Introduction
Glyphosate is the most widely used herbicide in the world as a result of its unique characteristics of having a broad spectrum of weed control, relatively safe environmental profile, and flexibility in crop rotation (Baylis Reference Baylis2000). Benbrook (Reference Benbrook2016) reported that as of 2016, approximately 8.2 billion kg of glyphosate has been applied worldwide since its commercialization in 1974, of which nearly 72% occurred between 2006 and 2016. The United States accounts for the use of 19% of glyphosate globally (1.6 billion kg) (Benbrook Reference Benbrook2016). Although glyphosate is a postemergence foliar-active herbicide, a considerable amount of glyphosate may reach the soil as wash-off from foliage and/or after release from decomposing plant tissues and direct application to soil (Blackshaw and Harker Reference Blackshaw and Harker2016; Gomes et al. Reference Gomes, Smedbol, Chalifour, Hénault-Ethier, Labrecque, Lepage, Lucotte and Juneau2014). Glyphosate is tightly adsorbed on soil particles and is rapidly degraded by microbes into aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) (Al-Rajab and Hakami Reference Al-Rajab and Hakami2014; Gomes et al. Reference Gomes, Smedbol, Chalifour, Hénault-Ethier, Labrecque, Lepage, Lucotte and Juneau2014). Glyphosate can moderately persist in the soil with a half-life of 20 to 100 d; in comparison, AMPA has a relatively longer half-life ranging from 76 to 240 d, making AMPA more persistent and more likely to accumulate in soil over subsequent years (Al-Rajab and Hakami Reference Al-Rajab and Hakami2014). Glyphosate and AMPA can be adsorbed onto soil particles, but this process is reversible under certain conditions such as high soil moisture and phosphorus fertilization in a variety of soils, including Arenosol, Acrisol, Ferralsol, Luvisol subsoil, and Regosol (Bott et al. Reference Bott, Tesfamariam, Kania, Eman, Aslan, Römheld and Neumann2011; Laitinen et al. Reference Laitinen, Siimes, Rämö, Jauhiainen, Eronen, Oinonen and Hartikainen2008). Desorbed glyphosate and AMPA accumulate in the soil solution and may become available for plant uptake weeks or months after the initial glyphosate application (Bott et al. Reference Bott, Tesfamariam, Kania, Eman, Aslan, Römheld and Neumann2011). Overuse of glyphosate has not only resulted in the evolution of glyphosate-resistant weeds but has raised concerns over the possible accumulation of glyphosate and its metabolite AMPA in the soil over time, along with its impact on the soil biome (Dion et al. Reference Dion, Harsh and Hill2001; Miles and Moye Reference Miles and Moye1988; Sprankle et al. Reference Sprankle, Meggitt and Penner1975).
Plants grown to provide seasonal soil cover and create conservational benefits are referred to as cover crops (Blanco-Canqui and Jasa Reference Blanco-Canqui and Jasa2019). Cover crops may reduce soil erosion, enhance nutrient scavenging, improve conservation of soil moisture by better rainwater infiltration, provide weed suppression, increase soil organic matter, improve soil microbial biodiversity, and boost soil health (Curran et al. Reference Curran, Lingenfelter and Tooker2021). Growers plant cover crops for various reasons depending on requirements, opportunities, resource availability, and their level of knowledge or awareness about the benefits of cover crops (Masiunas et al. Reference Masiunas, Weston and Weller1995; Williams et al. Reference Williams, Mortensen and Doran1998). The adoption of cover crops in the Midwestern United States has been increasing for several reasons, including the availability of government incentives for conservation and sustainable practices (SARE 2015). Nonetheless, complexity of weed control due to the continuous increase in the number of herbicide-resistant weeds is driving growers’ interest in using cover crops to diversify weed control strategies (Dorn et al. Reference Dorn, Jossi and Van Der Heijden2015). Cover crops suppress weeds by physically obstructing or shading emerging weed seedlings, competing for resources such as light, moisture, and nutrients, and/or through releasing allelopathic compounds that negatively affect weed growth (Baraibar et al. Reference Baraibar, Hunter, Schipanski, Hamilton and Mortensen2018; Sturm et al. Reference Sturm, Pateinatos and Gerhards2018). The weed-suppressing potential of a cover crop is species specific and primarily related to characteristics that include uniform emergence, creating a dense soil cover, rapid growth rate or biomass production per unit area, and plasticity to establish and thrive under variable weather conditions (Buchanan et al. Reference Buchanan, Kolb and Hooks2016; Campiglia et al. Reference Campiglia, Radicetti and Mancinelli2012; Dorn et al. Reference Dorn, Jossi and Van Der Heijden2015; Teasdale and Mohler Reference Teasdale and Mohler2000).
Commonly grown cover crop species in the Midwestern United States are in the Poaceae, Fabaceae, and Brassicaceae families. For example, Baraibar et al. (Reference Baraibar, Hunter, Schipanski, Hamilton and Mortensen2018) reported that cover crops such as grasses [cereal rye and oats (Avena sativa L.)] in monoculture or in mixture with legumes [medium red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) and winter field pea] or brassica species [forage radish (Raphanus sativus L.) and canola (Brassica napus L.)] resulted in greater weed biomass reduction compared to brassica or legume monoculture. Similarly, barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) resulted in greater weed suppression compared to vetch (Vicia sativa L.) in winter and early spring; however, in late May both species provided 55% to 63% reduction in weed density compared to winter fallow (Alonso-Ayuso et al. Reference Alonso-Ayuso, Quemada, Vanclooster, Ruiz-Ramos, Rodriguez and Gabriel2018). Likewise, Cornelius and Bradley (Reference Cornelius and Bradley2017) reported 68% to 72% reduction in density of field pennycress (Thlaspi arvense L.) and henbit (Lamium amplexicaule L.) with a mixture of cereal rye and hairy vetch. Cover crops have been evaluated to suppress difficult-to-control weeds such as herbicide-resistant Palmer amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri S. Watson) in agronomic crops (Montgomery et al. Reference Montgomery, McClure, Hayes, Walker, Senseman and Lawrence2018; Wiggins et al. Reference Wiggins, McClure, Hayes and Steckel2016).
Irrespective of their motivations for growing cover crops, growers encounter common challenges such as cover crop establishment, associated risks of introducing new insect and/or plant diseases, soil moisture use, cover crop termination methods, and termination time (Palhano et al. Reference Palhano, Norsworthy and Barber2018; SARE 2014). Cover crop establishment remains a challenge, in that limited information is available on location-specific planting time, optimum mixture of cover crop species, proper seed rate, inadequate soil moisture at seeding, and injury due to herbicide carryover (Cornelius and Bradley Reference Cornelius and Bradley2017; Keeling et al. Reference Keeling, Matches, Brown and Karnezos1996; Rogers et al. Reference Rogers, Talbert and Frans1986). Weed control strategies in corn (Zea mays L.)–soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] cropping systems in the Midwestern United States are predominantly based on herbicides; therefore, the impact of herbicide carryover is critical for establishing cover crops (Cornelius and Bradley Reference Cornelius and Bradley2017; Palhano et al. Reference Palhano, Norsworthy and Barber2018; Rector et al. Reference Rector, Pittman, Beam, Bamber, Cahoon, Frame and Flessner2020). For instance, Rector et al. (Reference Rector, Pittman, Beam, Bamber, Cahoon, Frame and Flessner2020) evaluated 30 preemergence and postemergence herbicides, including inhibitors of acetolactate synthase, 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase, very-long-chain fatty acids, protoporphyrinogen oxidase, and photosystem II commonly used in corn, soybean, and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) for potential impact on grass [winter wheat, winter barley, cereal rye, winter oats, annual ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum (Lam.) Husnot)], legumes (Austrian winter pea, crimson clover, and hairy vetch), and brassica [forage radish (Raphanus sativus L.) and rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)]. Results from this study indicated no impact of herbicide carryover on cover crop biomass, though it recorded injury of ≤20% in grass cover crops, 20% to 50% in brassica species, and ≤30% in legumes (Rector et al. Reference Rector, Pittman, Beam, Bamber, Cahoon, Frame and Flessner2020). On the contrary, Palhano et al. (Reference Palhano, Norsworthy and Barber2018) reported reduction in the emergence of leguminous (Austrian winter pea, crimson clover, and hairy vetch) and cruciferous cover crops (rapeseed) following the application of atrazine, diuron, fluridone, fomesafen, metribuzin, pyrithiobac, and sulfentrazone. In the same study, grass cover crops were not affected by soil-applied herbicides, with the exception of biomass reduction in barley following application of flumioxazin, fluridone, mesotrione, S-metolachlor, and sulfentrazone. Similarly, Cornelius and Bradley (Reference Cornelius and Bradley2017) reported that some commonly used corn and soybean herbicides have the potential to reduce emergence of cover crops depending on weather conditions, cover crop species, and herbicide.
Despite the evolution and widespread occurrence of glyphosate-resistant weeds, a statewide survey in Nebraska reported that glyphosate is the most widely used herbicide in glyphosate-resistant corn–soybean cropping systems (Sarangi and Jhala Reference Sarangi and Jhala2018). Multiple herbicide-resistant corn and soybean varieties have been adopted by growers in recent years. For example, dicamba/glyphosate-resistant soybean came to market in the 2017 growing season, and in the 2019 growing season, about 70% of soybean planted in Nebraska was dicamba/glyphosate-resistant, with this percentage expected to increase in the future (Jhala et al. Reference Jhala, Knezevic, Klein, Rees, Pryor and Creger2019). Corn/soybean resistant to 2,4-D choline/glyphosate/glufosinate have been commercialized in recent years (Shyam et al. Reference Shyam, Chahal, Jhala and Jugulam2021); additionally, soybean resistant to isoxaflutole/glufosinate/glyphosate, as well as soybean resistant to dicamba/glyphosate/glufosinate have recently become available commercially (Jhala Reference Jhala2019). Because the new generation of multiple herbicide–resistant corn/soybean includes the glyphosate resistance trait, glyphosate is likely to remain the most widely used herbicide, and the issue of glyphosate/AMPA accumulation in the soil may become more prominent, particularly in the Midwestern United States.
In the Midwest, cover crops are commonly planted in the fall before or after corn/soybean harvest. Cereal rye is a widely planted cover crop in the Midwest, though cover crop mixes, including cereal rye, crimson clover, radish, oats, radish, and hairy vetch are also popular (Plastina et al. Reference Plastina, Liu, Miguez and Carlson2020). Although research has been conducted to determine the residual effect of corn/soybean herbicides on cover crop emergence and biomass production (Cornelius and Bradley Reference Cornelius and Bradley2017), the impact of glyphosate or its metabolite (AMPA) on cover crops has not been explored. The objectives of this study were to evaluate the response of cover crop species, including cereal rye, crimson clover, field pea, hairy vetch, and winter wheat, to glyphosate and AMPA soil residue at different rates in silty clay loam soil, as well as the seed germination of these species in a 0.7 g L–1 solution of AMPA or glyphosate. We hypothesized that an increasing concentration of glyphosate or AMPA residue in soil will reduce the emergence and biomass accumulation of the cover crop species tested.
Materials and Methods
Greenhouse Study
A greenhouse study was conducted in 2017 at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln using soil collected from a local field near Lincoln, NE, with a history of glyphosate-resistant corn–soybean crop rotation and glyphosate application. Soil from a field with a history of glyphosate application was selected to simulate the realistic field soil situation, as previous research has reported that glyphosate concentration in soil is correlated with the cumulative doses and total number of applications rather than last spraying event dose (Primost et al. Reference Primost, Marino, Aparicio, Costa and Carriquiriborde2017). The soil was air-dried and put through a 5-mm sieve to remove clods and plant material. Unsterilized soil was used in this study to maintain soil microorganisms that play an important role in glyphosate or AMPA degradation under natural conditions (Singh and Walker Reference Singh and Walker2006; Sprankle et al. Reference Sprankle, Meggitt and Penner1975). Soil analysis was performed on representative samples at a commercial soil testing laboratory (Ward Laboratories, Kearney, NE) to determine the soil texture, organic matter, pH, and macro/micro-nutrients (Table 1). Soil samples were analyzed for the presence of glyphosate and/or AMPA residue in a laboratory (Waypoint Analytical, Memphis, TN) using high-performance liquid chromatography (Table 1).
Table 1. Soil texture, nutrient analysis, and glyphosate or aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) residue analysis of the soil used in a study to evaluate response of broadleaf and grass cover crop species to glyphosate or aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) soil residues in a greenhouse study at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
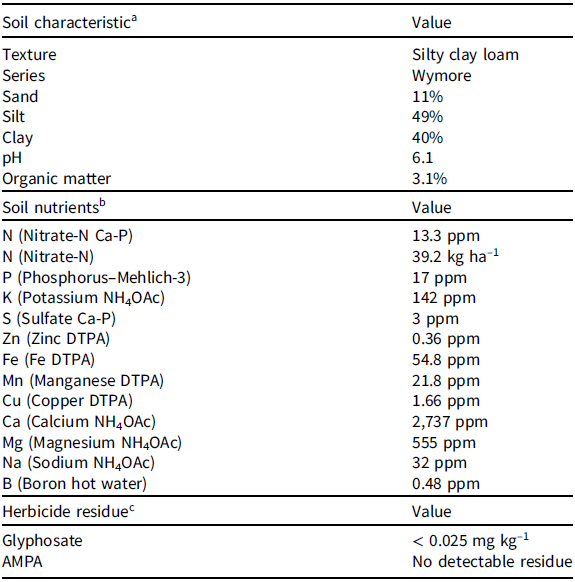
a Soil analysis to determine soil texture, organic matter, pH, and macro/micro-nutrients was conducted at Ward Laboratories, Kearney, NE.
b Abbreviation: DTPA, diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid.
c Soil samples were analyzed for the presence of glyphosate and/or AMPA residue at Waypoint Analytical, Memphis, TN.
Glyphosate and AMPA Treatments
Potassium salt of glyphosate and AMPA (Bayer Crop Science, St Louis, MO) with 58% and 99.2% purity of acid equivalent (ae), respectively, were used in this study. Pots were filled with 1 kg of soil thoroughly mixed with 0, 3.5, 7, 14, 35, 70, and 105 mg ae of glyphosate or AMPA. The application rates represent 0, 3.5, 7, 14, 35, 70, and 105 kg ae ha–1 of glyphosate or AMPA applied assuming a soil density of 1.5 g cm–3 and 6.7 cm of soil depth evenly receiving the treatment. Treatments were prepared for four replications together by mixing each concentration of glyphosate or AMPA with sieved soil to avoid the cumulation of measuring error, especially for the lower concentrations. For example, 3.5 mg ae kg–1 of glyphosate or AMPA treatment was prepared by mixing 14 mg ae of glyphosate or AMPA in 4 kg of finely sieved soil in a plastic box fixed with a closed lid and thoroughly mixed using a small, customized soil tumbler to ensure thorough mixing. To confirm the activity of samples as well as the sensitivity of cover crop species, technical-grade glyphosate at the labeled rate of 1.26 kg ha–1 and AMPA at 0.41 kg ha–1 was applied postemergence on 8- to 10-cm tall plants of all cover crop species tested in this study using a chamber track sprayer (DeVries Manufacturing Corp, Hollandale, MN) fitted with an 8001E nozzle (TeeJet; Spraying Systems Co., Wheaton, IL) calibrated to deliver 190 L ha–1 carrier volume at 207 kPa. The experiments were conducted separately for each species in a completely randomized design with four replications and repeated twice under the same treatments and growing conditions with a day/night temperature of 22 to 24/15 to 17 C and a 15-h photoperiod. Nutrients [fertilizer containing 10% total nitrogen (N), 5% available phosphate (P2O5), 14% soluble potash, 6% calcium (Ca), 2% magnesium (Mg), 3% sulfur (S), 0.12% iron (Fe), and 0.05% manganese; GH Inc., Sebastopol, CA] were added at a rate of 15 g L–1 of water twice a week.
Cover Crop Species
Four seeds of broadleaf cover crop species (crimson clover, field pea, and hairy vetch), and grass cover crop species (cereal rye and winter wheat) were planted at 1.5 to 3 cm depth separately in each experimental unit (a 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm plastic pot filled with glyphosate- or AMPA-treated soil). Following emergence, extra plants were thinned out to retain two plants per pot. Soil moisture was maintained at field capacity using Decagon 5TE soil moisture sensors (Decagon Devices, Pullman, WA) in representative pots for each species, and the amount of water required to maintain the soil moisture at field capacity was added daily.
Data Collection
The soil plant analysis development (SPAD) chlorophyll meter (SPAD-502; Minolta Camera Co. Ltd., Japan) was used to collect SPAD values as a diagnostic measure of plant growth from four fully expanded leaves starting from the top of the plant at 4 wk after planting. Plants were harvested 8 wk after planting to determine biomass accumulation. Shoot biomass was collected by cutting the plants close to the soil surface, then placing them in paper bags and drying them in an oven at 65 C to achieve a constant weight. Similarly, root biomass was collected by washing the roots carefully, then placing them in paper bags and drying them in an oven at 65 C. It is pertinent to mention that retaining 100% root biomass was not practical, and between 1% and 10% root biomass was likely lost during the washing process.
Seed Germination Study
As a follow-up to the greenhouse study, laboratory experiments were carried out to evaluate the impact of AMPA or glyphosate on seed germination of cereal rye, crimson clover, field pea, hairy vetch, and winter wheat. Seeds were soaked in Petri plates filled with 150 ml of a 0.7 g L–1 solution of AMPA or glyphosate (prepared by dissolving 0.7 g ae of glyphosate or AMPA in 1 L of water) (Chen et al. Reference Chen, Hathaway and Folt2004) and maintained at a day/night temperature of 22 to 24/15 to 17 C. The seeds were checked every day, and germination count was taken 8 to 10 d after beginning the study. The experiments were conducted separately for each cover crop species with AMPA or glyphosate in a completely randomized design with four replications and repeated twice.
Data Analysis
Data analysis was conducted in R, and the figures were developed using the package ggplot2 (R Core Team 2020). Data from multiple runs of the experiments were combined based on the ANOVA, considering run as a fixed factor. Following data visualization and model selection based on Akaike’s Information Criteria; linear regression models were used to analyze the data. Data from the seed germination study was subjected to ANOVA after checking the assumptions of normality using the Shapiro-Wilk test, and homogeneity of variance using Levene’s test in R. When ANOVA indicated that treatment effects were significant, mean separation was accomplished using Tukey test in R.
Results and Discussion
Experimental run-by-treatment interaction was not significant; therefore, data from multiple experimental runs were combined for analysis for greenhouse (pot) and laboratory (Petri plates) studies. Preliminary study of glyphosate or AMPA applied postemergence to 8- to 10-cm tall cereal rye, crimson clover, hairy vetch, field pea, and winter wheat confirmed the sensitivity to glyphosate and AMPA with 80% to 100% and 40% to 60% control, respectively, after 2 wk of application (data not shown). This strategy aimed at confirming that none of the cover crop species is glyphosate-resistant and at evaluating the activity of AMPA and glyphosate.
Greenhouse Study
The SPAD values of cereal rye, crimson clover, hairy vetch, field pea, and winter wheat grown in treatments including 3.5, 7, 14, 35, 70, and 105 mg ae of AMPA or glyphosate kg–1 of soil or nontreated soil were comparable, suggesting that increasing concentrations of AMPA or glyphosate had no impact on chlorophyll content (Table 2; Figure 1). Sun et al. (Reference Sun, Xu, Hao, An, Lu, Wu and Su2019) used a SPAD-502 chlorophyll meter to evaluate relative chlorophyll content in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) in response to bensulfuron-methyl residues in soil and reported that SPAD values were positively correlated to chlorophyll content. Linear regression model fit to the SPAD values of field pea grown on AMPA-treated soil, and cereal rye or winter wheat grown on glyphosate-treated soil had a P value < 0.05, though with no apparent biologically negative impact at the rates applied (Table 2; Figure 1). Glyphosate and/or AMPA have been reported to impair photosynthesis through degrading or inhibiting chlorophyll biosynthesis (Gomes et al. Reference Gomes, Smedbol, Chalifour, Hénault-Ethier, Labrecque, Lepage, Lucotte and Juneau2014; Mateos-Naranjo Reference Mateos-Naranjo, Redondo-Gómez, Cox, Cornejo and Figueroa2009; Zobiole et al. Reference Zobiole, Kremer, Oliveira, Constantin and Oliveira2011). Reduction in concentration of Mg, Mn (Cakmak et al. Reference Cakmak, Yazici, Tutus and Ozturk2009), and Fe (Marsh et al. Reference Marsh, Evans and Matrone1963) due to the chelating action of glyphosate following foliar application has been linked to the inhibition of the chlorophyll-biosynthetic pathway. Similarly, Serra et al. (Reference Serra, Nuttens, Larvor, Renault, Couée, Sulmon and Gouesbet2013) suggested that reduction of glycine, serine, and glutamate in AMPA-treated mouse-ear cress [Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh.] plants resulted in reduction of δ-aminolevulinic acid and chlorophyll content.
Table 2. Regression models fit on the soil plant analysis development (SPAD) values (an indirect measure of chlorophyll content in leaves used as a diagnostic of plant growth) in crimson clover, field pea, hairy vetch (dicot cover crop species), cereal rye, and winter wheat (monocot cover crop species) grown on soil treated with aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) or glyphosate under greenhouse conditions at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
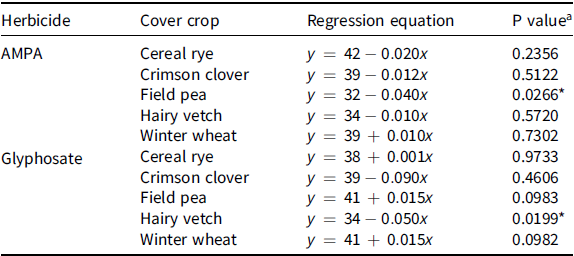
a
Asterisks (*) refer to P values < 0.05, meaning that null hypothesis
![]() $$\beta =0\;$$
is rejected and there is a significant relationship between variables in the linear regression model
$$\beta =0\;$$
is rejected and there is a significant relationship between variables in the linear regression model
![]() $$y = \alpha - \beta x$$
, where
$$y = \alpha - \beta x$$
, where
![]() $$y$$
is the response variable,
$$y$$
is the response variable,
![]() $$x$$
is the independent variable,
$$x$$
is the independent variable,
![]() $$\alpha $$
is an intercept, and
$$\alpha $$
is an intercept, and
![]() $$\beta $$
is the slope or coefficient of regression.
$$\beta $$
is the slope or coefficient of regression.
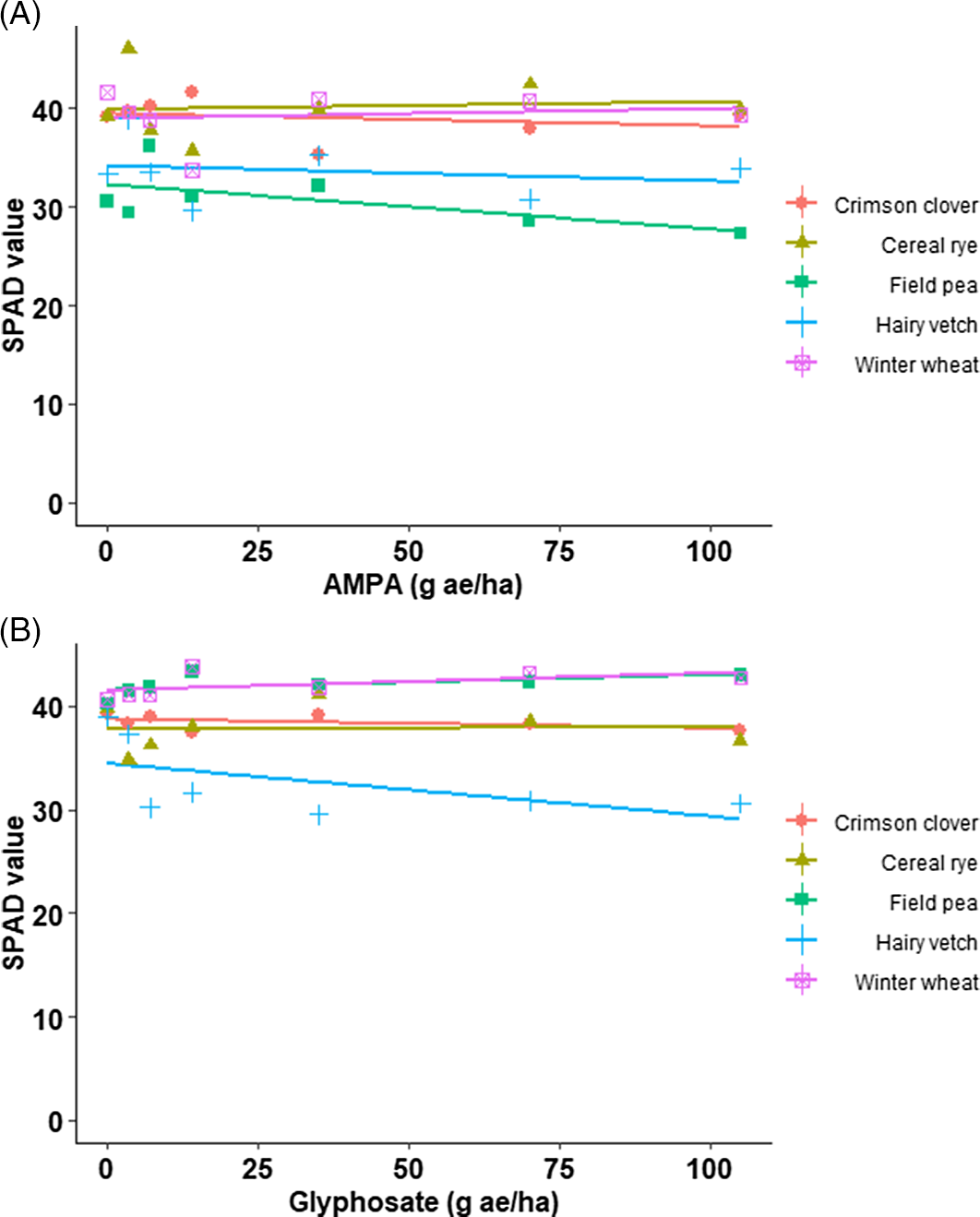
Figure 1. The soil plant analysis development (SPAD) value of crimson clover, field pea, hairy vetch (dicot cover crop species), and cereal rye and winter wheat (monocot cover crop species) grown on field soil treated with (A) aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) and (B) glyphosate under greenhouse conditions (22 to 24/15 to 17 C day/night temperature) at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
The shoot and root biomass of cover crop species were in the same range irrespective of AMPA or glyphosate rates and were comparable with the nontreated control (Table 2; Table 3; Figure 2 and Figure 3). For example, shoot biomass of crimson clover varied from 6 to 8 g with AMPA or glyphosate or the nontreated control (Figure 1). Blackshaw and Harker (Reference Blackshaw and Harker2016) estimated that glyphosate concentrations of 320, 150, and 350 mg kg–1 in sandy loam soil and 120, 80, and 90 mg kg–1 in loamy sand soil will be required for 20% shoot biomass reduction in wheat, field pea, and canola, respectively. Further, the same study predicted that AMPA concentrations of >500 mg kg–1 in sandy loam soil and 80, 40, and 20 mg kg–1 in loamy sand would be needed for 20% shoot biomass reduction in wheat, field pea, and canola, respectively. No cover crop injury was observed in current study, likely a result of greater glyphosate and/or AMPA adsorption in the soil due to higher clay content (40%) (Table 1). Glass (Reference Glass1987) concluded that glyphosate adsorption is positively correlated to the clay content in soil by observing a Freundlich adsorptive capacity (K) of 76 in Houston clay loam soil (52.6% clay) and 33 in Sassafras sandy loam soil (7.1% clay). Similarly, Sprankle et al. (Reference Sprankle, Meggitt and Penner1975) reported rapid inactivation of glyphosate in clay loam and muck soil compared to washed quartz sand. Other significant factors for glyphosate adsorption or availability in soil are phosphate concentration, pH, cation exchange capacity, soil organic matter, and soil moisture (Glass Reference Glass1987; Salazar and Appleby Reference Salazar and Appleby1982; Sprankle et al. Reference Sprankle, Meggitt and Penner1975).
Table 3. Regression models fit on above-ground and root biomass values in crimson clover, field pea, hairy vetch (dicot cover crop species), cereal rye, and winter wheat (monocot cover crop species) grown on soil treated with aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) or glyphosate under greenhouse conditions at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
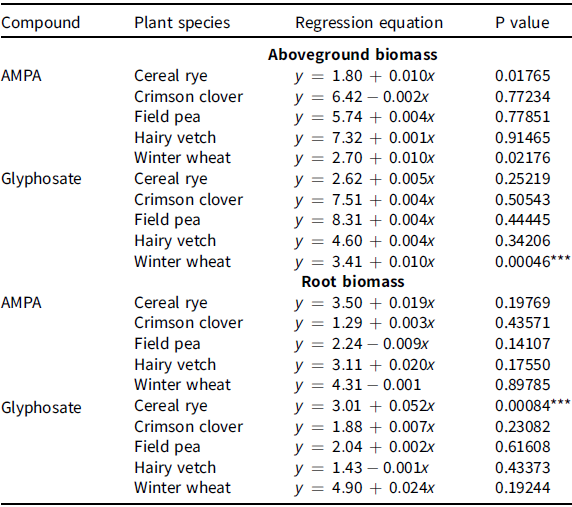
aAsterisks (***) refer to P values < 0.01, meaning that null hypothesis
![]() $$\beta =0\;$$
is rejected and there is a significant relationship between variables in the linear regression model
$$\beta =0\;$$
is rejected and there is a significant relationship between variables in the linear regression model
![]() $$y = \alpha - \beta x$$
, where
$$y = \alpha - \beta x$$
, where
![]() $$y$$
is the response variable,
$$y$$
is the response variable,
![]() $$x$$
is the independent variable,
$$x$$
is the independent variable,
![]() $$\alpha $$
is an intercept, and
$$\alpha $$
is an intercept, and
![]() $$\beta $$
is the slope or coefficient of regression.
$$\beta $$
is the slope or coefficient of regression.
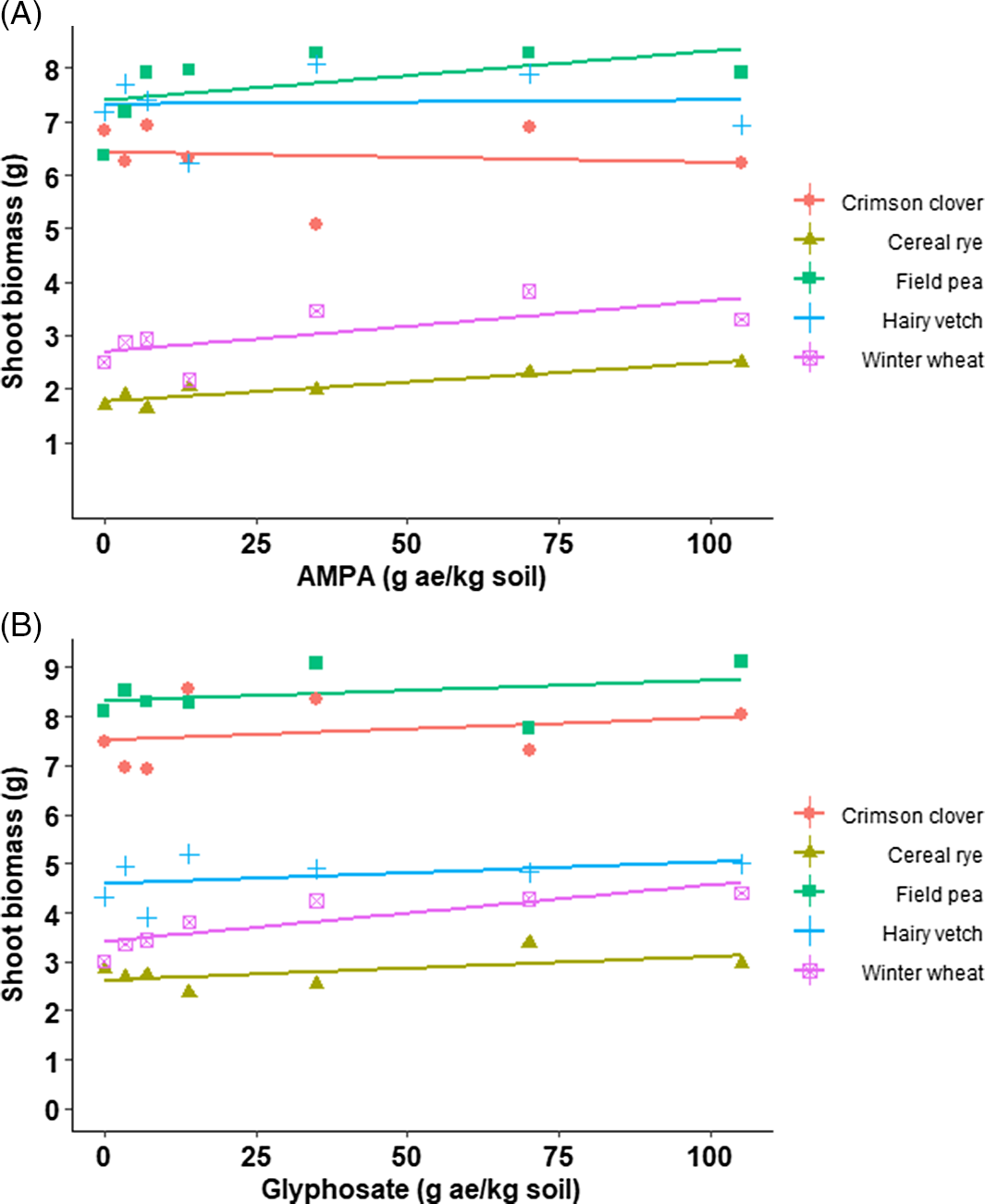
Figure 2. Shoot biomass (g) of crimson clover, field pea, hairy vetch (dicot cover crop species), and cereal rye and winter wheat (monocot cover crop species) grown on field soil treated with (A) aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) or (B) glyphosate under greenhouse conditions (22 to 24/15 to 17 C day/night temperature) at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
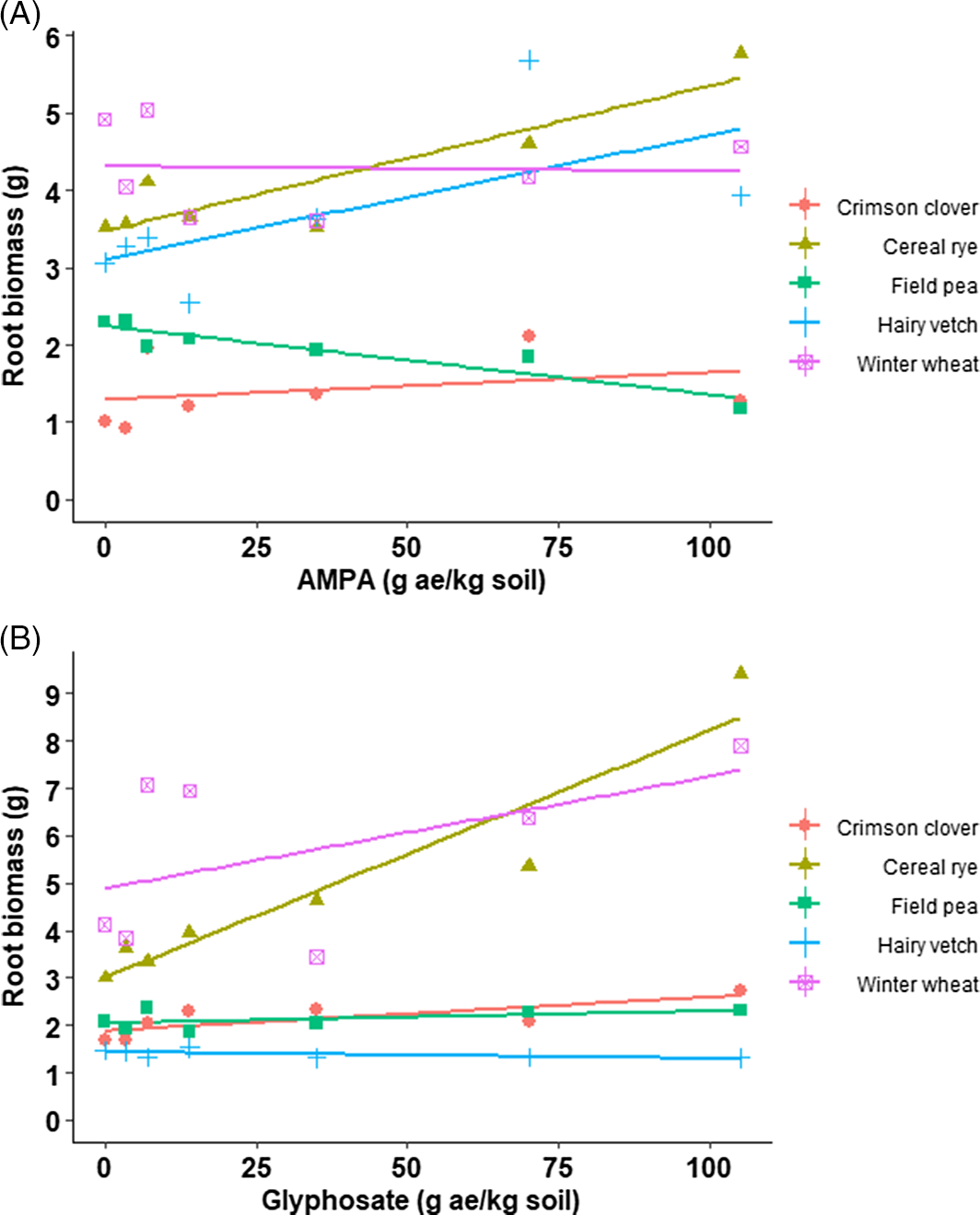
Figure 3. Root biomass (g) of crimson clover, field pea, hairy vetch (dicot cover crop species), and cereal rye and winter wheat (monocot cover crop species) grown on field soil treated with (A) aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) or (B) glyphosate under greenhouse conditions (22 to 24/15 to 17 C day/night temperature) at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
Seed Germination Study
Seed germination of crimson clover and field pea was comparable to the nontreated control, and there was no effect of soaking seeds in the 0.7 g L–1 glyphosate solution. Likewise, germination of all cover crop species soaked in the 0.7 g L–1 AMPA solution was comparable to the nontreated control (Table 4). Similarly, Segura et al. (Reference Segura, Bingham and Foy1978) reported no reduction in germination of Italian ryegrass [Lolium perenne L. ssp. multiflorum (Lam.) Husnot] and red clover (Trifolium pretense L.) with glyphosate at 1 or 2 kg ha–1 applied directly on seeds or on seeds covered with soil compared to the nontreated control. In contrast, germination of cereal rye, hairy vetch, and winter wheat seeds soaked in the 0.7 g L–1 glyphosate solution was reduced by 48%, 74%, and 45%, respectively, compared to the nontreated control (Table 4). Mondal et al. (Reference Mondal, Kumar, Haque and Kundu2017) reported 55% and 40% reduction in field pea seed germination with exposure to 3 and 4 mg L−1 glyphosate solution, respectively. Segura et al. (Reference Segura, Bingham and Foy1978) reported 6% and 23% reduction in Italian ryegrass seed germination and 19% and 20% reduction in germination of red clover with glyphosate at 4 kg ha–1 applied directly to covered and uncovered seeds, respectively, compared to the nontreated control. Grzesiuk et al. (Reference Grzesiuk, Dębski, Oknińska, Koczkodaj, Szwed and Horbowicz2018) revealed that glyphosate causes reduction in seed germination due to its interference with the level of indole-3-acetic acid, which is required for root and shoot development during germination and seedling growth in radish.
Table 4. Germination (%) of crimson clover, field pea, hairy vetch (dicot cover crop species) and cereal rye and winter wheat (monocot cover crop species) treated with a 0.7-g L–1 solution of aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) or glyphosate.
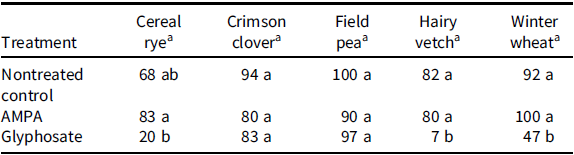
a Means within columns followed by the same letter are statistically not different, whereas means within columns with different letters are statistically different.
Practical Implications
The results of this study indicated that glyphosate and AMPA had no effect on emergence, growth, and biomass production of cover crop species, including cereal rye, crimson clover, hairy vetch, field pea, and winter wheat, in silty clay loam soil under greenhouse conditions. Germination of cereal rye, hairy vetch, and winter wheat seeds soaked in glyphosate solution was reduced by 48%, 74% and 45%, respectively, suggesting that under soil conditions, glyphosate was deactivated and remained unavailable for imbibition by the seed or root uptake. Similarly, Tesfamariam et al. (Reference Tesfamariam, Bott, Cakmak, Römheld and Neumann2009) reported lower toxicity on sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) grown on soil treated with glyphosate (55% to 70% biomass reduction) compared to soil containing residues released from decomposing glyphosate-treated perennial ryegrass (90% biomass reduction). The inactivation of glyphosate in soil has been attributed to adsorption on phosphate-binding sites and microbial degradation (Blake and Pallett Reference Blake and Pallett2018; Giesy et al. Reference Giesy, Dobson and Solomon2000; Sprankle et al. Reference Sprankle, Meggitt and Penner1975). Varying results have been reported in the literature about the effect of glyphosate residue and/or its metabolites, including AMPA on nontarget species as a result of dynamic interactions in soil influenced by diverse soil–physicochemical and biological properties (Piotrowicz-Cieślak et al. Reference Piotrowicz-Cieślak, Adomas and Michalczyk2010; Sacała et al. Reference Sacała, Demczuk, Grzyś and El-Ghany Hasaneen2011; Wagner et al. Reference Wagner, Kogan and Parada2003).
The results of this study showed no effect of glyphosate or AMPA residue in silty clay loam soil on any of the tested cover crop species under greenhouse conditions; however, seed germination of cereal rye, hairy vetch, and winter wheat was reduced when soaked in a 0.7 g L–1 solution of glyphosate. It must be noted, however, that glyphosate is a foliar-active herbicide applied before, during, or after planting glyphosate-resistant crops for weed control in the Midwest; therefore, it is unlikely that when cover crops are planted in the fall, a 0.7-g L–1 concentration of glyphosate will be present in silt clay loam soils to affect germination of cover crop species.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Greg Elmore of Bayer Crop Science for useful discussion and providing the glyphosate and AMPA used in this project. No conflicts of interest have been declared.










