Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 June 2018
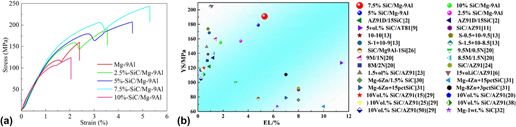
Nanosize SiCp (n-SiCp) reinforced Mg–9Al matrix composites (Mg–9Al–xSiC, x = 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 wt%) with nearly full densification are fabricated by the semisolid powder hot pressing technique assisted with ultrasonic. The effect of SiC nanoparticle contents on microstructures and mechanical properties of the composites is systematically investigated. Grain size and density of Mg–9Al–xSiC composites and morphology of bonding interfacial between the n-SiCp and matrix are found to be greatly dependent on the n-SiCp contents, resulting in the strength and ductility of the composites increase first and then decrease as the increase of n-SiCp contents. As the SiCp content increasing to 7.5 wt%, superior mechanical properties with the yield strength of 191 MPa, ultimate tensile strength of 248 MPa, and elongation to failure of 5.3% are achieved. The improved mechanical properties could be attributed to grain boundary strengthening, Orowan strengthening, and load transfer strengthening.