Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 November 2021
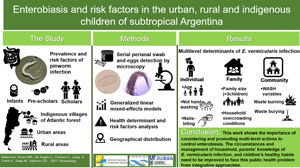
A cross-sectional survey to assess the prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis infection and its associated factors among the child population of infant, preschool and school age in the urban, rural and indigenous population of Iguazú city, in subtropical Argentina was presented. Additionally, the status of enterobiasis at country level was reviewed and analysed. Enterobius vermicularis presence was assessed employing an oviscopic serial sampling technique. Statistical analysis of socio-demographic determinants was performed by generalized linear mixed models at individual, household and community levels. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines were used to gather national information about E. vermicularis prevalence spanning the decade 2010–2020. A total of 916 children from 470 families participated. Overall prevalence was 29.8%, with 25.3, 30.7 and 34.2% detected for children inhabiting urban, rural and indigenous villages, respectively. The multi-level analysis showed that the presence of E. vermicularis was mostly determined by individual (e.g. age, playing habits, previous pinworm infection) and household-level factors (e.g. family size, overcrowding conditions). Interestingly, WASH variables, such as waste disposal, analysed at community level were also important. Data were analysed to provide eco-epidemiological features of enterobiasis in a heterogeneous subtropical child population in the same territory but with different socio-sanitary realities. The importance of promoting multi-level actions against the determinants identified, to control this public health problem integratively was evidenced. The scoping review of national data updated the state of knowledge of this parasitosis, identifying risk determinants and gaps in knowledge at country level.