Article contents
Colon cancer cells adhesion on polymeric nanostructured surfaces
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 December 2017
Abstract
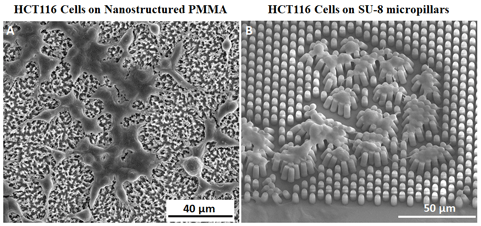
In this work, we report on the adhesion of HCT116 (human colon carcinoma cells) cultured on nanofibrillar polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and SU-8 micropillars substrates. Both surfaces enabled a good cell proliferation and promoted the formation of adherent interconnections with the fabricated nano- and microstructures. The three-dimensional immunofluorescence confocal characterization of the cells on nanotextured PMMA highlighted the expression of well-spread F-actin cytoskeletal networks as well as the presence of focal adhesions. This study provides thus interesting perspectives for further investigations on the force/adhesion mechanisms related to cancer cell growth and proliferation.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
References
- 6
- Cited by



