Article contents
Toward laboratory torsional spine magnetic reconnection
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 November 2017
Abstract
Magnetic reconnection is a fundamental energy conversion mechanism in nature. Major attempts to study this process in controlled settings on Earth have largely been limited to reproducing approximately two-dimensional (2-D) reconnection dynamics. Other experiments describing reconnection near three-dimensional null points are non-driven, and do not induce any of the 3-D modes of spine fan, torsional fan or torsional spine reconnection. In order to study these important 3-D modes observed in astrophysical plasmas (e.g. the solar atmosphere), laboratory set-ups must be designed to induce driven reconnection about an isolated magnetic null point. As such, we consider the limited range of fundamental resistive magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) and kinetic parameters of dynamic laboratory plasmas that are necessary to induce the torsional spine reconnection (TSR) mode characterized by a driven rotational slippage of field lines – a feature that has yet to be achieved in operational laboratory magnetic reconnection experiments. Leveraging existing reconnection models, we show that within a 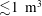 ${\lesssim}1~\text{m}^{3}$ apparatus, TSR can be achieved in dense plasma regimes (
${\lesssim}1~\text{m}^{3}$ apparatus, TSR can be achieved in dense plasma regimes ( ${\sim}10^{24}~\text{m}^{-3}$) in magnetic fields of
${\sim}10^{24}~\text{m}^{-3}$) in magnetic fields of 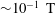 ${\sim}10^{-1}~\text{T}$. We find that MHD and kinetic parameters predict reconnection in thin
${\sim}10^{-1}~\text{T}$. We find that MHD and kinetic parameters predict reconnection in thin 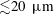 ${\lesssim}20~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m}$ current sheets on time scales of
${\lesssim}20~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m}$ current sheets on time scales of 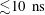 ${\lesssim}10~\text{ns}$. While these plasma regimes may not explicitly replicate the plasma parameters of observed astrophysical phenomena, studying the dynamics of the TSR mode within achievable set-ups signifies an important step in understanding the fundamentals of driven 3-D magnetic reconnection and the self-organization of current sheets. Explicit control of this reconnection mode may have implications for understanding particle acceleration in astrophysical environments, and may even have practical applications to fields such as spacecraft propulsion.
${\lesssim}10~\text{ns}$. While these plasma regimes may not explicitly replicate the plasma parameters of observed astrophysical phenomena, studying the dynamics of the TSR mode within achievable set-ups signifies an important step in understanding the fundamentals of driven 3-D magnetic reconnection and the self-organization of current sheets. Explicit control of this reconnection mode may have implications for understanding particle acceleration in astrophysical environments, and may even have practical applications to fields such as spacecraft propulsion.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2017
References
- 9
- Cited by


