Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 June 2022
Phyllotaxis, the regular arrangement of plant lateral organs, is an important aspect of quantitative plant biology. Some models relying on the geometric relationship of the shoot apex and organ primordia focus mainly on spiral phyllotaxis, a common phyllotaxis mode. While these models often predict the dependency of Fibonacci spirals on the Golden Angle, other models do not emphasise such a relation. Phyllotactic patterning in Asteraceae is one such example. Recently, it was revealed that auxin dynamics and the expansion and contraction of the active ring of the capitulum (head) are the key processes to guide Fibonacci spirals in gerbera (Gerbera hybrida). In this Insights paper, we discuss the importance of auxin dynamics, distinct phases of phyllotactic patterning, and the transition of phyllotaxis modes. These findings signify the local interaction among primordia in phyllotactic patterning and the notion that Fibonacci spirals may not need the Golden Angle.

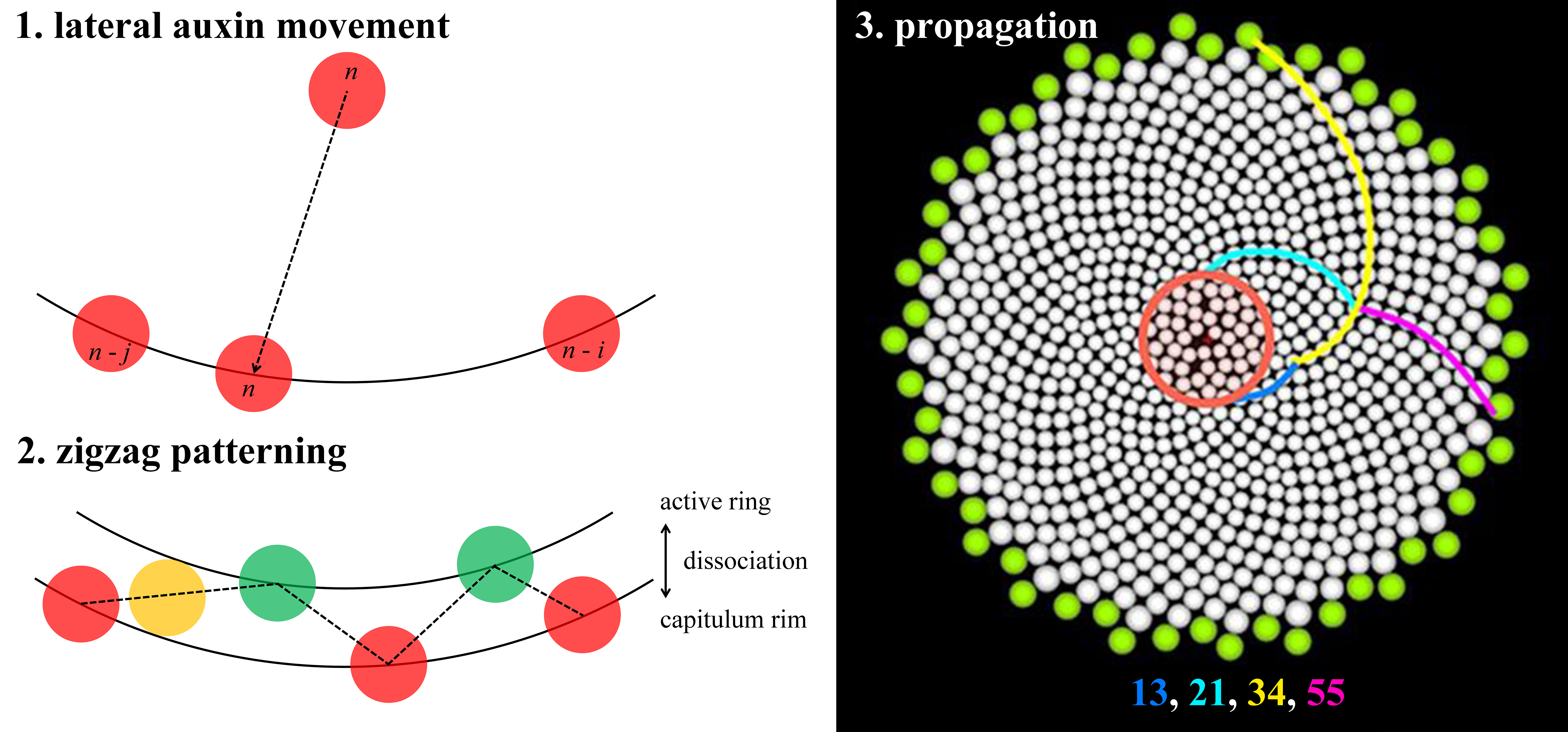
Fig. 1. Key patterning processes in gerbera (Gerbera hybrida) capitula development. (a) A capitulum (head) of G. hybrida with outer bracts and inner florets. Pink spiral, one out of 21 clockwise parastichies. Blue spiral, one out of 34 counter-clockwise parastichies. Note that 21 and 34 are two successive numbers of Fibonacci series. White lines, divergence angle of two florets. (b) Confocal images of DR5 reporter indicating that, at the beginning of the patterning process, auxin maxima emerge at approximately the same radial distance from a few discrete steps. (c) Details of DR5 patterning of a newly emerged maximum. The new maximum (P9) moves laterally towards its older neighbour (P1). (d) Predicted distribution of bract primordia (coloured dots) overlaid on confocal images of DR5 reporter. (e) Quantification of DR5 signal intensity in the same region as in (c). (f) Confocal images of DR5 reporter indicating that, as the patterning process continues, auxin maxima emerge closer to the centre. (g) Zigzag-like pattern front formed by initially emerged auxin maxima (on the white circle) and later emerged auxin maxima (on the red circle). Note the slight size difference between the white and the red circle. (h) A schematic diagram showing the lateral movement of auxin maxima. As a result, a long (L) gap and a short (S) gap are generated. Note that the lateral movement is always towards the older neighbour. White numbers in (b,f) and numbers in (h) indicate only positions and do not imply the order of emergence; yellow numbers in (b,d,f,g) indicate the total number of auxin maxima. (a) Modified from Elomaa (2017). (b–g) Modified from Zhang et al. (2021). (h) Derived from Zhang (2021).
Dear Prof. Hamant,
We wish to submit our manuscript, entitled “Fibonacci spirals may not need the Golden Angle”, to Quantitative Plant Biology, as an Insights paper.
Phyllotaxis, the arrangement of plant lateral organs, is a long-standing topic in the field of quantitative plant biology. It has been assumed that the appearance of Fibonacci spirals depends on the Golden Angle between successive organs in a global scale. However, using approaches such as quantitative live imaging and computer modeling, it was recently revealed that local, instead of global, interactions among primordia play the key role in phyllotactic patterning in the capitula (heads) of Asteraceae (Zhang et al., 2021. PNAS). In our manuscript, we give an overview of this work, highlight the importance of lateral auxin maxima movement, and discuss its potential implications in phyllotactic transitions. We believe that our manuscript is timely and well fit the scope of Quantitative Plant Biology.
Best wishes,
Xiaofeng Yin, Ph.D.
Department of Biological Sciences
Graduate School of Science
The University of Tokyo
Hongo 7-3-1, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan. 113-0033
Comments to Author: In this manuscript from Xiaofeng Yin and Hirokazu Tsukaya, the authors propose a new mechanism behind phyllotaxis formation involving the movement of newly formed auxin maxima dispensing with mathematical concept like the golden angle. The authors show data extracted from the model organism Gerbera hybrida comprising auxin quantification obtained from the DR5 reporter which helped them to identify auxin maxima around the apex and also performed a computer simulation of their proposed model.
I have some questions and observations regarding the evidence shown in the paper and its consequences:
- In Fig. 1C, the authors claim the presence of movement of maximum P9 towards its older maximum P1. However, to appreciate the displacement, it would be necessary to show P9 before its movement, maybe after its formation, or a time lapse of the same.
- Is it possible to quantify this auxin maxima movement phenomenon? Maybe in terms of distance travelled along the apex? When does a maximum move, immediately after formed? Is it an abrupt move or slow transition?
- Lines 74-76: I think it is necessary show this simulation of the model without auxin movement. Also, I am not sure about how are materials and methods presented in this kind of "Insights" paper, but model details (how the model has been made) should be presented.
- Lines 91-94: If the authors are suggesting the possible future development of a computer model, they should replace "a three-dimensional integrative model CAN robustly" with "a three-dimensional integrative model COULD robustly" as we cannot possible predict the outcome of an experiment beforehand.
- Lines 94-97: I am not an expert in gerbera, but maybe some data regarding the dynamics of the active ring should be presented and compared with the auxin data, as they claim that its symmetry is not necessary for the phyllotaxis formation.
Comments to Author: This is a nice synopsis of experimental/modeling work about the inception of Fibonacci patterns, especially in compositae inflorescences, up to the PNAS paper of Zhang et. al. (2021). This referee agrees with the fact that evidence in this paper shows that Fibonacci phyllotaxis does not need the Golden Angle a priori and that these pattern emerge from local interactions between primordia. But the referee is not sure that Zhang et. al. (2021) represents a departure in proving this thesis, which seems to be one of the central tenets of the article being refereed here.
Indeed, this referee differs with the authors in what they seem to imply: that only now, after the paper of Zhang et. al.(2021) do we understand why models do not need to assume the Golden Angle for the inception of Fibonacci patterns. In fact, most of the modeling work cited by the authors (Atela, 2011; Atela et al., 2003; Douady & Couder, 1996a, b, c; Douady & Golé, 2016; Godin et al., 2020; Golé et al., 2016; Mitchison, 1977) do not assume a priori a divergence angle close to the Golden Angle to generate Fibonacci patterns, and while they do often observe a convergence to that angle after variation of the growth parameter (ratio primordia size/meristem size), they also observe that, many times, this is not the case, even if the resulting pattern is Fibonacci. So, whereas it is important to point out, as the authors do, the all-too common misconception that the Golden Angle is the organizing principle behind Fibonacci phyllotaxis, this fact has been recognized and observed many times before, and for at least 25 years.
The observation of lateral motion of initia is something that seems new with Zhang et. al.’s work (albeit one needs to worry about the fact that the motion of these initia is detected via markers of auxin, not auxin itself). But this is not altogether in contrast with previous models. It could be seen as adding an interesting piece of prehistory to the positioning of primordia, rather than contradict the fact that, overall, primordia stay radially put once they have really formed, and that these positions determine in fine the position of the new primordium.
In other words, whereas this referee is ready to support the idea that the rich and interesting article of Zhang et. al. (2021) confirms what was known – that in plants, Fibonacci does not need thee Golden Angle and that phyllotaxis is a self-organizing process guided by local biochemical interactions, the referee is not sure that Zhang et. al. offers a “sharp contrast of paradigm” in that respect.
Since this sharp contrast seems to be a central part of this insight, this referee would like the messaging to be re-worked before this article is accepted.
In the meantime, here are some suggested corrections for minor issues in the paper.
39 Parastichies do not necessarily meet near/at 90 deg angles, even at their inception.
43 137.51 deg. (not 137.49)
59 Ambiguous phrase, that seems to contradict the main point of the authors: “Can Fibonacci spirals form without the Golden Angle? Not necessarily.” Consider an option such as: “Is the Golden Angle necessary for Fibonacci spirals to form? Not necessarily.”
80 Thus, without any prior assumptions related to the Golden Angle, the initial establishment of Fibonacci spirals can be robustly achieved.
121 why does the lateral auxin
129 “unequal change of the apex”. Do the authors mean “non-uniform” or “non-isotropic”?
147 Review the confusing grammar of “Especially, when the primordia …”
Comments to Author: The authors need to be careful in interpreting the literature. For example, many existing models, including the ones cited in this study, do not necessarily assume a priori a divergence angle. I would also like to suggest the authors to reconsider the interpretation of the observed lateral motion of DR5 signals (Zhang et al., 2021 PNAS and Galvan-Ampudia et al., 2020 eLife).
No accompanying comment.
No accompanying comment.
Comments to Author: This is an improvement over the first version.
A couple of small detail:
This referee does not believe Godin et. al. (2020) predicates a canalization towards the Golden Angle, but rather to Fibonacci phyllotaxis - two independent things as this paper is trying to establish. Also, spelling line 59: Various models do not make a priori assumptions relateD to the Golden Angle
Comments to Author: Please correct the a few minor points raised by the reviewer.
No accompanying comment.
No accompanying comment.
No accompanying comment.
No accompanying comment.
The regular arrangement of plant lateral organs, known as phyllotaxis, has been the subject of quantitative plant biology research for a long time (Adler et al., Reference Adler, Barabé and Jean1997; Barabé & Lacroix, Reference Barabé and Lacroix2020; Jean & Barabé, Reference Jean and Barabé1998; Yin, Reference Yin2021). Yet, there remains many unresolved questions (Yin & Kitazawa, Reference Yin and Kitazawa2021), such as the rapid and de novo phyllotactic patterning in the capitulum (head) of Asteraceae. Spiral and whorled are the two major phyllotaxis modes (Yin, Reference Yin2021). In the spiral mode, two families of eye-catching winding spirals called parastichies (Figure 1a) can be observed (Jean, Reference Jean1994). The numbers of parastichies are often successive numbers of Fibonacci series <1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34…> (Figure 1a). Neighbouring organs along a parastichy, nonetheless, are not ‘neighbours’ in terms of ontogeny. The next organ is formed in a different parastichy and usually forms a divergence angle (Figure 1a) with the previous one by 137.51°, which is the golden fraction of 360° and thus called the Golden Angle.
Fig. 1. Key patterning processes in gerbera (Gerbera hybrida) capitula development. (a) A capitulum (head) of G. hybrida with outer bracts and inner florets. Pink spiral, one out of 21 clockwise parastichies. Blue spiral, one out of 34 counter-clockwise parastichies. Note that 21 and 34 are two successive numbers of Fibonacci series. White lines, divergence angle of two florets. (b) Confocal images of DR5 reporter indicating that, at the beginning of the patterning process, auxin maxima emerge at approximately the same radial distance from a few discrete steps. (c) Details of DR5 patterning of a newly emerged maximum. The new maximum (P9) moves laterally towards its older neighbour (P1). (d) Predicted distribution of bract primordia (coloured dots) overlaid on confocal images of DR5 reporter. (e) Quantification of DR5 signal intensity in the same region as in (c). (f) Confocal images of DR5 reporter indicating that, as the patterning process continues, auxin maxima emerge closer to the centre. (g) Zigzag-like pattern front formed by initially emerged auxin maxima (on the white circle) and later emerged auxin maxima (on the red circle). Note the slight size difference between the white and the red circle. (h) A schematic diagram showing the lateral movement of auxin maxima. As a result, a long (L) gap and a short (S) gap are generated. Note that the lateral movement is always towards the older neighbour. White numbers in (b,f) and numbers in (h) indicate only positions and do not imply the order of emergence; yellow numbers in (b,d,f,g) indicate the total number of auxin maxima. (a) Modified from Elomaa (Reference Elomaa2017). (b–g) Modified from Zhang et al. (Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). (h) Derived from Zhang (Reference Zhang2021).
More than 150 years ago, Wilhelm Hofmeister made the pioneering postulation that a new organ is formed at the farthest position from existing ones on the growing shoot apex (Hofmeister, Reference Hofmeister, Bary, Irmisch and Sachs1868). Mary and Robert Snow tested and elaborated this postulation and suggested that a new organ is formed as soon as a minimum space becomes available (Snow & Snow, Reference Snow and Snow1931; Reference Snow and Snow1933; Reference Snow and Snow1935; Reference Snow and Snow1947). This repeating process can be conceptualised as a self-organising process of stacking new elements to existing ones on a circle or a cylinder (Atela, Reference Atela2011; Atela et al., Reference Atela, Golé and Hotton2003; Douady & Couder, Reference Douady and Couder1996a; Reference Douady and Couder1996b; Reference Douady and Couder1996c; Douady & Golé, Reference Douady and Golé2016; Godin et al., Reference Godin, Golé and Douady2020; Golé et al., Reference Golé, Dumais and Douady2016; Mitchison, Reference Mitchison1977). Various models suggest that geometric constraints of the shoot apex and organ primordia canalise phyllotaxis towards Fibonacci spirals (Battjes et al., Reference Battjes, Vischer and Bachmann1993; Godin et al., Reference Godin, Golé and Douady2020). In a special case, when assuming the Golden Angle as the divergence angle, Fibonacci spirals are the only solution, mathematically (Battjes & Prusinkiewicz, Reference Battjes, Prusinkiewicz, Jean and Barabé1998; Battjes et al., Reference Battjes, Vischer and Bachmann1993; Fowler et al., Reference Fowler, Hanan and Prusinkiewicz1989; Reference Fowler, Prusinkiewicz and Battjes1992; Godin et al., Reference Godin, Golé and Douady2020; Hirmer, Reference Hirmer1931).
Is the Golden Angle necessary for Fibonacci spirals to form? Not necessarily. Various models do not make a priori assumptions related to the Golden Angle, yet they can generate Fibonacci spirals (Atela, Reference Atela2011; Atela et al., Reference Atela, Golé and Hotton2003; Douady & Couder, Reference Douady and Couder1996a; Reference Douady and Couder1996b; Reference Douady and Couder1996c; Golé et al., Reference Golé, Dumais and Douady2016; Mitchison, Reference Mitchison1977). Notably, combining empirical and theoretical efforts, a recent study further revealed that the de novo establishment of Fibonacci spirals in the capitulum of gerbera (Gerbera hybrida) does not require the Golden Angle (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). A gerbera capitulum consists of outer bracts and inner florets on a receptacle (Figure 1a; Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). At the beginning of the patterning process, up to 13 bract primordia emerge at the capitulum rim in an approximately circular pattern with negligible radial distance differences, as indicated by DR5 promoter (an auxin signalling output reporter) (Figure 1b; Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). Curiously, these auxin maxima are not formed altogether at once but rather formed from a few discrete steps (Figure 1b; Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). In each step, the number of added maxima is the next Fibonacci number, which then quickly leads the number of total maxima to become Fibonacci numbers (Figure 1b; Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). Time-lapse imaging reveals one unique feature of auxin maxima dynamics that each maximum emerges at approximately halfway in between existing ones and subsequently moves laterally (Figure 1c,e,h; see Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021, fig. 5). Most importantly, the lateral movement is always towards its older neighbour and the total distance travelled could be as many as six to eight cells (Figure 1c,e,h; see Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021, fig. 5). The importance of lateral movement of auxin maxima is further explored by a computational model approximated as a growing circle. Without lateral movement, the circular model predicts that, in each step, the number of auxin maxima formed would be 1, 2, 4, 8, … instead and these maxima would be evenly distributed around the rim (see Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021, fig. S5). Such evenly distributed maxima could be considered as whorled modes (Yin, Reference Yin2021). With a certain range of lateral movement values towards the older neighbour, in contrast, the circular model predicts that the number of auxin maxima tends to be a Fibonacci number and maxima positions faithfully match the experimental observations (Figure 1d; Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). Thus, without any a priori assumptions related to the Golden Angle, the initial establishment of Fibonacci spirals can be robustly achieved.
As the patterning process continues, aside from the lateral movement, new auxin maxima are now positioned slightly closer to the centre of the capitulum (Figure 1f; Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). This is because the expansion rate of the competent zone for primordia initiation, the active ring, cannot keep pace with the growing capitulum (see Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021, fig. 6). Consequently, the active ring dissociates from the rim and the new auxin maxima form a zigzag-like pattern front (Figure 1g; Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). Following the gradual contraction of the active ring, the zigzag patterned auxin maxima are further propagated into a lattice on the capitulum. Parastichy numbers of this lattice decrease following the reversed order of Fibonacci sequence from outside to inside (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). Eventually, the pattern becomes chaotic in the centre due to limited space as the entire capitulum is consumed (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). Combining features including lateral movement of auxin maxima, differential dynamics between the active ring and the capitulum, and the actual shape of the receptacle, a three-dimensional integrative model can robustly simulate the entire patterning process (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). Strikingly, Fibonacci spirals can still be generated even when the active ring loses its radial symmetry, which is commonly observed in irregular and fasciated gerbera heads (Prusinkiewicz et al., Reference Prusinkiewicz, Zhang, Owens, Cieslak and Elomaa2022; Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). This indicates that phyllotactic patterning does not rely on the overall symmetry of the active ring but rather on the local interactions among primordia (Golé et al., Reference Golé, Dumais and Douady2016; Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). ‘Divergence section’, the arc length of the active ring covered by two successive primordia, is the potentially significant parameter in asymmetric systems (Prusinkiewicz et al., Reference Prusinkiewicz, Zhang, Owens, Cieslak and Elomaa2022).
Many models of phyllotaxis assume that the positions of auxin maxima are fixed once they are formed (Bayer et al., Reference Bayer, Smith, Mandel, Nakayama, Sauer, Prusinkiewicz and Kuhlemeier2009; Jonsson et al., Reference Jonsson, Heisler, Shapiro, Meyerowitz and Mjolsness2006; Smith et al., Reference Smith, Guyomarc'h, Mandel, Reinhardt, Kuhlemeier and Prusinkiewicz2006a). Following this assumption, phyllotaxis research mainly focuses on mechanisms that determine the positions of auxin maxima. Many factors including auxin concentration (Reinhardt et al., Reference Reinhardt, Mandel and Kuhlemeier2000; Reference Reinhardt, Pesce, Stieger, Mandel, Baltensperger, Bennett, Traas, Friml and Kuhlemeier2003), auxin signalling (Bhatia et al., Reference Bhatia, Bozorg, Larsson, Ohno, Jonsson and Heisler2016), auxin flux (Abley et al., Reference Abley, Sauret-Gueto, Maree and Coen2016; Stoma et al., Reference Stoma, Lucas, Chopard, Schaedel, Traas and Godin2008), auxin biosynthesis (Galvan-Ampudia et al., Reference Galvan-Ampudia, Cerutti, Legrand, Brunoud, Martin-Arevalillo, Azais, Bayle, Moussu, Wenzl, Jaillais, Lohmann, Godin and Vernoux2020; Pinon et al., Reference Pinon, Prasad, Grigg, Sanchez-Perez and Scheres2013; Yoshikawa et al., Reference Yoshikawa, Ito, Sumikura, Nakayama, Nishimura, Kitano, Yamaguchi, Koshiba, Hibara, Nagato and Itoh2014), cytokinin signalling (Lee et al., Reference Lee, Johnston, Yang, Gallavotti, Kojima, Travencolo, Costa Lda, Sakakibara and Jackson2009), mechanical signals (Feraru et al., Reference Feraru, Feraru, Kleine-Vehn, Martiniere, Mouille, Vanneste, Vernhettes, Runions and Friml2011; Hamant et al., Reference Hamant, Heisler, Jonsson, Krupinski, Uyttewaal, Bokov, Corson, Sahlin, Boudaoud, Meyerowitz, Couder and Traas2008; Heisler et al., Reference Heisler, Hamant, Krupinski, Uyttewaal, Ohno, Jonsson, Traas and Meyerowitz2010), and cell wall signatures (Braybrook & Peaucelle, Reference Braybrook and Peaucelle2013) are found to play a role in instructing the polarity of PIN1 proteins, which in turn guide the direction of auxin flow and the positions of auxin maxima (Heisler et al., Reference Heisler, Ohno, Das, Sieber, Reddy, Long and Meyerowitz2005; Okada et al., Reference Okada, Ueda, Komaki, Bell and Shimura1991; Reinhardt et al., Reference Reinhardt, Mandel and Kuhlemeier2000; Reference Reinhardt, Pesce, Stieger, Mandel, Baltensperger, Bennett, Traas, Friml and Kuhlemeier2003). More recently, it was revealed that local PIN1 polarity converges towards the radial auxin maxima movement route in Arabidopsis inflorescence meristem and the duration of cell exposure to auxin is another important factor in phyllotaxis (Galvan-Ampudia et al., Reference Galvan-Ampudia, Cerutti, Legrand, Brunoud, Martin-Arevalillo, Azais, Bayle, Moussu, Wenzl, Jaillais, Lohmann, Godin and Vernoux2020). In gerbera capitula, the discovery of lateral auxin maxima movement before any physical appearance of primordia initiation adds another layer of complexity concerning primordia’s ‘prehistory’. Backed up by computational models, it was shown that such ‘prehistory’ is the contributing factor that leads to the initial asymmetry and Fibonacci numbers of parastichies (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). Are there any additional factors that instruct PIN1 polarity in gerbera? How does PIN1 facilitate the lateral auxin maxima movement? And most importantly, why do the lateral auxin maxima always move towards the older neighbour and what is the cue to break the initial symmetry? Answers to these questions would further enrich our understanding of phyllotactic patterning in such a system.
Another implication of lateral auxin maxima movement is that it may prompt the transitions of phyllotaxis modes. The circular model predicts that without the lateral movement, whorled modes would appear instead of the spiral mode (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). Most eudicots experience at least one transition from whorled to spiral during their ontogeny (Meicenheimer, Reference Meicenheimer, Jean and Barabé1998). The transition between phyllotaxis modes can be explained as a non-uniform change of the apex (Meicenheimer, Reference Meicenheimer, Jean and Barabé1998; Meicenheimer & Zagórska-Marek, Reference Meicenheimer and Zagórska-Marek1989); changes of a suite of factors including auxin concentration and biosynthesis (Smith et al., Reference Smith, Guyomarc'h, Mandel, Reinhardt, Kuhlemeier and Prusinkiewicz2006a); and an age-dependent decrease of primordia inhibition field (Smith et al., Reference Smith, Kuhlemeier and Prusinkiewicz2006b). Lateral auxin maxima movement hence offers another possible explanation for the transitions between phyllotaxis modes. It is also of interest to note that distances of bracts to the stem centre are clustered upon maturity and each cluster corresponds to a discrete step of auxin maxima burst at the beginning of the patterning process (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Cieslak, Owens, Wang, Broholm, Teeri, Elomaa and Prusinkiewicz2021). This interesting pattern of bract primordia and their corresponding auxin maxima has properties of both whorled and spiral modes. On the one hand, the radial positioning of auxin maxima follows the whorled mode such that each step, or each individual auxin maxima burst, could be considered as a distinct ‘whorl’. On the other hand, the whorled mode has evenly distributed organ whereas the angular spacing of auxin maxima is not even and clearly following the spiral mode. This suggests that it might be an intermediate or transitional state between the spiral mode and the whorled mode. What, then, could cause this? One hint comes from a phenomenon known as ‘permutation’, an incorrect order of organs at correct angular positions. Permutation is found in sunflower (Couder, Reference Couder1998) as well as various Arabidopsis accessions and mutants (Besnard et al., Reference Besnard, Refahi, Morin, Marteaux, Brunoud, Chambrier, Rozier, Mirabet, Legrand, Laine, Thevenon, Farcot, Cellier, Das, Bishopp, Dumas, Parcy, Helariutta, Boudaoud and Vernoux2014; Fal et al., Reference Fal, Liu, Duisembekova, Refahi, Haswell and Hamant2017; Landrein et al., Reference Landrein, Refahi, Besnard, Hervieux, Mirabet, Boudaoud, Vernoux and Hamant2015). Permutation results from locally disrupted timing of organ initiation such as co-initiation while organ angular positions remain unaffected (Besnard et al., Reference Besnard, Refahi, Morin, Marteaux, Brunoud, Chambrier, Rozier, Mirabet, Legrand, Laine, Thevenon, Farcot, Cellier, Das, Bishopp, Dumas, Parcy, Helariutta, Boudaoud and Vernoux2014). Especially, when the size of primordia is small enough as compared to the apex, which is an attribute of gerbera capitula, the frequency of permutation would be high (Landrein et al., Reference Landrein, Refahi, Besnard, Hervieux, Mirabet, Boudaoud, Vernoux and Hamant2015; Mirabet et al., Reference Mirabet, Besnard, Vernoux and Boudaoud2012). Nonetheless, the most common permutations involve a series of two or three organs in Arabidopsis inflorescence meristem (Besnard et al., Reference Besnard, Refahi, Morin, Marteaux, Brunoud, Chambrier, Rozier, Mirabet, Legrand, Laine, Thevenon, Farcot, Cellier, Das, Bishopp, Dumas, Parcy, Helariutta, Boudaoud and Vernoux2014), whereas as many as eight simultaneous auxin maxima could form in gerbera capitula at the beginning of the patterning process. Regardless, it is extremely intriguing to further dissect the mechanisms that lead to this ‘hybrid’ pattern to deepen our understanding on the transition between phyllotaxis modes.
Phyllotaxis as a self-organising process of stacking new elements is well characterised down to the molecular level; and models with this feature often emphasise the relationship between the Golden Angle and Fibonacci spirals. In sharp contrast to this paradigm, various models do not make a priori assumptions related to the Golden Angle, yet they can generate Fibonacci spirals. Phyllotactic pattering in gerbera capitula offers yet another compelling example. After all, Fibonacci spirals may not need the Golden Angle. This urges us to reconsider phyllotaxis as a simple patterning process depending on local interactions.
Acknowledgements
We thank Paula Elomaa for critical reading on an earlier version of the manuscript; Paula Elomaa and Teng Zhang for sharing figures and intriguing discussion on unpublished results and two reviewers for their insightful suggestions.
Financial support
This work is supported by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan (Scientific Research on Priority Areas and Scientific Research on Innovative Areas, Grant No. JP 19H05672) and Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Postdoctoral Fellowship for Research in Japan (Grant No. P19085).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Authorship contributions
X.Y. conceived the paper. X.Y. and H.T. wrote the paper.