Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 January 2022
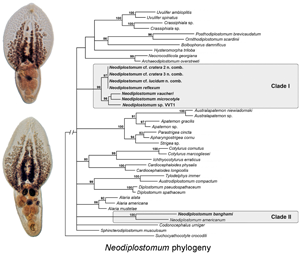
Fibricola and Neodiplostomum are diplostomid genera with very similar morphology that are currently separated based on their definitive hosts. Fibricola spp. are normally found in mammals, while Neodiplostomum spp. typically parasitize birds. Previously, no DNA sequence data was available for any member of Fibricola. We generated nuclear ribosomal and mtDNA sequences of Fibricola cratera (type-species), Fibricola lucidum and 6 species of Neodiplostomum. DNA sequences were used to examine phylogenetic interrelationships among Fibricola and Neodiplostomum and re-evaluate their systematics. Molecular phylogenies and morphological study suggest that Fibricola should be considered a junior synonym of Neodiplostomum. Therefore, we synonymize the two genera and transfer all members of Fibricola into Neodiplostomum. Specimens morphologically identified as Neodiplostomum cratera belonged to 3 distinct phylogenetic clades based on mitochondrial data. One of those clades also included sequences of specimens identified morphologically as Neodiplostomum lucidum. Further study is necessary to resolve the situation regarding the morphology of N. cratera. Our results demonstrated that some DNA sequences of N. americanum available in GenBank originate from misidentified Neodiplostomum banghami. Molecular phylogentic data revealed at least 2 independent host-switching events between avian and mammalian hosts in the evolutionary history of Neodiplostomum; however, the directionality of these host-switching events remains unclear.