Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 October 2021
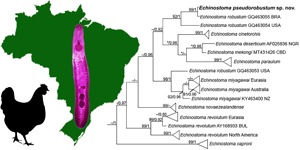
Although Echinostoma robustum (currently a synonym of E. miyagawai) was reported in the Americas based on molecular data, morphological support on adult parasites is still required. Herein, a new species of Echinostoma is described based on worms found in a chicken from Brazil. Molecular phylogenetic analyses based on 28S (1063 bp), ITS (947 bp) and Nad-1 (442 bp) datasets reveal the inclusion of the new species within Echinostoma ‘revolutum’ species complex. Moreover, it was verified the conspecificity between cercariae previously identified as E. robustum in Brazil [identical ITS and only 0.3% of divergence (1 nucleotide) in Nad-1]. Species discovery analyses show that these two isolates form an independent lineage (species) among Echinostoma spp. Compared to E. miyagawai, the new species presents relatively high divergence in Nad-1 (7.88–9.09%). Morphologically, the specimens are distinguished from all nominal species from the ‘revolutum’ species complex by the more posterior position of the testes (length of post-testicular field as a proportion of body length about 20%). They further differ from E. miyagawai and South American Echinostoma spp. by the higher proportion of forebody to the body length. Therefore, combined molecular and morphological evidence supports the proposal of the species named here as Echinostoma pseudorobustum sp. nov.