Other
Special Topics
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, p. 190
-
- Article
- Export citation
Forthcoming in PMLA
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, p. 190
-
- Article
- Export citation
Editorial
Editor's Column: What's in a Name? Revisiting Author-Anonymous Reviewing
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 191-197
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Research Article
Passion and Fashion in Joanna Baillie's “Introductory Discourse”
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 198-213
-
- Article
- Export citation
“Abroad and at Home”: Sexual Ambiguity, Miscegenation, and Colonial Boundaries in Edgeworth's Belinda
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 214-228
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ethnography, Thievery, and Cultural Identity: A Rereading of Michel Leiris's L'Afrique fantôme
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 229-242
-
- Article
- Export citation
On Dialogic Speech
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 243-256
-
- Article
- Export citation
Forum
Critiques
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 257-258
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critiques
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 258-259
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critiques
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 259-260
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critiques
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 260-261
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critiques
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 261-262
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critiques
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 262-263
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critiques
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 263-264
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critiques
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, p. 264
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critiques
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 264-265
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critiques
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 265-266
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Reworkings
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 266-267
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Reworkings
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 267-268
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Reworkings
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 268-269
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation


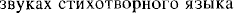 ”; Jakubinskij 163-76) became the cornerstone of formalist criticism and “served as the activating principle for the Formalists' treatment of the fundamental problems of poetics” (Èjchenbaum 8). Yakubinsky thus laid the foundation for structuralism. However, he soon moved away from the formalists' preoccupation with poetic and literary texts and devoted himself to the social dimension of the functions and forms of language.
”; Jakubinskij 163-76) became the cornerstone of formalist criticism and “served as the activating principle for the Formalists' treatment of the fundamental problems of poetics” (Èjchenbaum 8). Yakubinsky thus laid the foundation for structuralism. However, he soon moved away from the formalists' preoccupation with poetic and literary texts and devoted himself to the social dimension of the functions and forms of language.