No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 April 2022
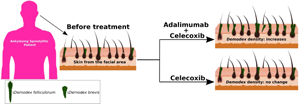
Demodex infestation and density changes remain one of the main challenges in some clinical settings. Tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) inhibitors have been recommended as a first-line treatment for ankylosing spondylitis (AS). However, there have been no studies investigating the impact of TNF-α inhibitor adalimumab on changes in the Demodex density in patients with AS. The aim of this study was to investigate Demodex density changes before and after adalimumab treatment and analyse the relationship between the Demodex density and clinical characteristics in AS. It was found that the Demodex density was positively correlated with age and C-reactive protein levels and the number of Demodex mites could increase after adalimumab treatment in AS.
These authors contributed equally to this work.