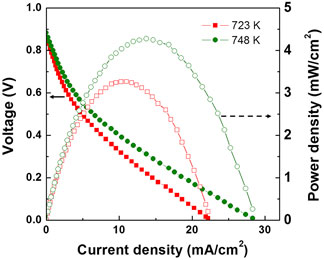
Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Shi, Ruijuan
Chen, Wei
Hu, Wenli
Liu, Junlong
Li, Huiquan
Wang, Hongtao
and
Sheng, Liangquan
2018.
Low Melting Point Glass Powder (glass) used as an Additive to Zr0.88Y0.08Eu0.04O2- (ZYE) Electrolyte for Intermediate Temperature SOFCs.
International Journal of Electrochemical Science,
Vol. 13,
Issue. 11,
p.
10821.
Wang, Chang
Du, Ruifeng
Han, Yan
and
Wang, Hongtao
2019.
The Intermediate Temperature Electrochemical Properties of Silver and Aluminum Double-Doped Strontium Silicate.
International Journal of Electrochemical Science,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 7,
p.
6009.
Shi, Ruijuan
Du, Ruifeng
Liu, Junlong
and
Wang, Hongtao
2019.
Study of the Electrical Conductivity of Al(III) Doped Sr0.6Na0.4SiO3-a.
International Journal of Electrochemical Science,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 6,
p.
4986.
Miao, Hui
Chen, Wei
Hu, Wenli
and
Wang, Hongtao
2019.
Characterization and Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Performances of BaCe0.9Tm0.1O3-α-KCl-NaCl Composite Electrolyte.
International Journal of Electrochemical Science,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 5,
p.
4066.
Troncoso, L.
Arce, M. D.
Fernández-Díaz, M. T.
Mogni, L. V.
and
Alonso, J. A.
2019.
Water insertion and combined interstitial-vacancy oxygen conduction in the layered perovskites La1.2Sr0.8−xBaxInO4+δ.
New Journal of Chemistry,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 15,
p.
6087.
Chen, Wei
Hu, Wenli
and
Wang, Hongtao
2019.
Intermediate Temperature Electrochemical Properties of Al and K Double Doped Strontium Silicate.
International Journal of Electrochemical Science,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 9,
p.
9092.
Ma, Zhuang
Zhao, Zengwu
Guo, Xingqi
and
Guo, Wentao
2023.
Selective precipitation and non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of britholite from low grade REE-bearing slag.
Journal of Rare Earths,
Vol. 41,
Issue. 11,
p.
1812.
Ma, Zhuang
Zhao, Zengwu
Guo, Wentao
and
Guo, Xingqi
2023.
Effect of TiO<sub>2</sub> Addition and Cooling Rate on Crystallization Behavior of Separated Slag Containing Low-grade RE.
ISIJ International,
Vol. 63,
Issue. 8,
p.
1274.
Hidaka, Shigekazu
Takagi, Kenji
and
Yamamoto, Takahisa
2024.
Highly c-axis-oriented apatite-type lanthanum silicate thin films fabricated by magnetron sputtering under bias.
Materials Chemistry and Physics,
Vol. 326,
Issue. ,
p.
129852.
Kthiri, Khouloud
Mehnaoui, Mohamed
Ihzaz, Nejib
and
Hidouri, Mustapha
2025.
Lanthanides-strontium oxyapatites containing magnesium electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cells: Structure and ionic conductivity.
Materials Chemistry and Physics,
Vol. 340,
Issue. ,
p.
130787.