No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 January 2019
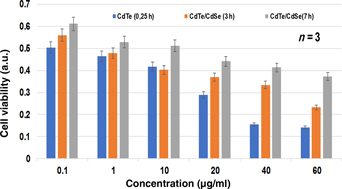
LM-8 is a murine osteosarcoma cell line associated with bone tumor in young adult and children. It contains the nuclear factor-κB which make this cell high resistance to irradiation thus limiting its treatment only to chemotherapy and surgery which has become a source of concerned for cancer therapy. In addressing this problem, we herein report the synthesis of CdTe/CdSe core/shell quantum dots (QDs) via a simple, reproducible method and its cytotoxic action against the LM-8 cell line. The cell viability study shows that the as-synthesized QDs are toxic to the LM-8 cell line in a concentration- and time-dependent manner.