Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Kriegseis, Jochen
Kinzel, Matthias
and
Rival, David E.
2013.
On the persistence of memory: do initial conditions impact vortex formation?.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 736,
Issue. ,
p.
91.
Huang, Yuqi
Venning, James
Thompson, Mark C.
and
Sheridan, John
2015.
Vortex separation and interaction in the wake of inclined trapezoidal plates.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 771,
Issue. ,
p.
341.
Han, Xingsi
and
Morgans, Aimee S.
2015.
Simulation of the flame describing function of a turbulent premixed flame using an open-source LES solver.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 162,
Issue. 5,
p.
1778.
Mons, V.
Chassaing, J.-C.
Gomez, T.
and
Sagaut, P.
2016.
Reconstruction of unsteady viscous flows using data assimilation schemes.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 316,
Issue. ,
p.
255.
Hemmati, Arman
Wood, David H.
and
Martinuzzi, Robert J.
2016.
Characteristics of distinct flow regimes in the wake of an infinite span normal thin flat plate.
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,
Vol. 62,
Issue. ,
p.
423.
Boddupalli, Nibodh
Goenka, Vikash
and
Chandra, Laltu
2017.
Fluid flow analysis behind heliostat using LES and RANS: A step towards optimized field design in desert regions.
Vol. 1850,
Issue. ,
p.
110001.
Boddupalli, Nibodh
Singh, Gurveer
Chandra, Laltu
and
Bandyopadhyay, Bibek
2017.
Dealing with dust – Some challenges and solutions for enabling solar energy in desert regions.
Solar Energy,
Vol. 150,
Issue. ,
p.
166.
Benhamadouche, S.
Arenas, M.
and
Malouf, W.J.
2017.
Wall-resolved Large Eddy Simulation of a flow through a square-edged orifice in a round pipe at Re = 25,000.
Nuclear Engineering and Design,
Vol. 312,
Issue. ,
p.
128.
Mulleners, Karen
Mancini, Peter
and
Jones, Anya R.
2017.
Flow Development on a Flat-Plate Wing Subjected to a Streamwise Acceleration.
AIAA Journal,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 6,
p.
2118.
Boddupalli, Nibodh
Singh, Gurveer
Chandra, Laltu
and
Bandyopadhyay, Bibek
2017.
Reprint of: Dealing with dust – Some challenges and solutions for enabling solar energy in desert regions.
Solar Energy,
Vol. 154,
Issue. ,
p.
134.
Teimourian, Amir
Hacisevki, Hasan
and
Bahrami, Arian
2017.
Experimental study on flow past two inclined flat plates in tandem arrangement.
Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,
Vol. 169,
Issue. ,
p.
1.
Mahmood, Imran
and
Raza, Ali
2017.
Therapeutic Equipment for Brain-Hyperthermia Using Convective Spray Cooling.
Journal of Medical Devices,
Vol. 11,
Issue. 3,
Boddupalli, Nibodh
Yadav, Navneet Kumar
and
Chandra, Laltu
2018.
The unsteady flow features behind a heliostat in a narrow channel at a high Reynolds number: Experiment and Large Eddy Simulation.
International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,
Vol. 136,
Issue. ,
p.
424.
Rolfo, Stefano
Kopsidas, Konstantinos
Rahman, Shahnurriman A.
Moulinec, Charles
and
Emerson, David R.
2018.
Effect of Large Scale 3-D Structures on the Flow Around a Heated Cylinder at Low Reynolds Number.
Flow, Turbulence and Combustion,
Vol. 101,
Issue. 2,
p.
553.
Hemmati, Arman
Wood, David H.
and
Martinuzzi, Robert J.
2018.
On simulating the flow past a normal thin flat plate.
Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,
Vol. 174,
Issue. ,
p.
170.
Hemmati, Arman
Wood, David H.
and
Martinuzzi, Robert J.
2019.
Wake dynamics and surface pressure variations on two-dimensional normal flat plates.
AIP Advances,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 4,
Fogaing, Mireille B. Tadie
Hemmati, Arman
Lange, Carlos F.
and
Fleck, Brian A.
2019.
Performance of Turbulence Models in Simulating Wind Loads on Photovoltaics Modules.
Energies,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 17,
p.
3290.
Kahil, Yacine
Benhamadouche, Sofiane
Berrouk, Abdallah Sofiane
and
Afgan, Imran
2019.
Simulation of subcritical-Reynolds-number flow around four cylinders in square arrangement configuration using LES.
European Journal of Mechanics - B/Fluids,
Vol. 74,
Issue. ,
p.
111.
Shademan, Mehrdad
and
Naghib-Lahouti, Arash
2020.
Effects of aspect ratio and inclination angle on aerodynamic loads of a flat plate.
Advances in Aerodynamics,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 1,
Wang, Xikun
Chen, Jiaqi
Zhou, Bo
Li, Yajie
and
Xiang, Qingjiang
2021.
Experimental investigation of flow past a confined bluff body: Effects of body shape, blockage ratio and Reynolds number.
Ocean Engineering,
Vol. 220,
Issue. ,
p.
108412.
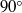 $90\textdegree $) and then at oblique (
$90\textdegree $) and then at oblique (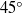 $45\textdegree $) incidence flow direction with a uniform steady inlet. The results are in complete agreement with the direct numerical simulation (DNS) and experimental data, thereby serving as a validation for the present simulations. For the normal (
$45\textdegree $) incidence flow direction with a uniform steady inlet. The results are in complete agreement with the direct numerical simulation (DNS) and experimental data, thereby serving as a validation for the present simulations. For the normal (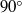 $90\textdegree $) uniform inflow case, coherent vortices are alternately shed from both leading edges of the plate, whereas for the oblique (
$90\textdegree $) uniform inflow case, coherent vortices are alternately shed from both leading edges of the plate, whereas for the oblique (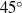 $45\textdegree $) uniform inflow case the vortices shed from the two sides of the plate interact strongly resulting in a quasi-periodic force response. The normal flat plate is then analysed with an incident gust signal with varying amplitude and time period. For these incident coherent gust cases, a reference test case with variable coherent inlet is first studied and the results are compared to a steady inlet simulation, with a detailed analysis of the flow behaviour and the wake response under the incident gust. Finally, the flat plate response to 16 different gust profiles is studied. A transient drag reconstruction for these incident coherent gust cases is then presented based on a frequency-dependent transfer function and phase spectrum analysis.
$45\textdegree $) uniform inflow case the vortices shed from the two sides of the plate interact strongly resulting in a quasi-periodic force response. The normal flat plate is then analysed with an incident gust signal with varying amplitude and time period. For these incident coherent gust cases, a reference test case with variable coherent inlet is first studied and the results are compared to a steady inlet simulation, with a detailed analysis of the flow behaviour and the wake response under the incident gust. Finally, the flat plate response to 16 different gust profiles is studied. A transient drag reconstruction for these incident coherent gust cases is then presented based on a frequency-dependent transfer function and phase spectrum analysis.

