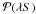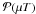Newcastle Disease (ND) is regarded as one of the major diseases of poultry because of the devastating losses that the virulent form of the ND virus can impose on both commercial and domestic chickens. However, the disease can be controlled through the administration of effective vaccines. Almost all the commercially available ND vaccines require refrigeration and begin to deteriorate rapidly after 1-2 hours if left at room temperature (around 25°C). Subsequently, because maintaining an adequate supply of refrigerated facilities may be a difficult task in many countries with unreliable electrical supplies, the development and large scale production of an effective thermostable ND vaccine seems imperative to support the poultry industry. Such vaccines should be resilient to damage associated with either very cold or hot environments so there are no concerns about the viability of the vaccine in response to temperatures fluctuations that can occur in extreme environments when the difference in temperature during cold and warm seasons can vary greatly. In the following review paper, the development of such a vaccine is discussed, including molecular characterisation, organ tropism of vaccine strains, production, as well as administration methods and their efficacy. It addition, the potential payback has been calculated alongside opportunities provided by removing vaccines from cold chain storage.