Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 October 2020
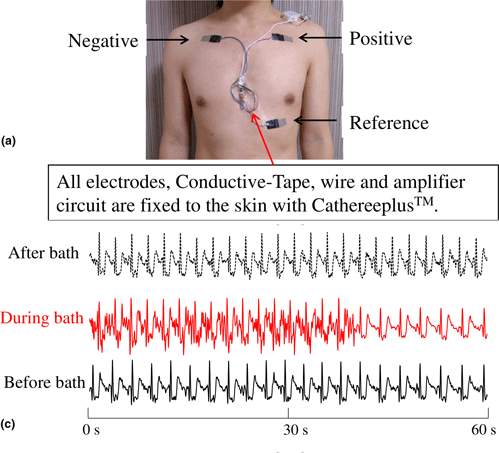
Waterproof bioelectrodes enable long-term biological monitoring and the assessment of performances of athletes in water. Existing gel electrodes change their electrical properties even when covered with a waterproof film. Here, the authors present the poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS)/poly(styrene-butadiene-styrene) (SBS) bi-layer nanosheet and waterproof film for a comfortable waterproof bioelectrode. PEDOT:PSS/SBS is fully foldable with a conductivity loss of only 5%. This foldable nanosheet electrode provides a reliable electrical connection between the skin and the wire. The waterproof film-covered bioelectrode enables continuous monitoring of electrocardiograms in water, showing a signal-to-noise ratio of 21.5 dB for the R wave and 17.5 dB for the T wave, comparable to atmospheric measurements, and sensing a change in heart rate from 79 to 131 bpm during bathing.