Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 February 2022
Finding a common point in a finite intersection of sets, say, $C=\cap _{i=1}^{n} F(T_i)$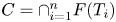 , where each $T_i$
, where each $T_i$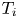 is a non-expansive-type mapping, is a central task in mathematics as it cuts across different areas of application, such as road design and medical image reconstruction. There are many algorithms for approximating solutions of such problems. Of particular interest in the implementation of these algorithms are cost and speed. This is due to the large computations to be performed at each step of the iterative process. One of the most efficient methods that optimizes the time of computation and cost of implementation is the asynchronous-parallel algorithm method. In this paper, we prove a weak convergence theorem for the asynchronous sequential inertial (ASI) algorithm (introduced by Heaton and Censor in [H. Heaton and Y. Censor, Asynchronous sequential inertial iterations for common fixed points problems with an application to linear systems, J. Glob. Optim. 74 (2019), 95–119.] ) for strictly pseudo-contractive mappings in Hilbert spaces. Under additional mild conditions, we also obtain a strong convergence theorem. Finally, we apply the ASI algorithm to solving convex minimization problems and Hammerstein integral equations.
is a non-expansive-type mapping, is a central task in mathematics as it cuts across different areas of application, such as road design and medical image reconstruction. There are many algorithms for approximating solutions of such problems. Of particular interest in the implementation of these algorithms are cost and speed. This is due to the large computations to be performed at each step of the iterative process. One of the most efficient methods that optimizes the time of computation and cost of implementation is the asynchronous-parallel algorithm method. In this paper, we prove a weak convergence theorem for the asynchronous sequential inertial (ASI) algorithm (introduced by Heaton and Censor in [H. Heaton and Y. Censor, Asynchronous sequential inertial iterations for common fixed points problems with an application to linear systems, J. Glob. Optim. 74 (2019), 95–119.] ) for strictly pseudo-contractive mappings in Hilbert spaces. Under additional mild conditions, we also obtain a strong convergence theorem. Finally, we apply the ASI algorithm to solving convex minimization problems and Hammerstein integral equations.