No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 December 2024
Magnetic reconnection is a basic particle acceleration mechanism in laboratory and astrophysical plasmas. Two-dimensional models have been critical to understanding the onset of reconnection in laboratory experiments, but are fundamentally limited in diagnosing ion acceleration along open magnetic field lines. These shortcomings have opened the way to three-dimensional (3-D) models of torsional reconnection, where localized rotational perturbations to a fan-spine magnetic null point topology have demonstrated bulk particle acceleration along open magnetic field lines. Previous computational studies of the torsional fan reconnection mode using both solar and laboratory parameters demonstrated collimated jet formation and acceleration along the spine axis, wherein the bulk particle final kinetic energy spectra were shown to fall within a relatively narrow range (${\sim }2$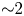 keV). This paper introduces typical laboratory plasma parameters in the torsional spine mode of 3-D reconnection models to diagnose its efficacy in inducing rapid ion acceleration. Using laboratory-scale length helium plasma parameters typical of capacitive discharges (singly ionized helium), we solve for relativistic particle trajectories using solutions to the steady-state, resistive, kinematic magnetohydrodynamic equations in the fan-spine topology. We find that particle acceleration at the reconnection site is highly dependent on the injection radius, and the peak accelerated particles ($\approx$
keV). This paper introduces typical laboratory plasma parameters in the torsional spine mode of 3-D reconnection models to diagnose its efficacy in inducing rapid ion acceleration. Using laboratory-scale length helium plasma parameters typical of capacitive discharges (singly ionized helium), we solve for relativistic particle trajectories using solutions to the steady-state, resistive, kinematic magnetohydrodynamic equations in the fan-spine topology. We find that particle acceleration at the reconnection site is highly dependent on the injection radius, and the peak accelerated particles ($\approx$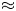 3 keV) are trapped about the magnetic null point. While a jet is formed by ions injected close to the peak fan plane perturbation radius, their final ion kinetic energies are an order of magnitude lower ($\approx$
3 keV) are trapped about the magnetic null point. While a jet is formed by ions injected close to the peak fan plane perturbation radius, their final ion kinetic energies are an order of magnitude lower ($\approx$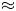 0.3 keV) than the mirrored particles. Analysing the time dependence of their limited representative energy spectra shows the torsional spine mode particles follow an evolution much different than the narrow spectra of the torsional fan mode. These results have implications for diagnostic expectations of future laboratory plasma experiments designed to induce the torsional spine reconnection mode.
0.3 keV) than the mirrored particles. Analysing the time dependence of their limited representative energy spectra shows the torsional spine mode particles follow an evolution much different than the narrow spectra of the torsional fan mode. These results have implications for diagnostic expectations of future laboratory plasma experiments designed to induce the torsional spine reconnection mode.