Article contents
Doping of TiO2 nanopowders with vanadium for the reduction of its band gap reaching the visible light spectrum region
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 June 2014
Abstract
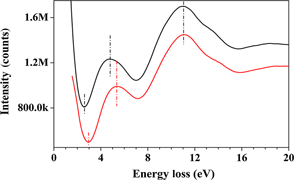
Titanium oxide (TiO2) nanoparticles (NPs) were doped with vanadium using a novel, facile, and inexpensive method. The TiO2 NPs were dispersed in a vanadyl oxalate solution prepared by dissolving vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) in oxalic acid. A short heat treatment at 400 °C applied to the dried mixture resulted in the doping of TiO2 with a net measured decrease of its band gap by about 0.5 eV, making this important semiconductor material usable in the visible light spectrum.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2014
References
1.Fujishima, A. and Honda, K.: Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238, 37–38 (1972).Google Scholar
2.Wu, J.C.S. and Chen, C.H.: A visible-light response vanadium-doped titania nanocatalyst by sol-gel method. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 163, 509–515 (2004).Google Scholar
3.Klosek, S. and Raftery, D.: Visible light driven V-doped TiO2 photocatalyst and its photooxidation of ethanol. J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 2815–2819 (2001).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
4.Zhou, W., Liu, Q., Zhu, Z., and Zhang, J.: Preparation and properties of vanadium-doped TiO2 photocatalysts. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 43, 035301 (2010).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
5.Sene, J.J., Zeltner, W.A., and Anderson, M.A.: Fundamental photoelectrocatalytic and electrophoretic mobility studies of TiO2 and V-doped TiO2 thin-film electrode materials. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 1597–1603 (2003).Google Scholar
6.Gu, D.E., Yang, B.C., and Hu, Y.D.: V and N co-doped nanocrystal anatase TiO2 photocatalysts with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation. J. Catal. Commun. 9, 1472–1476 (2008).Google Scholar
7.Ohtani, B., Prieto-Mahaney, O.O., Li, D., and Abe, R.: What is Degussa (Evonik) P25- crystalline composition analysis, reconstruction from isolated pure particles and photocatalytic activity test. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 216, 179–182 (2010).Google Scholar
8.McComb, D.W.: Bonding and electronic structure in zirconia pseudopolymorphs investigated by electron energy-loss spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 54, 7094–7120 (1996).CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed
9.Pan, A., Zhang, J.G., Nie, Z., Cao, G., Arey, B.W., Li, G., Liang, S., and Liu, J.: Facile synthesized nanorod structured vanadium pentoxide for high-rate lithium batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 9193–9199 (2010).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
10.Fischer, D.W.: X-ray band spectra and molecular-orbital structure of rutile TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 5, 4219–4226 (1972).Google Scholar
11.Pascual, J., Camassel, J., and Mathieu, H.: Fine structure in the intrinsic absorption edge of TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 18, 5605–5614 (1978).Google Scholar
12.Sanjines, R., Tang, H., Berger, H., Gozzo, F., Margaritondo, G., and Levy, F.: Electronic structure of anatase TiO2 oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 75, 2945–2951 (1994).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- 3
- Cited by


