Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 June 2018
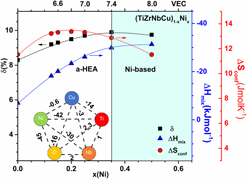
The atomic structure, electronic structure, and physical properties of (TiZrNbCu)1−xNix (x ≤ 0.5) metallic glasses (MGs) were studied in both the high-entropy (0 < x < 0.35) and the higher Ni concentration range (x ≥ 0.35). Atomic structure studies performed with X-ray diffraction and synchrotron powder diffraction provided average atomic volumes, structure factors, radial distribution functions, coordination numbers, and packing densities. Electronic structure studies performed using photoemission spectroscopy and low-temperature specific heat provided information about the electronic density of states within the valence band and at the Fermi level and also about interatomic bonding and atomic vibrations [from the Debye temperature and the boson peak (BP)]. Variations of both atomic structure and electronic structure with x showed a clear change for x ≥ 0.35, which corresponds to a valence electron number ≥7.4. All physical properties, namely, thermal stability parameters, Debye temperatures, BPs, magnetic, elastic, and electronic transport properties, change their concentration-dependence for x ≥ 0.35. The results are compared with those for binary and ternary MGs of the same elements.
This section of Journal of Materials Research is reserved for papers that are reviews of literature in a given area.