3 Airway management
Practical Emergency Resuscitation and Critical Care, ed. Kaushal Shah, Jarone Lee, Kamal Medlej and Scott D. Weingart. Published by Cambridge University Press. © Kaushal Shah, Jarone Lee, Kamal Medlej and Scott D. Weingart 2013.
Introduction
Airway management is one of the core fundamental skills of the emergency medicine or critical care physician.
Airway management is time-critical and can literally mean the difference between life and death.
Airway management encompasses the overlapping management of oxygenation, ventilation, and airway protection.
Airway principles (Table 3.1)
Planning, recognizing failure, and decision-making are top priorities.
Maintenance of calm permits proper decision-making. Undue haste is detrimental to critical decision-making.
Specific time-sensitive exceptions include acidosis, impending airway obstruction, and hypoxia.
Each aspect of airway management is modular. Components can be mixed as needed (e.g., video laryngoscopy with a bougie; awake intubation after preoxygenation with noninvasive ventilation).
Table 3.1. Principles for safe emergency airway management

Recognizing failure (Figure 3.1)
When first-line techniques fail to result in intubation, early identification of failure is paramount.
If unsuccessful, laryngoscopy should be abandoned and oxygen restored with mask ventilation.
Extraglottic airways (EGA) can be placed quickly and may provide better ventilation than bag-mask ventilation.
If an intubation attempt fails and reoxygenation fails, a cricothyroidotomy must be performed immediately.
Failure to recognize a “can’t intubate, can’t oxygenate” scenario will result in the patient’s death.
Figure 3.1. (© Reuben Strayer & emupdates.com, used with permission. Adapted from: Reuben Strayer. Emergency Department Intubation Checklist v13. 2012. http://emupdates.com/2012/07/08/emergency-department-intubation-checklist-v13/; accessed July 23, 2012).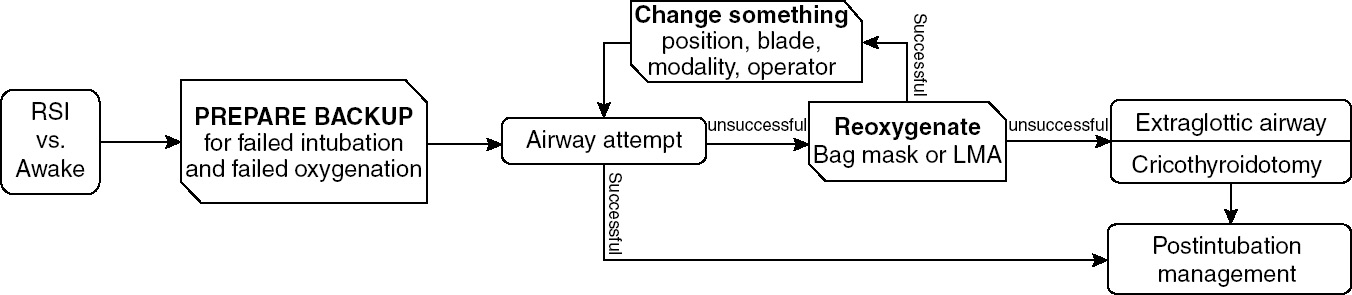
Decision to intubate (Table 3.2)
Many factors at play must be balanced, including:
Early management of a sick patient
Potential danger of paralyzing a patient
Limited clinical evaluation of an intubated patient
Noninvasive ventilation
In patients protecting their airway, noninvasive ventilation (NIV) may be appropriate.
Many patients will improve dramatically with NIV and avoid intubation.
NIV provides:
Up to 100% FiO2
Pressure-support, decreasing the work of breathing
PEEP, overcoming shunt physiology (e.g., severe pneumonia, acute pulmonary edema).
Although alteration in mental status is a traditional relative contraindication to NIV, critically ill emergency department (ED) patients can be closely monitored by experienced airway operators.
NIV can be used to achieve two simultaneous goals:
Oxygenation
Oxygenation is the primary concern in airway management.
As hemoglobin and oxygen bind cooperatively, desaturation is slow above SpO2 90%.
Below 90%, hemoglobin molecules quickly lose bound oxygen, and critical hypoxia can occur in seconds.
Due to the technical aspects of pulse oximetry, there is a lag of up to 2 minutes in the measured SpO2. Therefore, a reading in the 80–90% range may indicate that the actual SpO2 is much lower.
Laryngoscopy should be abandoned when SpO2 reads 90% in order for the patient to be reoxygenated.
Laryngoscopy and intubation
Positioning
Proper positioning is essential for laryngoscopy.
The same positioning principles will aid in preoxygenation and mask ventilation.
Proper positioning lifts the anterior pharyngeal structures off the posterior pharynx and optimizes glottis view.
A combination of head, neck, and body positioning can be used to optimize both of these goals.
Jaw thrust: lifting the jaw anteriorly by the angles of the mandible to open the pharynx.
Ear-to-sternal-notch: the patient’s head should be elevated in order for the external auditory meatus to be at the same level as the manubrium, in a plane parallel to the ceiling (Figure 3.2a).
Some patients (including: obese, with pleural effusions, at risk for vomiting) may benefit from elevating the head of the bed to 30 degrees while maintaining the same positioning principles (Figure 3.2b).
Positioning for a video laryngoscope (VL):
VL with conventional blades: positioning is unchanged.
VL with an angulated blade: completely neutral head and neck position, with the head flat on the bed and the face plane parallel to the ceiling.
Figure 3.2. Patient positioning.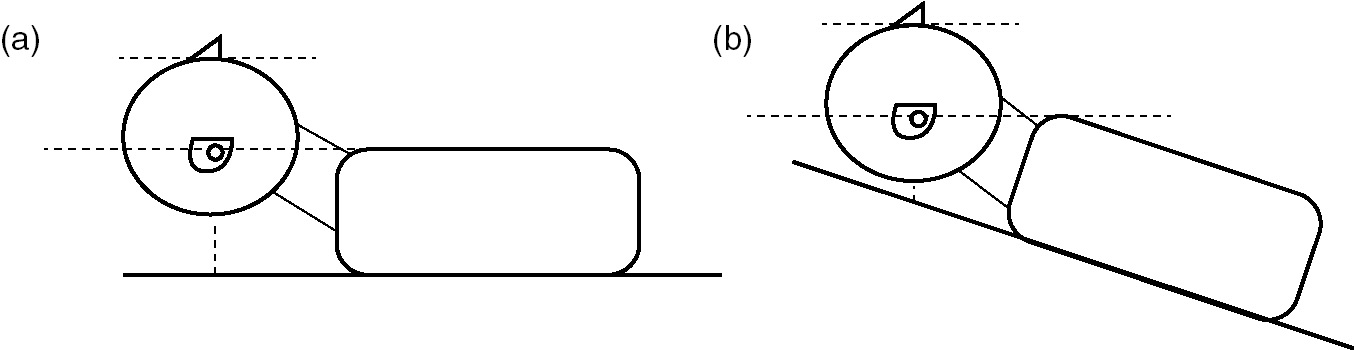
Preoxygenation
The goal of preoxygenation is not merely to achieve an SpO2 of 100%, but also to de-nitrogenate the lungs, completely filling the lungs with oxygen to act as an oxygen reservoir during laryngoscopy.
Preoxygenate with a non-rebreather mask (NRB) set to 15 liters per minute or higher, for at least 3 minutes.
If hypoxia persists despite high-flow oxygen, the patient is likely shunting and may require PEEP delivered via NIV.
Obtunded hypoxic patients, if still ventilating on their own, may be safer to ventilate with NIV under close supervision than with bag-mask ventilation.
In the apneic patient, bag-mask ventilation (BMV) should be performed.
Two-operator technique will provide a better mask seal as one operator can use both hands to secure the mask to the patient’s face.
Nasal trumpets and oral airways, if tolerated, can be invaluable in maintaining pharyngeal patency.
Use slow, smooth, controlled breaths of only half the volume of a standard bag.
Patients obtunded due to severe metabolic acidosis will require a much faster respiratory rate, and must be ventilated during the apneic period to avoid cardiac arrest.
Most bags accept a PEEP valve if necessary.
Ventilators can be attached to masks, allowing for control of tidal volumes, respiratory rate, and PEEP if needed.
Fully obtunded and apneic patients oxygenate better with the rapid placement of an EGA.
Apneic oxygenation and oxygenation during laryngoscopy
NRB should be left in place during the apneic period.
As the oxygen in the lungs is filtered into the body, an O2-gradient is established allowing passive flow of oxygen from the high-FiO2 of the NRB to the lungs.
A nasal cannula set to 15 lpm will similarly provide high-flow oxygen during laryngoscopy.
If there are insufficient oxygen wall adaptors to provide three sources of oxygen (bag-mask, NRB, and nasal cannula), place a portable oxygen tank under the bed to provide a third source.
Extraglottic airways
Numerous EGA options exist, primarily laryngeal tubes (mainly used in the pre-hospital setting) and laryngeal masks.
EGA are typically used as rescue devices when it is difficult to provide BMV.
Laryngeal masks do not fully “secure” the airway as vomit may dislodge them.
Many second-generation laryngeal masks permit intubation through the mask.
Laryngoscopy
Principles of laryngoscopy are identical for direct and video laryngoscopy, with the exception of different positioning.
Suction should be available under the patient’s right shoulder. Two or more Yankauer suction tips may be necessary if blood, vomit, or copious secretions are expected.
Various devices exist for video laryngoscopy.
Many devices use traditional curved blades and may be used either directly or with the video monitor.
Devices with angulated or indirect blades are operated similarly but do not allow for direct visualization.
Angulated blades will often insert too far; if the glottis cannot be seen, withdraw slowly.
Lifting the handle straight toward the ceiling may also improve the view.
Video devices improve views but may be defeated by blood, mucus, or vomit.
Tube delivery may be more difficult as the angle of attack to the trachea is steeper.
Stylets vastly improve tube control and delivery and should be shaped straight to the cuff, then angled to 35 degrees.
Deliver the tube from the side (3-o’clock): rotation about the long axis will give subtle control in the vertical axis, and the tube will not obscure the glottic view.
A partial glottic view is sufficient if the tube can be directed above the posterior cartilages (Figure 3.3).
Tube delivery with angulated VL is often facilitated with malleable stylets shaped similarly to the blade, or with proprietary stylets.
Bimanual laryngoscopy
Bimanual laryngoscopy includes both external laryngeal manipulation (ELM) and head mobilization.
ELM is best achieved with the aid of an assistant.
ELM is not cricoid pressure.
Bougie
The bougie is a valuable adjunct, particularly in partial glottis views.
The bougie is threaded through the glottis and the tube is delivered “over the wire.”
When advanced gently, the bougie will be stopped by a terminal bronchus after 40 cm of insertion if it is properly located in the airway. If in the esophagus, the bougie will advance indefinitely.
Confirmation of placement
Traditional indicators such as chest rise, auscultation, humidity in the tube, chest radiography, and SpO2 are helpful but unreliable.
The preferred method for confirmation of endotracheal intubation is capnography.
Colorimetric capnography: disposable litmus-paper devices that change color from purple to yellow.
Only accurate if color change persists over 6 breaths.
Inaccurate if the airway is soiled by vomit.
Waveform capnography: nearly 100% accurate, end-tidal capnography is near gold-standard.
Capnography should also be used to confirm ventilation with EGA.
Rapid sequence intubation (RSI)
RSI is the simultaneous administration of a paralytic and an induction agent.
The overwhelming majority of ED intubations use RSI.
Adequate preoxygenation is a prerequisite for safe RSI.
One goal of RSI is to avoid positive-pressure ventilation during the apneic period to minimize the risk of vomiting by avoiding gastric insufflation.
RSI has been proven to be safe and effective as paralysis optimizes intubating conditions.
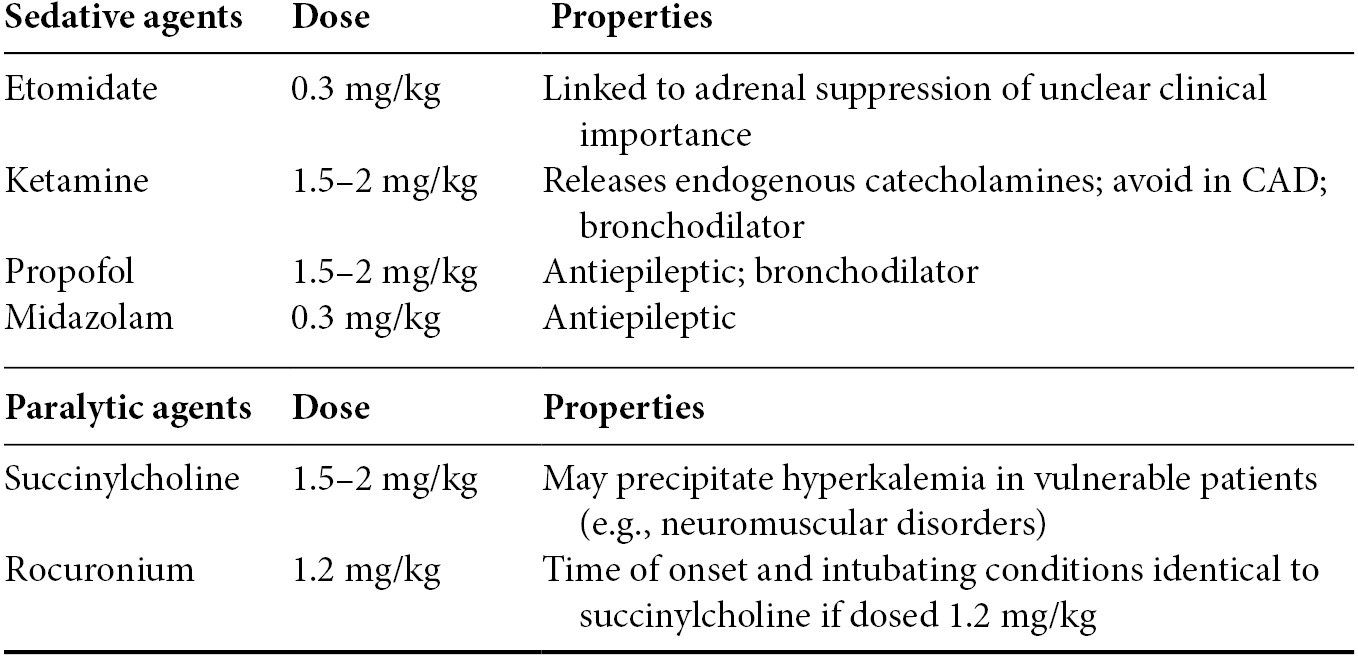
RSI medications (Table 3.3)
The cornerstone of RSI is the simultaneous use of a potent sedative and fast-acting paralytic.
Etomidate, propofol, and midazolam may precipitate hypotension. For potential hypotension or hypovolemia, reduce the induction dose by 50% or more.
Earlier concerns about use of ketamine in elevated intracranial pressure are unfounded.
Onset of paralysis is 30–45 seconds with either succinylcholine or high dose rocuronium.
Succinylcholine is widely used but may precipitate hyperkalemia. At-risk populations include:
Neuromuscular disorders (acquired and congenital)
Sepsis, burns, and crush injuries (generally only vulnerable >3 days after onset)
Preexisting hyperkalemia
While succinylcholine has a shorter duration of action than rocuronium (8–10 minutes vs. 45 minutes), the patient will critically desaturate prior to return of muscle tone if the tube cannot be placed.
Table 3.3. RSI medications
Hemodynamics
Induction of anesthesia may be detrimental to hemodynamics.
Sedation blunts the sensation of noxious stimuli, decreasing endogenous catecholamines.
Intubation and mechanical ventilation results in the shift from physiological negative-pressure ventilation to positive-pressure ventilation, which decreases preload.
Hemodynamics should be optimized prior to intubation, through fluid resuscitation and/or vasopressors as indicated.
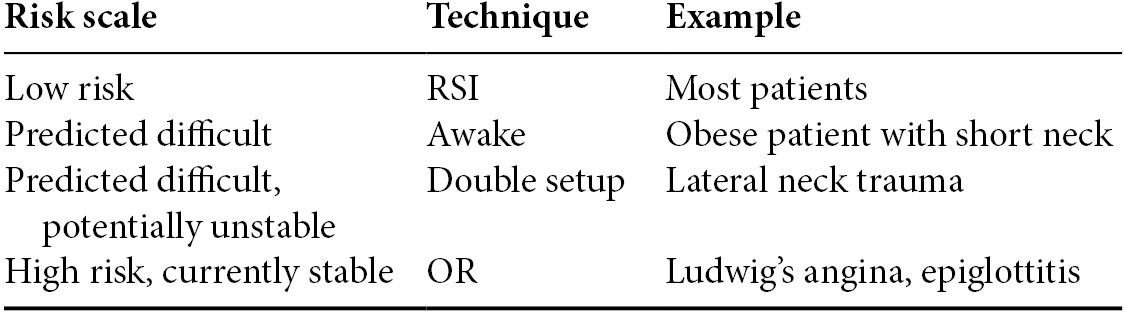
Assessing airway difficulty (Table 3.4)
In the potentially difficult airway, awake intubation allows for an increased safety margin.
Predicting the difficult airway is difficult.
The gestalt of an experienced physician is likely equal to or superior to specific rules, and is usually informed by similar elements.
Features that potentially increase intubation difficulty include:
Obesity
Short neck
Decreased neck mobility
Small mouth opening
Recessed chin
As most ED intubations utilize RSI, comfort and skill with awake technique may be limited.
While maintaining the patient’s respiratory drive confers a clear level of safety, intubating conditions are not optimized.
Awake intubation is straightforward, adds only a few minutes of time, and even if unsuccessful, has taken little from the patient.
A failed awake intubation can easily be converted to an RSI, but a paralyzed patient requires definitive airway control.
Most patients are safe for RSI.
Some potentially difficult patients may be safe for paralysis but will benefit from a double setup:
Fully prepared for cricothyroidotomy
Equipment open at the bedside
Cricothyroid membrane marked
Neck sterilized
While one physician is ready to immediately perform the surgical airway if needed, a separate physician takes a single attempt at RSI
A double setup will help overcome the cognitive burden of identifying the need for surgical airway if necessary.
If time allows, some patients may benefit from techniques not possible in the ED and should be considered for definitive control in the operating room (OR).
Sedative-only intubation, while seemingly attractive, is potentially dangerous.
Intubating without paralysis means conditions are not optimized.
The dose of sedative necessary for the patient to tolerate laryngoscopy will obliterate respiratory drive, eliminating the benefit of avoiding paralysis.
Sedation alone is unlikely to diminish airway reflexes; the risk of vomiting and aspiration caused by laryngoscopy is high.
Accordingly, all ED patients undergoing intubation should receive sedation and either paralytics or topicalization.
Table 3.4. Technique for increasing levels of risk
Alternative airway techniques
Awake intubation
Awake intubation refers to the use of topical anesthetic instead of paralytic agents to facilitate intubation, while maintaining the patient’s respiratory drive and protective airway reflexes.
“Awake intubation” is a misnomer, as patients require some level of sedation.
Most sick patients can be intubated awake.
Awake intubation takes minimal extra time and provides a wide safety margin in the potentially difficult airway.
Ketamine, ketofol, or dexmedetomidine are optimal agents as they maintain respiratory drive and airway reflexes.
Video laryngoscopy should be used if available, as the intubating conditions will not be optimized via paralysis.
Delayed sequence intubation (DSI)
Hypoxic patients may not tolerate preoxygenation due to delirium.
Under close monitoring, these patients may benefit from delayed sequence intubation; the use of a sedative to allow for proper preoxygenation, followed by paralysis and intubation.
Sedative dosing should be adjusted to maintain the patient’s airway reflexes and respiratory drive.
Ketamine is the first-line agent for DSI as it will not blunt airway reflexes or respiratory drive.










