Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 January 2009
Absolute summability according to Cesàro's method has been defined by Fekete for positive integral orders, as follows:—
Denoting the rth partial sum of a series Σun by 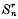 and its rth mean, namely2
and its rth mean, namely2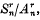 , by
, by 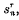 we can regard
we can regard 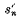 as the sum of the series
as the sum of the series
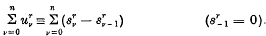 .
.
page 173 note 1 Math, ès Term. Ert. (1911), pp. 719–726.Google Scholar
page 173 note 2 ![]()
page 175 note 1 If i or j is zero, we omit the corresponding sum.
page 176 note 1 an–1, n vanishes, if we take ![]() . This follows, if we suppose
. This follows, if we suppose ![]() true for n = 0.
true for n = 0.
page 177 note 1 It should be observed that Σ1 and Σ2 do not occur when k = 0.