Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 August 2022
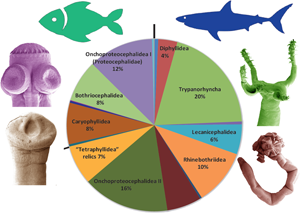
The tapeworms of fishes (Chondrichthyes and Actinopterygii) account one-third (1670 from around 5000) of the total tapeworm (Platyhelminthes: Cestoda) species diversity. In total 1186 species from 9 orders occur as adults in elasmobranchs (sharks, rays and chimaeras), and 484 species from 8 orders mature in ray-finned fishes (referred to here as teleosts). Teleost tapeworms are dominated by freshwater species (78%), but only 3% of elasmobranch tapeworms are known from freshwater rays of South America and Asia (Borneo). In the last 2 decades, vast progress has been made in understanding species diversity, host associations and interrelationships among fish tapeworms. In total, 172 new species have been described since 2017 (149 from elasmobranchs and 23 from teleosts; invalidly described taxa are not included, especially those from the Oriental region). Molecular data, however, largely limited to a few molecular markers (mainly 28S rDNA, but also 18S and cox1), are available for about 40% of fish tapeworm species. They allowed us to significantly improve our understanding of their interrelationships, including proposals of a new, more natural classification at the higher-taxonomy level (orders and families) as well as at the lower-taxonomy level (genera). In this review, we summarize the main advances and provide perspectives for future research.