To the Editor—Catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) are the most common healthcare-associated infection (HAI), accounting for one-third of infections acquired in hospitals in the United States.Reference Klevens, Edwards and Richards 1 The National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) methodology for detecting CAUTI employs active surveillance with standardized definitions applied by infection preventionists and is currently considered the gold standard for surveillance.Reference Horan, Andrus and Dudeck 2 However, NHSN surveillance typically requires utilizing trained infection preventionists to perform surveillance that is relatively labor intensive. Several studies evaluating the surveillance CAUTI using administrative codes from ICD-9-CM (International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification, code 996.64) revealed that the ICD-9 code performed poorly. Reference Cass, Kelly, Probst, Addy and Mckeown 3 – Reference van Mourik, van Duijn, Moons, Bonten and Lee 7 ICD-10-CM was implemented on October 1, 2015, 8 and to date, no study has evaluated it for the detection of CAUTI.
The purpose of this study was to compare CAUTI data abstracted via ICD-10-CM to NHSN surveillance data to determine the utility of the ICD-10 code as a surrogate for the NHSN CAUTI metric.
All patients medical records with the ICD-10-CM code related to CAUTI (T83.51XA, infection and inflammatory reaction due to indwelling urinary catheter, initial encounter) were retrieved via the Vizient (formerly University Healthcare Consortium) database at the University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics for the period October 1, 2015, through September 30, 2016. Data from NHSN surveillance were identified for the same period. Cases detected by either method were compared. Using NHSN as the gold standard, the sensitivity and positive predictive value of the ICD-10-CM code metric were calculated.
CAUTI was considered present on admission (POA) if the NHSN urinary infection criterion occurred during the following period: the day of admission to an inpatient location (calendar day 1), the 2 days before admission, or the calendar day after admission (calendar day 2). CAUTI was considered an HAI if the NHSN site-specific infection criterion occurred on or after calendar day 3 of admission to an inpatient location (where the day of admission was calendar day 1). 9 Infection events identified by ICD-10-CM were subsequently characterized as HAIs by applying the NHSN date criteria to more directly compare the 2 metrics.
We identified 46 CAUTI cases via active surveillance using the NHSN criteria. For the same period, there were 58 cases of CAUTI according to the ICD-10-CM metric. Of these 58 ICD-10-CM–coded cases, only 1 case (1.7%) was detected via NHSN criteria; all discordant cases were reviewed to confirm that they did not meet NHSN criteria. The sensitivity of the ICD-10-CM code metric to identify CAUTI was 1.7% (95% CI, 0.3%–9.1%) and the positive predictive value was 2.2% (95% CI, 0.4%–11.3%). When the POA cases were eliminated using the NHSN criteria, 41 cases of ICD-10 CAUTI remained. This adjustment led to a sensitivity of 2.4% (95% CI, 0.4%–12.6%) and positive predictive value of 2.2% (95% CI, 0.4%–11.3%) (Table 1).
TABLE 1 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes and NHSN CAUTI Criteria Analysis Results After Removal of ICD-10 Present on Admission CasesFootnote a
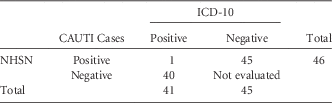
NOTE. ICD-10-CM, International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification; NHSN, National Health Safety Network; CAUTI, catheter-associated urinary tract infection.
a The sensitivity of the ICD-10-CM code metric to identify CAUTI was 2.4% (95% CI, 0.4% to 12.6%).
We further analyzed the CAUTI ICD-10-CM cases to determine why they did not meet NHSN criteria. Among these case patients, 1 of 58 (1.7%) did not have a urinary catheter present. Contaminated urine cultures (≥3 organisms present) were misclassified as infections in 6 of 58 cases (10.3%), and in 5 of 58 cases (8.6%), no urine culture was obtained. Lastly, in 15 of 58 cases (25.9%), bacteriuria was present (1 or 2 organisms), but the colony count did not reach the NHSN metric threshold of ≥100,000 CFU/mL.
The study period comprised 233,921 patient days. The CAUTI rate was 0.24 CAUTIs per 1,000 patient days using the ICD-10-CM metric; this rate was 0.18 when POA cases were eliminated. The CAUTI rate was 0.20 per 1,000 patient days using the NHSN metric.
The NHSN CAUTI metric and the ICD-10-CM CAUTI-like code produce widely discrepant results. Even when ICD-10 cases that were POA were removed to better align with the NHSN criteria, the sensitivity of the ICD-10 metric was only 2.4%. Importantly, no patient safety indicator from AHRQ is available for CAUTI as there is for central venous catheter-related bloodstream infection.Reference Marra, Jansen and Edmond 10 This was the primary reason that we used the administrative code (ICD-10-CM) to compare to NHSN surveillance data for detecting CAUTI.
Our results demonstrate that updating ICD-9-CM with more codes to produce ICD-10-CM did not improve the ability of administrative data to identify CAUTIs. The date of the event is an important element used to meet an NHSN site-specific infection criterion, including CAUTI, and that is one reason that administrative data fail to accurately identify cases of HAI.
This study has several limitations. First, it was performed in a single medical center. In addition, we did not review the negative cases via either method, and we assumed that traditional surveillance (NHSN) is the gold standard surveillance method. Therefore, it was not possible to calculate the specificity because our aim was to compare only NHSN and ICD-10-CM CAUTI identified cases. Given that CAUTI is a relatively rare event, we can assume that the specificity of the ICD-10-CM metric is high.
In summary, we found that ICD-10-CM has an extremely low sensitivity for detecting CAUTI cases; it failed to detect 98.3% of the infections at our institution. Almost all cases identified via ICD-10-CM did not fulfill the NHSN criteria. Thus, administrative coding for this HAI is not a useful tool for use as a surveillance method.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Financial support: No financial support was provided relevant to this article.
Potential conflicts of interest: All authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.



