Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 July 2018
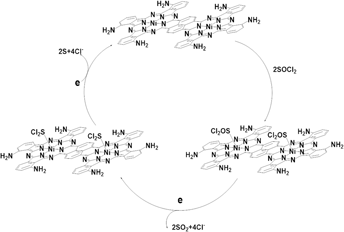
Two series of binuclear metal phthalocyanine complexes M2(PcTN)2Nap and M2(PcTA)2Nap (M = Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Cu2+) were designed and synthesized through the liquid solvent method and amination reaction. Elemental analysis, IR, and UV-vis spectroscopy were applied to characterize the compounds. To evaluate their catalytic performance, all the compounds were respectively added into the electrolyte of Li/SOCl2 battery systems as well as three-electrode systems for cyclic voltammetry (CV) measurements. The research studies indicate that the average discharge voltage and discharge time of the battery could be effectively enhanced by 0.2440 V and 810.7 s when compared with the battery in the absence of the compounds. As for capacities of the batteries containing catalysts, they were also found to have an improvement of 51.78–91.62%. Among the effects of diverse metal ions on the catalytic performance of phthalocyanines, the complexes whose center metal ions were Mn2+ or Co2+ exhibited relatively high catalytic performance. Meanwhile, combined with experimental results of CV analyses, the suggested catalytic mechanism of binuclear phthalocyanines for catalyzing Li/SOCl2 batteries had been proposed.
These authors contributed equally to this work.