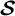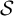2 results
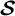 $\mathcal{\textbf{S}}$
-adic characterization of minimal ternary dendric shifts
$\mathcal{\textbf{S}}$
-adic characterization of minimal ternary dendric shifts
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 42 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2021, pp. 3393-3432
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Morphisms preserving the set of words coding three interval exchange∗∗∗
-
- Journal:
- RAIRO - Theoretical Informatics and Applications / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / January 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2012, pp. 107-122
- Print publication:
- January 2012
-
- Article
- Export citation