Article contents
A highly efficient and antifouling microfluidic platform for portable hemodialysis devices
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 March 2018
Abstract
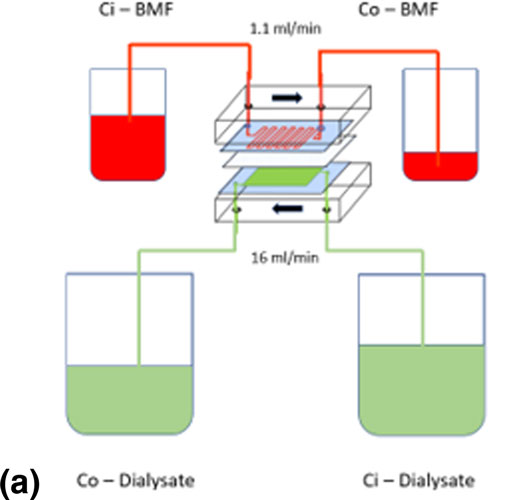
End-stage renal disease (ESRD) is a life-threatening illness that presents significant healthcare challenges. About 90% of ESRD patients receive hemodialysis treatment, but the currently available hemodialysis systems are bulky and prone to complications. We report the design of a microfluidic hemodialysis device composed of two polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) chambers separated by a cellulose ester (CE) membrane. The polyethylene glycol-passivated PDMS and CE surfaces reduced platelet adhesion by 74% and 86%, respectively. Moreover, the device exhibited a higher urea clearance rate per unit area than a healthy kidney. The reported design sets the foundation for a next-generation biomimetic portable hemodialysis device.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2018
References
- 7
- Cited by



