No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
An Elementary Proof of the Theorems of Cauchy and Mayer
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 January 2009
Extract
Attention has recently been drawn to the obscurity of the usual presentations of Mayer's method of solution of the total differential equation
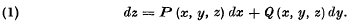
This method has the practical advantage that only a single integration is required, but its theoretical discussion is usually based on the validity of some other method of solution. Mayer's method gives a result even when the equation (1) is not integrable, but this cannot of course be a solution. An examination of the conditions under which the result is actually an integral of equation (1) leads to a proof of the existence theorem for (1) which is related to Mayer's method of solution in a natural way, and which moreover appears to be novel and of value in the presentation of the subject.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society , Volume 4 , Issue 3 , August 1935 , pp. 112 - 117
- Copyright
- Copyright © Edinburgh Mathematical Society 1935


