Making the physical environment more conducive to healthy behaviour is an important part of health promotion(Reference Cowburn and Stockley1–Reference Glanz and Mullis3). Especially in the ecological approach to health promotion, environmental factors are considered central to achieving health behaviour change and subsequent improvements in public health(Reference Sallis and Owen4). With regard to nutrition, environmental factors are important determinants of both food consumption (i.e. what people eat)(Reference Sobal and Wansink5) and food purchasing (i.e. the food products people buy)(Reference Glanz and Yaroch2). Therefore, besides the physical location where people eat, the point of purchase provides a promising location to attempt to change food purchasing and, as a consequence, food consumption(Reference Glanz and Yaroch2). In particular, four promising in-store health-promoting strategies have been identified(Reference Glanz and Yaroch2): (i) providing point-of-purchase product health information; (ii) increasing the availability of healthy products; (iii) reducing the prices of healthy products; and (iv) increasing promotion and advertising for healthy products. The present review focused on the first strategy. A systematic literature review was conducted to investigate whether product health information can affect food purchasing in supermarkets and grocery stores. Supermarkets and grocery stores were chosen because together they make up the largest food retail chain in the USA(6) and other Western countries(7). Convenience stores, restaurants and other out-of-home food outlets were excluded because these offer a very different setting, making the effects of product health information difficult to compare. Because self-reports of food purchasing behaviour may not be accurate, the review only included studies that investigated the effect of product health information at the point of purchase by actual sales data on the item or product category level. These data could be provided by stores’ sales records or obtained by investigating customer receipts.
Many researchers have pointed out that offering product health information at the point of purchase might be a promising way to target food purchasing(Reference Cowburn and Stockley1, Reference Glanz and Mullis3, Reference Glanz, Hewitt and Rudd8, Reference Van Kleef, Van Trijp and Paeps9). According to Grunert and Wills(Reference Grunert and Wills10), providing consumers with information about the nutritional content of individual food products at the point of purchase is one of the major instruments in trying to bring about healthier eating practices. The advantages of this approach are that it enables consumers to more easily judge which product is healthier(Reference Van Kleef, Van Trijp and Paeps9, Reference Balasubramanian and Cole11–Reference Seymour, Yaroch and Serdula13), making the physical environment more conducive to healthy food purchasing(Reference Cowburn and Stockley1–Reference Glanz and Mullis3), while retaining consumer freedom of choice(Reference Grunert and Wills10). In addition, conveying relevant information about the nutritional content of food products contributes to consumer protection(Reference Cowburn and Stockley1, Reference Van Kleef, Van Trijp and Paeps9).
There are several different ways in which product health information can be conveyed. One especially well-known instance of the use of product health information is back-of-pack (BOP) nutrition labelling. A notable example of this practice is the Nutrition Fact Panel, which provides nutritional information and has been placed on packaged foods in the USA since the enforcement of the Nutrition Labeling and Education Act in 1990. It is estimated that 96·3 % of processed and packaged foods regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration have a Nutrition Fact Panel on the back of the package(Reference Brandt, Moss and Ferguson14). BOP nutritional information on food products is also increasingly used in Europe, with a recent study finding penetration of 85 %(Reference Storcksdieck-Bonsmann, Fernández Celemín and Larrañaga15). This is partly the result of the 1990 European Union Council Directive (90/496/EEC), which requires food products that are advertised with a health claim to carry nutritional information. In addition to BOP nutrition labelling, simpler front-of-pack (FOP) labels can be used to show the percentage of Guideline Daily Amounts (GDA) for several key nutrients or to indicate the general healthfulness of food products(Reference Van Kleef, Van Trijp and Paeps9, Reference Smith, Stephen and Dombrow16, Reference Van Kleef and Dagevos17). Examples of the latter approach are the Green Keyhole logo that is used in Sweden(Reference Larsson, Lissner and Wilhelmsen18) and the Pick the Tick logo that is used in New Zealand(Reference Scott and Worsley19). Besides nutritional information on food packages, however, there are several other ways to convey product health information, such as attaching information to shelves(Reference Schucker, Levy and Tenney20), using posters that are placed next to or over the product rack(Reference Russo, Staelin and Nolan21) or audio messages that are played in supermarkets and grocery stores(Reference Connell, Goldberg and Folta22). The present review focuses on all ways in which information about the nutritional qualities of food products is communicated to consumers at the point of purchase.
What do we know about the actual effectiveness of product health information at the point of purchase? Can product health information actually increase the likelihood that consumers buy healthy products? Or is the effect of product health information bound to be limited? Given its great potential and its increased use, it is important to investigate whether product health information at the point of purchase can be an effective means to stimulate healthy food purchasing.
The effects of product health information on perceptions, attitudes and purchase intentions have received ample attention in the literature. Such research suggests that many consumers value product health information and indicate that it would greatly influence their purchase decisions(Reference Arsenault and Glanville23, Reference Hunt, Lefebvre and Hixson24). With regard to the Nutrition Fact Panel, research shows that many consumers indicate they pay attention to it(25, Reference Kristal, Levy and Patterson26). Also, there is evidence from experimental studies that product health information can affect attitudes and intentions(Reference Kozup, Creyer and Burton27, Reference Burton, Biswas and Netemeyer28). There are several reasons, however, why the public health effects of product health information may be more limited than these studies suggest. First, although many consumers have a positive attitude towards product health information, it is questionable how well they understand it. Many consumers think that product health information is too complicated(Reference Kristal, Levy and Patterson26) and it has been argued that many of them have a limited understanding of the information(Reference Cowburn and Stockley1). Understanding may also differ greatly between different consumers. A recent study conducted in six European countries suggests that understanding of product health information differs significantly between countries(Reference Grunert, Fernandez-Celemin and Wills29), with high understanding found in the UK, Sweden and Germany, and more limited understanding found in France, Poland and Hungary. A second reason why the public health effects of product health information may be limited is that the positive effects of product information may only be present in consumers who are knowledgeable about nutrition and are motivated to use the information(Reference Howlett, Burton and Kozup30–Reference Szykman, Bloom and Levy32). Especially motivation is likely to be an important determinant of use, as a recent study shows that interest in healthy eating is a stronger predictor of the use of product health information than nutrition knowledge(Reference Grunert, Fernandez-Celemin and Wills29). Thus, product health information may only be effective in the small subset of the population that is already motivated to eat in a healthy way. Finally, most studies that have investigated the effects of product health information have relied on self-reported outcome measures(Reference Kristal, Levy and Patterson26, Reference Kozup, Creyer and Burton27, Reference Steenhuis, van Assema and van Breukelen33), which are open to bias. Studies that did not rely on self-reported assessments, but observed actual use of product health information, showed that actual use is much lower than reported use(Reference Mhurchu and Gorton34). Studies that use a combination of observation and qualitative methods generally yield lower estimates of usage than studies that use self-report methodologies(Reference Grunert, Wills and Fernandez-Celemin35). Thus, although it is clear that product health information at the point of purchase can potentially make physical environments more conducive to healthy food purchasing and, consequently, to healthy food consumption, it is important to investigate the extent to which product health information actually influences food purchase decisions.
In contrast to the many studies that investigated the effect of product health information on attitudes, intentions or self-reported behaviour, only a limited amount of studies have investigated the effects of product health information on actual purchase behaviour(Reference Seymour, Yaroch and Serdula13). In one early study by Muller(Reference Muller36), product health information resulted in increased purchasing of healthy products. However, several other studies failed to find significant effects(Reference Achabal, McIntyre and Bell37) or found significant effects for some products, but not for other products(Reference Teisl and Levy38). Because of these inconsistent findings, the first aim of the present research was to establish how much evidence exists to date on the effectiveness of product health information at the point of purchase. Also, if the overall effect of product health information proves inconsistent over studies, it is important to investigate potential reasons for this. Thus, the second aim of the research was to investigate whether explanations can be found to account for the inconsistencies in the empirical findings.
In the present study, it was investigated whether product health information can affect purchase behaviour by means of a systematic review of the existing literature. Because actual purchase decisions are more relevant to health promotion practice than perceptions, attitudes or intentions, the study focused on research investigating actual purchase behaviour. Also, because studies that rely on self-reported data are open to bias, the present study focused on research that used sales data provided by stores or retrieved from customer receipts as the main outcome measure. The present study is the first one to give a comprehensive overview of the behavioural effects of product health information. One previous overview, published in 2007(Reference Grunert and Wills10), focused solely on studies performed in the European Union. Another, published in 2005, was concerned with understanding and use of product health information instead of behavioural effects(Reference Cowburn and Stockley1). One other review that did focus on behavioural effects was published over 20 years ago, in 1989(Reference Mayer, Dubbert and Elder39). Finally, one review(Reference Seymour, Yaroch and Serdula13) published in 2004 did not include all relevant studies that investigated the effects of product health information on purchases. The present review's contribution to the literature is that it focuses primarily on purchase behaviour instead of understanding, attitude or intentions. It furthermore aims to provide an up-to-date and comprehensive overview of studies, not confined by geography.
Method
Identifying relevant studies
To identify relevant publications in the time period up to January 2010, the present study conformed to standard procedures for systematic reviewing(Reference Egger, Davey Smith and Altman40, Reference Oliver and Peersman41) and used the following search strategy. First, references were retrieved from the electronic databases Web of Science, ERIC, Medline and Google Scholar, using the following key words: ‘supermarket’, ‘store’, ‘food outlet’, ‘shop’, ‘grocery’, ‘groceries’, ‘nutrition’, ‘food’, ‘information’, ‘label’, ‘poster’, ‘fact sheet’, ‘intervention’, ‘nutrient’, ‘health’, ‘disease’, ‘risk’, ‘sales’, ‘purchase’, ‘market share’. Second, studies retrieved from prior reviews that included the effects of point-of-purchase health promotion(Reference Grunert and Wills10, Reference Seymour, Yaroch and Serdula13) were examined. Third, cross-references in the obtained reports were checked (‘backward searching’ or ‘snowball method’). Finally, all available issues appearing during or after 1980 of the journals Journal of the American Dietetic Association, Preventive Medicine and Public Health Nutrition were searched manually. These journals were chosen because initial searches identified these particular journals as likely to publish on the subject of interest.
Inclusion criteria
Seven inclusion criteria were used to gather an optimal sample of studies. Only studies were included that:
1. Investigated the effects of product health information, i.e. health information at the product level.
2. Took place in supermarkets or grocery stores.
3. Used an experimental design (compared a product health information condition with a control condition).
4. Used sales data as the outcome measure of interest.
5. Were published in English.
6. Were published between 1980 and 2010.
7. Were published in peer-reviewed journals, books or book chapters. This was decided because published work tends to be peer-reviewed and is potentially of greater quality than unpublished work.
Initial searches yielded 159 articles that had the potential to be included in the review. The author read all abstracts to establish whether they met the inclusion criteria. In case of doubt, the author closely read the remainder of the article to establish whether it should be included. Of all 159 articles:
1. One hundred and eighteen articles (74 % of the total) were excluded because they did not meet the first inclusion criterion and did not investigate the effects of product health information. For instance, thirty-one articles (19 %) focused on the determinants of eating behaviour, mostly using an observational design (e.g. reference Reference McEachern and Seaman42), fifteen articles (9 %) reported (biochemical) research into the nutritional content of various foods (e.g. reference Reference Aidoo, Tester and Morrison43), and fourteen articles (9 %) were excluded because they dealt with food availability, food regulation or taxing issues (e.g. reference Reference Hamilton, Mhurchu and Priest44) or with the agricultural system or food chain (e.g. reference Reference Stathers, Chigariro and Mudiwa45).
2. Of the remaining forty-one articles, all met the second inclusion criterion, reporting research that had taken place in supermarkets or grocery stores.
3. Of the remaining forty-one articles, six (4 %) were excluded that did investigate the effects of in-store product health information but did not use an experimental design. Balasubramanian and Cole(Reference Balasubramanian and Cole11), for instance, investigated the effect of product health information by comparing consumer behaviour before and after the introduction of the Nutrition Fact Panel, but did not compare an intervention group with a control group(Reference Arsenault and Glanville23, Reference Wagner, Winett and Walbertrankin46).
4. Of the remaining thirty-five articles, nineteen (12 %) were excluded that did investigate the effects of in-store product health information, but did not use sales data as the outcome measure. For instance, Steenhuis et al.(Reference Steenhuis, van Assema and van Breukelen33) investigated the effects of product health information in supermarkets in the Netherlands, but used self-reported behaviour as the primary outcome measure (see also reference Reference Connell, Goldberg and Folta22).
5. Of the remaining sixteen articles, all met inclusion criteria 5, 6 and 7 and qualified for inclusion in the present review.
In total, sixteen articles (10 %), reporting seventeen studies, met all inclusion criteria.
Coding of study characteristics
For all included studies, sample characteristics, treatment characteristics and model characteristics were coded. Coding was done by the author and an expert colleague and resulted in a joint probability of agreement of 0·80. Disagreements were resolved through discussion. Sample characteristics were: the number of supermarkets that participated in the study, the number of product categories under investigation (and the specific product categories if less than ten product categories were investigated) and the study period (in weeks). Treatment characteristics were: the way product health information was provided (for instance, posters, labels or both) and whether the intervention had additional components besides the point-of-purchase product health information. Furthermore, previous research suggests that product health information can have different effects depending on whether it stresses the presence of healthy nutrients, such as vitamins and fibre, or the absence of unhealthy nutrients, such as sugar and fat(Reference Russo, Staelin and Nolan21). Therefore, for all studies, it was coded whether the product health information focused on healthy nutrients, unhealthy nutrients or both. Model characteristics were: statistical approach, used covariates and dependent variable. With regard to study effectiveness, study results were coded as effective (+) if sales of healthy products increased significantly relative to the control group, as partially effective (+/0) if a significant effect was found for some, but not all products under investigation, as not effective (0) if no significant effect was found, as counter effective (−) if sales of healthy products decreased significantly relative to the control group, and as divergently effective (+/−) if sales of healthy alternatives increased in some product categories, but decreased in other product categories. Finally, if retrievable from the paper, the location of the study (country, city, state) was coded.
Results
Study characteristics
In total, sixteen articles were retrieved, reporting seventeen studies. All studies were conducted in the USA, except for one, which was conducted in Canada(Reference Muller36). All studies were conducted in urban areas. With regard to sample characteristics, Table 1 shows that the studies varied widely in terms of the numbers of included sites and product categories, and the intervention periods. The number of sites ranged from one to 372, the number of product categories ranged from one to seventeen, and the intervention period ranged from 2 weeks to 208 weeks.
Table 1 Sample characteristics of the included studies and their effects on sales
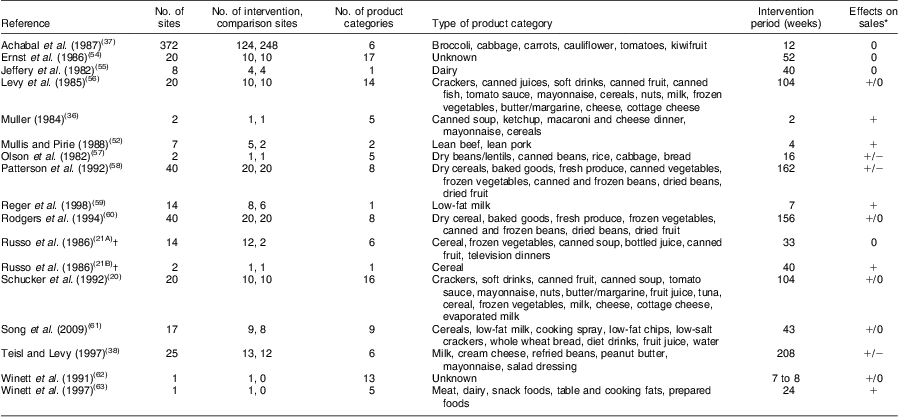
*+, effective (sales of healthy products increased significantly relative to the control group); +/0, partially effective (a significant effect was found for some, but not all products under investigation); 0, not effective (no significant effect was found); −, counter effective (sales of unhealthy products increased significantly relative to the control group); +/−, divergently effective (sales of healthy alternatives increased in some product categories, whereas sales of unhealthy alternatives increased in other product categories).
†Russo et al. (1986)(Reference Russo, Staelin and Nolan21) reported on two studies; these studies are represented in the tables as Russo et al. (1986)(21A) and Russo et al. (1986)(21B).
The retrieved studies also showed a wide variety in treatment characteristics. As can be seen in Table 2, product health information was delivered using shelf tags (eleven studies; 65 % of total), posters (six studies; 35 %), brochures (four studies; 24 %), flyers (three studies; 18 %), a multimedia, public-access system (two studies; 12 %) and in one case (6 %) package labels. Addressed nutrients were fat (thirteen studies; 76 %), calories (eight studies; 47 %), sodium/salt (seven studies; 41 %), cholesterol (six studies; 35 %), fibre (five studies; 29 %), vitamins (four studies; 24 %), minerals (three studies; 18 %), sugar (two studies; 12 %), protein (one study; 6 %) and carbohydrate (one study; 6 %). Three studies (18 %) used only information focusing on the presence of healthy nutrients, eight studies (47 %) used information that focused on the absence or diminished presence of unhealthy nutrients, and six studies (35 %) used information that focused on both healthy and unhealthy information. Furthermore, nine studies (53 %) assessed the effects of only product health information, whereas in eight studies (47 %) product health information was complemented with additional treatment, such as mass-media campaigns, local publicity, in-store taste testing and cooking demonstrations.
Table 2 Treatment characteristics of the included studies and their effects on sales

NA, not available.
*+, effective (sales of healthy products increased significantly relative to the control group); +/0, partially effective (a significant effect was found for some, but not all products under investigation); 0, not effective (no significant effect was found); −, counter effective (sales of unhealthy products increased significantly relative to the control group); +/−, divergently effective (sales of healthy alternatives increased in some product categories, whereas sales of unhealthy alternatives increased in other product categories).
With regard to model characteristics, the retrieved studies also showed a wide variety. As can be seen in Table 3, regression, ANOVA and analysis of covariance were used most frequently as the method of statistical analysis (seven studies; 41 %). These techniques are natural choices when the difference between a treatment and a control group is the focal question of interest. However, it is possible that the long-term effects of product health information are different from the short-term effects. In this case, it is not only relevant to investigate the effects of product health information in the current period, but, since these effects extend beyond the current period, it is also relevant to identify their behavioural impact in future periods. Time series analysis has become the natural tool of application for the potential difference between the current and long-run impact. These tools have been applied in only three studies (18 %; see Table 3).
Table 3 Model characteristics of the included studies

ANCOVA, analysis of covariance; TSCSREG, time series cross-sectional regression analysis; SES, socio-economic status; NA, not available.
Even though in the present review only studies that derived their outcome measure from sales data were included, significant variety was also found in the specific operationalization of the outcome measure. Nine studies (53 %) used product sales as the outcome measures, two of which (12 %) assessed product sales volume (e.g. ounces) and seven (41 %) did not specify whether they assessed sales volume or sales revenue. Two studies assessed sales for entire product categories (12 %) and five studies assessed targeted products’ market shares (29 %). In addition, three studies (18 %) calculated the nutritional quality of all sold products. One study, for instance, rated all targeted products as more or less healthy on a scale from 0 to 100. This rating was based on the presence or absence of the specific nutrient that was targeted in the product health information. When a product was accompanied by information about more than one nutrient, these ‘performance scores’ were averaged across all nutrients. Given each product's performance score and product sales, a mean purchase performance was computed for the intervention and control groups, which could then be compared.
Effectiveness of product health information
As can be seen in Table 1 and 2, overall evidence for the effectiveness of product health information at the point of purchase is mixed. Of all seventeen studies, five studies yielded a positive effect on product sales (29 %) and five studies yielded positive findings for some products but not for all products (29 %). Ten studies thus yielded evidence for the (partial) effectiveness of product health information. In contrast, three studies yielded an increase in healthy purchases for some products, but a decrease in healthy purchases for other products (18 %). Moreover, four studies yielded no evidence of any increase in healthy purchases (24 %; see Table 4).
Table 4 Evidence for effectiveness of the included studies

Entries in table are reference numbers.
*+, effective (sales of healthy products increased significantly relative to the control group); +/0, partially effective (a significant effect was found for some, but not all products under investigation); 0, not effective (no significant effect was found); −, counter effective (sales of unhealthy products increased significantly relative to the control group); +/−, divergently effective (sales of healthy alternatives increased in some product categories, whereas sales of unhealthy alternatives increased in other product categories).
Explanations for inconsistent findings
Given that the overall effect of product health information on healthy purchases is inconsistent over studies, it is important to investigate whether explanations can be found to account for these inconsistencies. It was therefore investigated whether the likelihood of a significant effect may have been affected by study characteristics, such as the number of included sites and the number of product categories. Because the present study did not employ meta-analytic methodology, the effects of these study characteristics could not be quantified and should be interpreted with caution. Future empirical research should be employed to investigate these effects more thoroughly.
Close inspection of Tables 1 and 2 reveals no differential effectiveness for studies differing in the number of included sites, the number of product categories, the nature of the product categories or the specific treatment (delivery of the product health information). However, the length of the intervention period, the presence or absence of additional intervention components, and the type of nutrients that were included in the provided information did seem to affect the likelihood that the intervention was effective. With regard to intervention length, close inspection of Table 1 reveals that five studies investigated interventions which lasted longer than a year (i.e. more than 52 weeks). All five of these studies yielded an increase in healthy purchases, although two studies yielded divergent findings, showing increases in healthy purchases in some product categories, but decreases in other product categories. Interventions that lasted a year or less, however, produced increases in healthy purchases in seven instances, but no effects in four instances (see Table 5).
Table 5 Evidence for effectiveness of the included studies, split by intervention period, presence or absence of additional intervention components, and type of nutrient
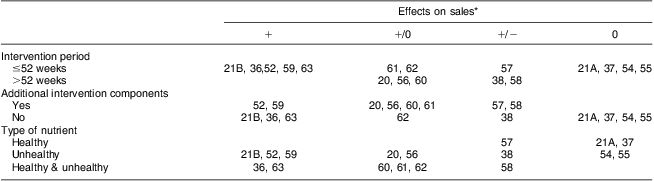
Entries in table are reference numbers.
*+, effective (sales of healthy products increased significantly relative to the control group); +/0, partially effective (a significant effect was found for some, but not all products under investigation); 0, not effective (no significant effect was found); −, counter effective (sales of unhealthy products increased significantly relative to the control group); +/−, divergently effective (sales of healthy alternatives increased in some product categories, whereas sales of unhealthy alternatives increased in other product categories).
Furthermore, the effectiveness of interventions that included intervention components additional to the product health information was compared with the effectiveness of interventions that relied exclusively on product health information. As can be seen in Table 5, eight interventions made use of additional intervention components, all of which resulted in increases in healthy purchases, although two studies also resulted in decreases in healthy purchases for some product categories. Of the nine interventions that did not include additional intervention components, five resulted in increased healthy purchases, whereas four did not yield any change in purchases.
With regard to the type of nutrients, Table 5 shows the study results for interventions that conveyed information about the presence of healthy nutrients (e.g. vitamins, minerals, fibre) v. the absence of unhealthy nutrients (e.g. calories, fat, sugar). As can be seen, the number of interventions that exclusively made use of information concerning healthy nutrients was limited. Of these three interventions, two yielded no evidence for effectiveness and one intervention resulted in divergent findings. Interventions that targeted unhealthy nutrients fared better, however, with six out of eight studies showing an increase in healthy purchases, although one study also showed a decrease in healthy purchases in some product categories. Interventions that targeted both healthy and unhealthy nutrients were most effective, with all six studies showing increases in healthy purchases, one of which also showed a decrease in healthy purchases in some product categories.
Discussion
Main findings and implications for practice
Information about the healthy and the unhealthy qualities of products can have a great influence on consumer behaviour. When for instance the American Dental Association unexpectedly endorsed Crest toothpaste for healthy teeth, Crest's market share increased permanently by 18 %(Reference Wichern and Jones47). It has therefore been argued that providing consumers with information about the nutritional content of individual food products at the point of purchase is one of the major instruments in trying to bring about healthier eating practices(Reference Grunert and Wills10). The present review set out to gather evidence from the literature about the effects of product health information on purchase decisions by actual consumers in real-life shopping settings. Overall, the studies’ results are mixed. Thus, in contrast to the vast potential that product health information is said to have(Reference Cowburn and Stockley1, Reference Glanz and Mullis3, Reference Glanz, Hewitt and Rudd8, Reference Van Kleef, Van Trijp and Paeps9), the current review shows that the actual evidence for its effectiveness is not very convincing.
It is noteworthy that three studies found that the intervention had diverging effects for different product categories. In these studies, the intervention resulted in healthier purchases for some food products, but in unhealthier purchases for other food products. Teisl and Levy(Reference Teisl and Levy38), for instance, found that the intervention increased sales of healthy products for milk, creamed cheese, beans and peanut butter but had the opposite effect for salad dressing and mayonnaise. Teisl and Levy propose that consumers opted for the healthy alternative when the healthy and unhealthy products did not differ too much in taste, as they suppose was the case with milk, creamed cheese, beans and peanut butter. However, after having chosen the healthy alternative for one or more of these products, consumers might have reasoned that, in light of their previous healthy choice, they were now entitled to the unhealthy alternative for salad dressing and mayonnaise, products for which Teisl and Levy argue the unhealthy alternative has superior taste over the healthy alternative. Thus, consumers tried to increase the total utility of their purchases while keeping their health risk equal. Teisl and Levy propose that consumers act as if they have ‘health risk budgets’ and may compensate healthy purchases with unhealthy purchases (for evidence of ‘risk compensation’ in other domains see references Reference Kalichman, Eaton and Pinkerton48–Reference Pinkerton50). It is important to note that Teisl and Levy propose the existence of ‘health risk budgets’ as a post hoc explanation for their research findings and do not offer much in the way of concrete empirical evidence for their reasoning. In fact, there is generally little direct empirical evidence that consumers compensate healthy food purchases with unhealthy ones. One study by Bolton and colleagues(Reference Bolton, Cohen and Bloom51) did find that participants who were offered a weight-loss pill exhibited stronger high-fat eating intentions than participants who were offered no such pill, but that study did not assess actual compensation between different food products at the point of purchase. Nevertheless, Teisl and Levy's reasoning offers an interesting hypothesis that should be tested in future research. If risk compensation does indeed occur in the supermarket, it can explain the mixed and generally modest effects of product health information on healthy purchase decisions. With regard to intervention studies, the possible existence of risk compensation suggests that such studies should investigate the effects of product health information on a wide variety of products, also including products that were not targeted in the intervention, since they may act as unhealthy ‘compensation’ for healthy purchase decisions. If only a limited number of products is investigated, the health effects of product health information may be overestimated(Reference Teisl and Levy38). Such research should also investigate whether risk compensation can be influenced by other factors, such as price and availability. For instance, it may well be that in some product categories healthy products are generally more expensive than unhealthy products, whereas in other product categories, healthy and unhealthy products cost the same. Consumers may be tempted to buy the healthy product in those categories in which healthy and unhealthy products are equally expensive and compensate these purchases with unhealthy products in categories in which unhealthy products are cheaper than healthy products. Thus, instead of a trade-off between health and taste, as proposed by Teisl and Levy, there may be a trade-off between health and price or between health and yet another factor. Future research is needed to shed more light on this phenomenon.
In the present review, it was investigated whether certain factors can impede or facilitate the effectiveness of interventions making use of product health information, thus potentially functioning as effect modifiers. Although no meta-analysis was performed to test the effects of these factors for statistical significance, the results do suggest three propositions that should be tested in future research. First, it seems that interventions that are implemented for more than a year are more likely to be effective than interventions that are implemented for a shorter period. Possibly, consumers do not react immediately to product health information, but take some time to contemplate their options, which results in a lagged effect. In any case, the sustainability of the intervention seems to be an important determinant of intervention effectiveness(Reference Glanz and Yaroch2).
It was also found that interventions which included additional components besides the product health information were more likely to be effective than interventions that provided product health information only. Perhaps product health information alone is not sufficient to capture consumers’ attention. Alternatively, consumers may find product health information difficult to understand(Reference Cowburn and Stockley1, Reference Van Kleef, Van Trijp and Paeps9) and the additional intervention components may have helped them make sense of the nutritional information. On the other hand, research by Grunert and colleagues(Reference Grunert, Fernandez-Celemin and Wills29, Reference Grunert, Wills and Fernandez-Celemin35) suggests that motivation, and not understanding, is the biggest obstacle for product health information to be effective. Perhaps additional intervention components are necessary to motivate people to follow a healthy diet, in order for product health information to be able to influence purchase behaviour.
Another finding was that interventions that targeted only the presence of healthy nutrients in product health information were less likely to be effective than interventions that targeted unhealthy nutrients or both healthy and unhealthy nutrients. According to Russo et al.(Reference Russo, Staelin and Nolan21), the limited effectiveness of information about healthy nutrients can be explained by the fact that a lack of healthy nutrients in one's diet can easily be compensated for by taking dietary supplements. Thus, a consumer who wants to increase her vitamin C intake does not have to change her dietary pattern dramatically; she can also start taking vitamin pills. According to Russo et al., information about unhealthy nutrients is more effective, because there is no such shortcut to compensate for consuming too much fat or sodium. For this reason, product health information may be more effective when it addresses the absence of unhealthy nutrients rather than the presence of healthy nutrients.
Implications for research
The retrieved studies differed widely with regard to sample characteristics, treatment characteristics and model characteristics. With regard to product categories, for example, the different studies covered bread, crackers and cereals, fresh, dried and processed fruits, fresh and processed vegetables, dairy, meat and sweets. The retrieved studies furthermore included small-scale, short-term interventions but also interventions that took place at dozens of sites and lasted for more than a year. In two respects, however, the retrieved studies form a somewhat limited evidence base. First, all retrieved studies were conducted in the USA and Canada. To be able to generalize from studies on the sales effects of product health information, more of such studies should be performed in Europe, Australia and, especially, non-Western countries. Second, in the retrieved studies, the information about the nutritional quality of specific products was conveyed predominantly with the help of shelf tags, posters and brochures. Only one study displayed the information on the products’ packaging(Reference Mullis and Pirie52) and no study assessed the effects of simple FOP labels that indicate the general healthfulness of food products(Reference Van Kleef, Van Trijp and Paeps9, Reference Smith, Stephen and Dombrow16). Because this approach is increasingly used in supermarkets and grocery stores, research is needed that investigates whether such health logos can influence consumers’ purchase decisions in a real-life setting.
Another limitation of the retrieved studies is that several potentially important factors that can influence the effects of product health information have not been accounted for in most studies. Dekimpe and Hanssens(Reference Dekimpe and Hanssens53), for instance, identify six possible ways in which a variable such as product health information can influence the sales of a product: (i) instantaneous effects (the information has an impact within the same time period); (ii) carry-over effects (the information has an impact in future periods); (iii) purchase reinforcement (the information may attract new consumers or cause consumers to imitate others); (iv) feedback effects (the information offering is influenced by current and past sales); (v) firm specific decision rules; and (vi) competitive reactions. No retrieved study in the present review accounted for these relevant aspects of market dynamics. Future research could analyse the impact of product health information using sales and marketing-mix data that contain information on all of the aforementioned mechanisms of market dynamics.
Strength and limitations
One of the strengths of the present review is the fact that only studies were included that used objectively assessed purchase behaviour as the outcome measure. As seen above, the effects of product health information on perceptions, attitudes and purchase intentions have received ample attention in the literature, but intentions do not always translate into behaviour and therefore the public health effects of product health information may be more limited than suggested by studies that rely on attitudes and intentions as outcome measures. Self-reported behaviour is preferable to attitudes and intentions as an outcome measure, but the problem with self-reported behaviour is that it is open to bias, such as socially desirable responding. The present review therefore focused on research that used sales data as the main outcome measure.
A limitation of the present review is that the conclusions could not be strengthened by meta-analytic procedures. As can be seen in Table 3, although the only studies included were those that derived their outcome measure from sales data, the retrieved studies differed widely in the specific operationalization of the outcome measure. Some studies assessed product sales volume (e.g. ounces), other studies used sales revenue or market shares and yet others calculated the nutritional quality of all purchased products. A bigger problem was that in most studies results were presented separately for different products. In many studies, this yielded mixed findings (an effect was found for some, but not all products under investigation) or diverging findings (sales of healthy alternatives increased in some product categories, but decreased in other product categories), which made it impossible to calculate an overall effect size for the study and rendered a qualitative assessment of study findings preferable.
Conclusions
Overall, the evidence for the effectiveness of product health information is mixed. Although product health information clearly has vast potential to influence consumers’ purchase decisions(Reference Cowburn and Stockley1, Reference Glanz and Mullis3, Reference Glanz, Hewitt and Rudd8, Reference Van Kleef, Van Trijp and Paeps9), more research is needed to determine how the effectiveness of product health information can be further improved. Based on the present review, it seems that interventions are more likely to be successful when they are implemented for longer than a year, when they are accompanied by additional promotional activities and when they target the absence of unhealthy nutrients, such as fat, sugar or calories, instead of or in addition to the presence of healthy nutrients, such as minerals, vitamins or fibre. Future research should investigate these possibilities. Especially needed are studies that investigate the effectiveness of general health logos and studies that are conducted outside North America. Such studies should also account for the real-life market dynamics stemming from consumer responses, competitor reactions and own-firm market actions.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Wageningen UR Strategic Research Programme ‘Plant and Animal for Human Health’ which is financed by the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs, Agriculture and Innovation. No conflicts of interest are reported by the author. The author would like to thank Marcel Kornelis for assistance with coding papers and Marcel Kornelis and Hans Dagevos for commenting on a previous version of this manuscript.







