Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 November 2020
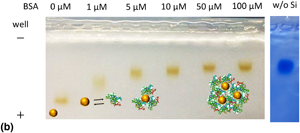
The interaction between negatively charged all-inorganic silicon quantum dots (Si QDs) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) is studied. It is shown that a small difference in the size of Si QDs affects the structure of Si QD–BSA composites significantly. When the diameter of Si QDs is 4 nm, a heterodimer (~20 nm) composed of one Si QD and one BSA molecule is a preferable and stable structure. On the other hand, when the diameter is 7 nm, the size of the composites increases to ~50 nm. The Si QD–BSA composites exhibit stable photoluminescence in the near-infrared range in phosphate-buffered saline.