Book contents
- Frontmatter
- Contents
- List of contributors
- Foreword (1)
- Foreword (2)
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Section 1 Organization of neonatal transport
- Section 2 Basics in cardiopulmonary resuscitation of newborn infants
- Basic equipment setup for initial neonatal care and resuscitation
- Drugs for neonatal emergencies
- Postnatal cardiopulmonary adaptation
- ABC Techniques and Procedures
- Sunctioning
- Stimulation, oxygen supplementation, bag-and-mask ventilation (M-PPV), pharyngeal/bi-nasal CPAP, and pharyngeal positive pressure ventilation
- Endotracheal intubation and gastric tube placement
- Laryngeal mask airway (LMA)
- Chest compressions
- Peripheral venous access
- Umbilical vein/artery catheterization (UVC, UAC)
- Central venous access (internal jugular vein)
- Intraosseous access
- Cord clamping
- Management of high-risk infants in the delivery room
- Monitoring in the delivery room and during neonatal transport
- Hygiene in the delivery room and during neonatal transport (infection control)
- When to call a pediatrician to the delivery room
- Checklist for the postnatal treatment of newborn infants
- Assigning individual duties in the delivery room
- Clinical assessment of the newborn infant
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation of newborn infants at birth
- Volume therapy and sodium bicarbonate supplementation in preterm and term newborn infants
- Absolute and relative indications for neonatal transport and NICU admission
- Communication with mother and father
- Coordinating neonatal transport and patient sign-out to the NICU team
- Documentation and feedback after neonatal emergency transport
- Ethics in neonatal intensive care
- Perinatal images of preterm and term infants
- Mechanical ventilation of the neonate
- Questions for review (basics)
- References (Section 2)
- Section 3 Classic and rare scenarios in the neonatal period
- Section 4 Transport
- Section 5 Appendix
- Index
- Plate section
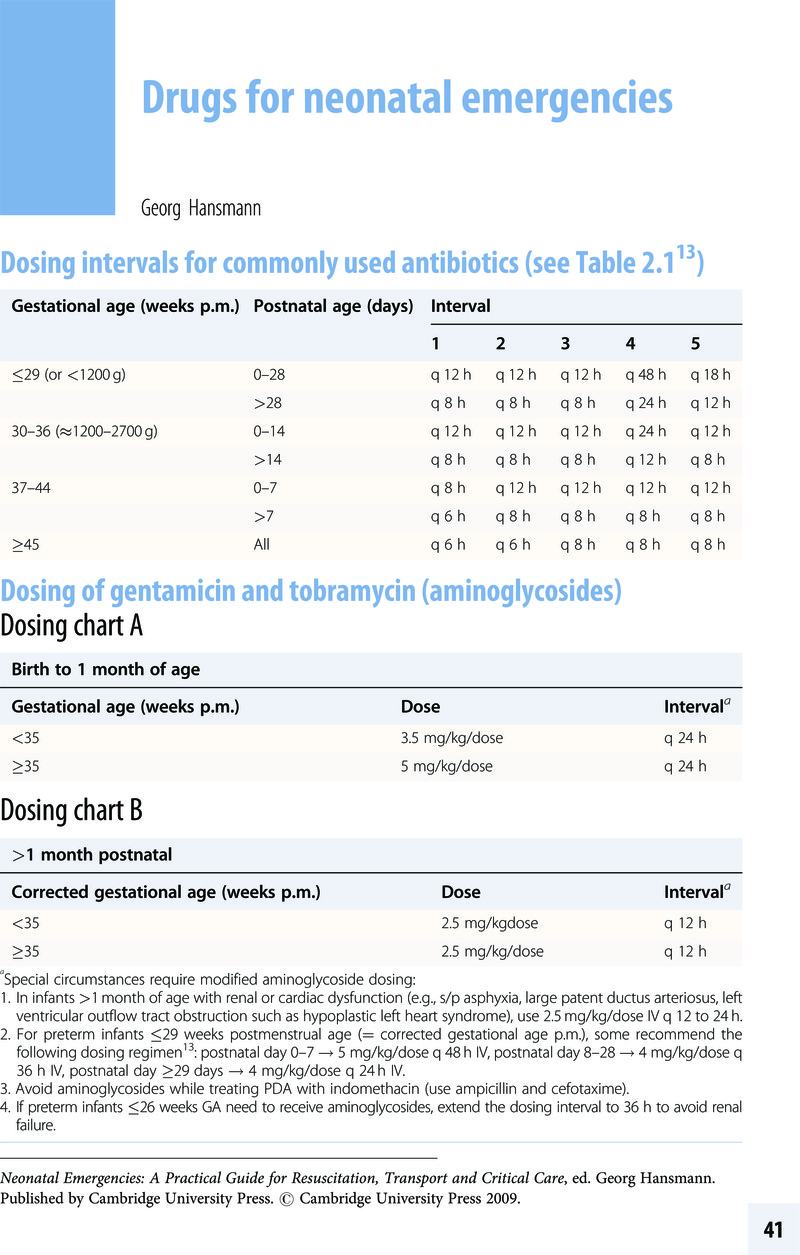
Drugs for neonatal emergencies
from Section 2 - Basics in cardiopulmonary resuscitation of newborn infants
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 March 2012
- Frontmatter
- Contents
- List of contributors
- Foreword (1)
- Foreword (2)
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Section 1 Organization of neonatal transport
- Section 2 Basics in cardiopulmonary resuscitation of newborn infants
- Basic equipment setup for initial neonatal care and resuscitation
- Drugs for neonatal emergencies
- Postnatal cardiopulmonary adaptation
- ABC Techniques and Procedures
- Sunctioning
- Stimulation, oxygen supplementation, bag-and-mask ventilation (M-PPV), pharyngeal/bi-nasal CPAP, and pharyngeal positive pressure ventilation
- Endotracheal intubation and gastric tube placement
- Laryngeal mask airway (LMA)
- Chest compressions
- Peripheral venous access
- Umbilical vein/artery catheterization (UVC, UAC)
- Central venous access (internal jugular vein)
- Intraosseous access
- Cord clamping
- Management of high-risk infants in the delivery room
- Monitoring in the delivery room and during neonatal transport
- Hygiene in the delivery room and during neonatal transport (infection control)
- When to call a pediatrician to the delivery room
- Checklist for the postnatal treatment of newborn infants
- Assigning individual duties in the delivery room
- Clinical assessment of the newborn infant
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation of newborn infants at birth
- Volume therapy and sodium bicarbonate supplementation in preterm and term newborn infants
- Absolute and relative indications for neonatal transport and NICU admission
- Communication with mother and father
- Coordinating neonatal transport and patient sign-out to the NICU team
- Documentation and feedback after neonatal emergency transport
- Ethics in neonatal intensive care
- Perinatal images of preterm and term infants
- Mechanical ventilation of the neonate
- Questions for review (basics)
- References (Section 2)
- Section 3 Classic and rare scenarios in the neonatal period
- Section 4 Transport
- Section 5 Appendix
- Index
- Plate section
Summary
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Neonatal Emergencies , pp. 41 - 62Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2009

