The crystal structure of a morimotoite garnet, ideally Ca3(Ti4+Fe2+)Si3O12, from the Ice River alkaline complex, British Columbia, Canada was refined by the Rietveld method, space group 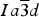 $Ia\overline 3 d$ , and monochromatic synchrotron high-resolution powder X-ray diffraction (HRPXRD) data. Electron-microprobe analysis indicates a homogeneous sample with a formula {Ca2.91Mg0.05Mn2+ 0.03}Σ3[Ti1.09Fe3+ 0.46Fe2+ 0.37Mg0.08]Σ2(Si2.36Fe3+ 0.51Al0.14)Σ3O12. The HRPXRD data show a two-phase intergrowth. The reduced χ 2 and overall R(F 2) Rietveld refinement values are 1.572 and 0.0544, respectively. The weight percentage, unit-cell parameter (Å), distances (Å), and site occupancy factors (sofs) for phase-1 are as follows: 76.5(1)%, a = 12.156 98(1) Å, average <Ca–O> = 2.4383, Ti–O = 2.011(1), Si–O = 1.693(1) Å, Ca(sof) = 0.943(2), Ti(sof) = 0.966(2), and Si(sof) = 1.095(3). The corresponding values for phase-2 are 23.5(1)%, a = 12.160 67(2) Å, average <Ca–O> = 2.452, Ti–O = 1.988(3), Si–O = 1.704(3) Å, Ca(sof) = 1.063(7), Ti(sof) = 1.187(7), and Si(sof) = 1.220(8). The two phases cause strain that arises from structural mismatch and gives rise to low optical anisotropy. Because the two phases are structurally quite similar, a refinement using a single-phase model with anisotropic displacement parameters shows no unusual displacement ellipsoid for the O atom that requires a “split O-atom position”, as was done in previous studies.
$Ia\overline 3 d$ , and monochromatic synchrotron high-resolution powder X-ray diffraction (HRPXRD) data. Electron-microprobe analysis indicates a homogeneous sample with a formula {Ca2.91Mg0.05Mn2+ 0.03}Σ3[Ti1.09Fe3+ 0.46Fe2+ 0.37Mg0.08]Σ2(Si2.36Fe3+ 0.51Al0.14)Σ3O12. The HRPXRD data show a two-phase intergrowth. The reduced χ 2 and overall R(F 2) Rietveld refinement values are 1.572 and 0.0544, respectively. The weight percentage, unit-cell parameter (Å), distances (Å), and site occupancy factors (sofs) for phase-1 are as follows: 76.5(1)%, a = 12.156 98(1) Å, average <Ca–O> = 2.4383, Ti–O = 2.011(1), Si–O = 1.693(1) Å, Ca(sof) = 0.943(2), Ti(sof) = 0.966(2), and Si(sof) = 1.095(3). The corresponding values for phase-2 are 23.5(1)%, a = 12.160 67(2) Å, average <Ca–O> = 2.452, Ti–O = 1.988(3), Si–O = 1.704(3) Å, Ca(sof) = 1.063(7), Ti(sof) = 1.187(7), and Si(sof) = 1.220(8). The two phases cause strain that arises from structural mismatch and gives rise to low optical anisotropy. Because the two phases are structurally quite similar, a refinement using a single-phase model with anisotropic displacement parameters shows no unusual displacement ellipsoid for the O atom that requires a “split O-atom position”, as was done in previous studies.