Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 July 2018
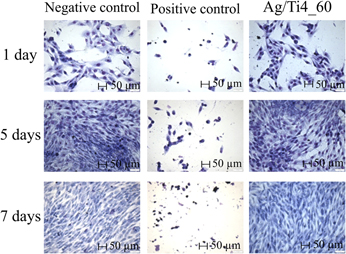
Contamination by bacterial biofilms has a strong negative impact, especially on the surface of prostheses, implants, pins, and other medical-surgical devices. To prevent their formation, one of the alternatives is the modification of the metal surface incorporating silver by low-energy ion implantation, thus avoiding initial bacteria adhesion to the modified surface and further development of the biofilm. The bactericidal properties of silver atoms incorporated on commercially pure titanium surfaces by low-energy ion implantation (4 keV) were evaluated. The surface modifications were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry, glow discharge-optical emission spectroscopy, contact angle measure, optical profilometry, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The microbiological assays were conducted by using Escherichia coli (E. coli). The results demonstrated a reduction on bacterial counting. No toxic effect of silver was detected on human MG-63 cells. The choice of parameters to obtain a bactericidal and nontoxic biomaterial for human cells should consider the ideal combination “energy + silver concentration”. Therefore, it can be considered for industrial application.
This section of Journal of Materials Research is reserved for papers that are reviews of literature in a given area.