal of the intervention.
The present study was a feasibility pilot which was not powered for significance testing for impact outcomes( Reference Lancaster, Dodd and Williamson 19 ). Descriptive statistics such as frequencies, percentages and pre–post change (Δ; with 95 % CI) were computed for attitudes, knowledge and F&V intake using the statistical software package IBM SPSS Statistics Version 22.0.
Results
Feasibility
Feasibility of collaboration with churches was demonstrated. Allowing time for building relationships with church teams throughout the study fostered their involvement. Process measures indicated the feasibility of delivering a faith-based intervention. Participant recruitment at churches was practical, with 1000+ screeners completed, over one-fifth eligible and 97 % enrolment. The intervention fidelity was 97 %; one participant in each group completed some but not all of the coaching sessions. These two participants did not complete the follow-up interview, hence retention was 97 % and this left thirty-five participants in the F&V intervention and thirty-six controls for analyses.
Participants’ baseline characteristics
There were no statistically significant differences at the P < 0·05 level in baseline characteristics between the control and intervention groups (Table 1). Participants’ mean age was 36 years; over half were female (59 %), married (58 %), employed (62 %), and spoke Korean only or mostly (55 %). Most identified as Korean (80 %) and were born in Korea (89 %). Most participants were high-school graduates (97 %) and in good to very good health (94 %). Twenty-seven per cent of participants were overweight or obese. Participants attended church six times monthly, on average.
Changes in attitudes and knowledge
Table 2 shows that at baseline, 71 % of intervention participants rated taste as most important in choosing food, followed by nutrition (9 %); at follow-up, nutrition became most important (80 %), followed by taste (9 %). Controls rated taste as most important in choosing food (47 % at baseline and follow-up), followed by nutrition (22 % at baseline, 36 % at follow-up).
Table 2 Participants’ attitudes, knowledge and behaviours, by experimental group and period, in the feasibility pilot of a faith-based intervention to increase fruit and vegetable intake among Korean Americans, Southern California, 2009–2013
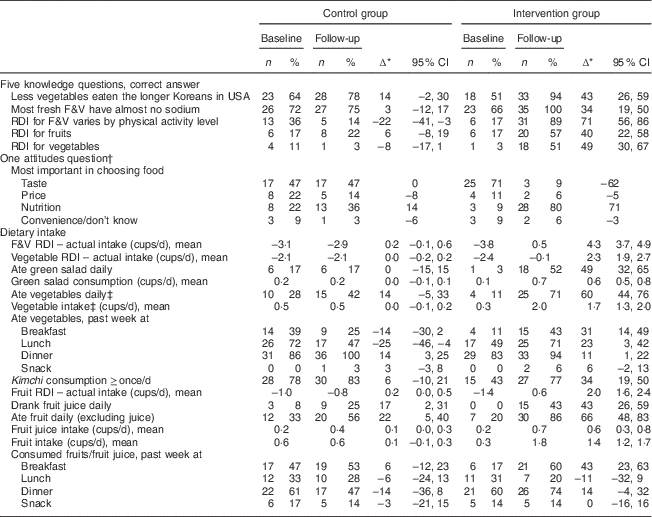
F&V, fruit and vegetables; RDI, recommended daily intake.
* ∆ indicates change in percentage or mean from baseline to follow-up within group; ∆ values are rounded.
† For the one attitudes question, n, % and ∆ are provided for each of the four possible answer categories shown.
‡ Green salad excluded.
The intervention group’s knowledge was lower than controls’ at baseline, but surpassed controls’ at follow-up. The RDI for vegetables was least known at baseline (3 % in intervention group, 11 % in controls); at follow up, knowledge of the vegetable RDI increased in the intervention group (to 51 %) but not the controls.
Changes in fruit and vegetable intake
Fruits and vegetables
The intervention group’s daily F&V intake increased from 3·8 cups below to 0·5 cups above the RDI. The controls’ intake increased slightly, from 3·1 cups below to 2·9 cups below the RDI.
Vegetables
Intervention participants reduced the gap between their recommended and actual vegetable intake from −2·4 cups/d at baseline to −0·1 cups/d at follow-up. They increased green salad intake (from 0·1 to 0·7 cups/d) and other vegetable intake (from 0·3 to 2 cups/d). Vegetable consumption increased throughout the day, especially at breakfast. Controls’ vegetable intake did not increase. Both groups increased daily kimchi intake from baseline to follow-up as follows: from 43 to 77 % among intervention participants; from 78 to 83 % among controls.
Fruits
The intervention group increased daily fruit intake from 1·4 cups below the RDI at baseline to 0·6 cups above at follow-up. They increased fruit juice and fruits, from 0·2 to 0·7 cups/d and from 0·3 to 1·8 cups/d, respectively. Consumption increased most at breakfast.
The controls’ daily fruit intake increased slightly from 1·0 cups below the RDI to 0·8 cups below at follow-up. Fruit juice increased from 0·2 to 0·4 cups/d, but fruit intake remained at 0·6 cups/d.
Fruit and vegetable intervention assessment
Church activities
Most intervention participants (91 %) reported that their pastor mentioned F&V in sermons, that fellow church congregants (83 %) discussed diet with them and that they attended F&V activities at church (89 %); 65 % rated the activities as very helpful.
Coaching sessions
Finding time for coaching sessions was very or somewhat easy (75 %), the number of sessions was just right (86 %), the duration of sessions was just right (94 %), setting goals was very/somewhat helpful (97 %), talking with their coach was helpful (100 %) and their coach listened (100 %).
Educational materials
Most participants read their binder (100 %) and used the shopping bag (94 %), pen (100 %) or magnet (100 %).
Perceived effectiveness
All F&V intervention participants were somewhat/very confident about maintaining improvements. Barriers to meeting goals included: lack of F&V availability, forgetting because of busy schedules and disliking the taste. Most found the binder helpful in achieving goals (74 %) and would recommend the programme to someone else (97 %).
Discussion
The present study is the first faith-based feasibility pilot addressing F&V intake among Korean Americans. Feasibility was demonstrated for the study procedures, including recruitment of churches and individual participants. Several factors favoured the conduct of the pilot. The church coordinator was pivotal for coordinating multiple church teams and church activities. Allocating time throughout the study for church collaboration helped maintain ties and handle unforeseen changes including church leadership changes. Another critical factor was engaging the sociocultural and spiritual influences. Participants’ attendance at church activities and participation by pastors and fellow churchgoers exceeded expectations. Having a centralized coach trained in motivational interviewing, instead of one at each church, was more practical. Use of and satisfaction with the study materials and coaching sessions were high.
Pilot results were favourable for knowledge, attitudes and behaviours. Our results should be interpreted with caution as the pilot sample size was limited. The intervention group’s knowledge of the F&V RDI increased, but left room for improvement. Inadequate knowledge has been associated with deficient intake( Reference Krebs-Smith, Graubard and Kahle 20 , Reference Watters, Satia and Galanko 21 ). In our study, although nearly half of participants could not state the vegetable RDI after the intervention, their intake approximated the RDI.
Study limitations include self-reported F&V intake, which may have been over-reported( 18 , Reference Bogers, Dagnelie and Westerterp 22 ). There is need for reliable F&V assessment tools that are validated with biomarkers, including our modified National Cancer Institute screener. Our F&V RDI were based on contemporary guidelines that are comparable to 2010 guidelines( 1 ), with slightly different age grouping. Updating to current guidelines is needed.
The current pilot suggests that Korean Americans can be reached through their church and that a faith-based community intervention study can be implemented to increase F&V intake. Although pilot results appear promising, further research is needed to evaluate the efficacy of the intervention.
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgements: The authors acknowledge the church leaders, church members and study participants who made this study possible. Financial support: This pilot study was supported partially by the Flight Attendant Medical Research Institute (FAMRI). FAMRI had no role in the design, analysis or writing of this article. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. Authorship contributions: S.C.H. conceived of and conducted the study, supervised the data analyses and drafted the manuscript. S.O. analysed the data, conducted the literature review and helped draft the manuscript. Ethics of human subject participation: This study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki and all procedures involving human subjects/patients were approved by the San Diego State University Institutional Review Board. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants.





