Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 August 2018
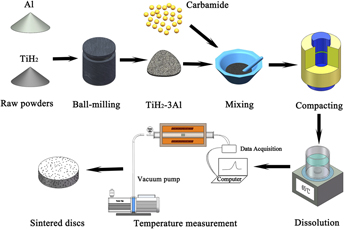
Porous TiAl3 intermetallics were synthesized by the thermal explosion (TE) reaction from TiH2–75 at.% Al elemental powders combining with carbamide as the space holder. The results showed that the space holder particles were removed completely by dissolving in water before sintering and the violent exothermic reaction occurred from the temperature of 672–1193 °C within a few seconds. After TE, TiAl3 was the dominant phase in sintered products and the open porosity of 60.8% was obtained without space holder, while the porosity considerably increased to 81.4% with the addition of 60 vol% carbamide particles. The pore-forming mechanism can be concluded as follows: the sphere large pores replicated from carbamide particles and the small pores generated by the TE reaction. Moreover, porous TiAl3 intermetallics possess the excellent oxidation resistance at 650 °C in air, which enabled them good candidate materials for improving the service life and the accuracy of filtration under special conditions.