Introduction
Reintroductions are attempts to restore locally extinct populations. Ultimately, reintroduced populations should demonstrate demographic and behavioural processes comparable to those of native populations. However, many reintroduction attempts have failed (Armstrong & Seddon, Reference Armstrong and Seddon2008) and recently established reintroduced populations suffer from demographic and behavioural disequilibrium. For example, founders may exhibit altered behaviours because of previous captivity or inexperience in the wild, which may decrease their ability to survive or reproduce (Sarrazin & Legendre, Reference Sarrazin and Legendre2000). Assessments of reintroduction are under-documented and monitoring needs to be improved (Sutherland et al., Reference Sutherland, Armstrong, Butchart, Earnhardt, Ewen and Jamieson2010). Evaluation preceding release would help in the design and optimization of the cost-effectiveness of reintroduction release strategies (Schaub et al., Reference Schaub, Zink, Beissmann, Sarrazin and Arlettaz2009; Sutherland et al., Reference Sutherland, Armstrong, Butchart, Earnhardt, Ewen and Jamieson2010).
Most reintroductions are of large vertebrates with high dispersal abilities (Seddon et al., Reference Seddon, Soorae and Launay2005), making them particularly prone to leave the release area (Le Gouar et al., Reference Le Gouar, Mihoub, Sarrazin, Ewen, Armstrong, Parker and Seddon2011; Mihoub et al., Reference Mihoub, Robert, Le Gouar and Sarrazin2011). This can generate conflicts with humans (Thirgood & Redpath, Reference Thirgood and Redpath2008) or suboptimal habitat selection (Steffens et al., Reference Steffens, Seddon, Mathieu and Jamieson2005). Suboptimal habitat selection can diminish the growth and viability of the reintroduced population (e.g. Mihoub et al., Reference Mihoub, Le Gouar and Sarrazin2009). Thus, habitat use has to be assessed to project the long-term viability of reintroduced populations. Projections of the habitat use of a species can facilitate management actions (e.g. prevention of human-related conflicts and adequate design of protected areas) and provide an evaluation of a programme's success and information for enhancing monitoring schemes.
Relating species occurrence to the ecological features of the environment provides opportunities to determine a species’ requirements and spatial distribution. It also offers analytical ways to manage biological resources. Geographical modelling offers powerful tools to estimate habitat suitability and predict distribution ranges (Seoane et al., Reference Seoane, Bustamante and Diaz-Delgado2004). Habitat suitability models calibrated with presence–absence data may not be reliable when absences do not reflect unsuitable habitats (Engler et al., Reference Engler, Guisan and Rechsteiner2004), and habitat suitability models using presence-only data are more appropriate at low densities (e.g. in reintroductions; Hirzel et al., Reference Hirzel, Posse, Oggier, Crettenands, Glenz and Arlettaz2004).
We examined the nesting habitat of a Eurasian black vulture Aegypius monachus population reintroduced in France, using habitat suitability modelling based on the presence-only approach and considering temporal ordering of nest site establishment, conducting spatial validation to provide robustness. We aimed to (1) determine nesting habitat features of this reintroduced population, (2) compare these features to those of natural populations of the species in Europe, (3) provide conservation management recommendations based on the habitats predicted to be suitable for the species in this region, and (4) indicate whether the increasing number of nest locations since the beginning of the reintroduction affect the accuracy of habitat suitability models to predict locations of subsequent nests. If chronologically based predictions are reliable over a large spatial extent, this approach could be useful for other reintroduction programmes.
Species and study area
The Eurasian black vulture is one of the largest raptors in the western Palaearctic but has declined across its entire range, from Spain in the west to Mongolia and Russia in the east, and is categorized as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List (BirdLife, 2012). Black vultures are scavengers that mainly inhabit rocky and mountainous forested zones (Cramp & Simmons, Reference Cramp and Simmons1980; Moran-Lopez et al., Reference Moran-Lopez, Sanchez-Guzman, Costillo Borrego and Villegas Sanchez2006a). Although they breed on cliffs in non-forested areas of Central Asia, they usually build their nests on the tops of large trees (Poirazidis et al., Reference Poirazidis, Goutner, Skartsi and Stamou2004; Gavashelishvili et al., Reference Gavashelishvili, McGrady and Javakhishvili2006) and defend an exclusive territory of 50 m radius around the nest (Cramp & Simmons, Reference Cramp and Simmons1980).
The Grands Causses region of southern France is a mountainous karstic area in which rivers have created deep canyons separating large limestone plateaus. The landscape includes flat open areas and abrupt cliffs bordered with steep forested slopes, offering habitat for both foraging and nesting for many raptor species.
Two other vulture species inhabit this region: a reintroduced population of griffon vultures Gyps fulvus (c. 800 individuals) and a few breeding native Egyptian vultures Neophron percnopterus. Before the reintroduction, black vultures in the Grands Causses were last recorded at the beginning of the 20th century, probably coinciding with the extirpation of the species from France (Eliotout et al., Reference Eliotout, Lécuyer and Duriez2007) as a result of poisoning and shooting.
A total of 53 juvenile and immature black vultures were released in the region (Fig. 1) from 1992 to 2004. Since then, two other programmes to reintroduce black vultures have been initiated in southern France, in the French Alps and in the Verdon region in 2004 and 2005, respectively. The first pairs bred in 1996 in the Grands Causses (Eliotout et al., Reference Eliotout, Lécuyer and Duriez2007), and we used data on all 39 black vulture nests discovered in this region from 1996 to 2008. A 225 km2 area has been regularly surveyed since the reintroductions began, with particular attention paid to locations where nests were detected post-1996. Because of the low number of observers, rugged landscape and large spatial extent the whole area could not be monitored but wider surveys with more volunteers were conducted twice per year during the breeding season. Because of the difficulties of detecting nests, some may have been overlooked. We did not consider pairs that defended territories without building a nest. Because of the high rate of ring loss, individual identification of breeders was not systematic.

Fig. 1 Map of suitable nesting habitat for the black vulture Aegypius monachus in the Grands Causses (the black circle indicates the release site). Predictions result from the Maxent model built with all 39 nest-site locations as training data and 10,000 background points (see text for further details). The shaded rectangle on the inset indicates the location of the main map in southern France.
Methods
Selection of spatial scale and environmental variables
The selection of ecological factors for the habitat suitability modelling was based on knowledge of the species. In Europe black vultures seem to select their nesting sites based on the orientation of the slope (e.g. north facing) and on the presence of large trees such as Juniperus (Cramp & Simmons, Reference Cramp and Simmons1980; Fargallo et al., Reference Fargallo, Blanco and Soto-Largo1998; Poirazidis et al., Reference Poirazidis, Goutner, Skartsi and Stamou2004; Gavashelishvili et al., Reference Gavashelishvili, McGrady and Javakhishvili2006; Moran-Lopez et al., Reference Moran-Lopez, Sanchez, Costillo, Corbacho and Villegas2006b). We used four topographic variables (elevation, slope, slope orientation, mean exposition to sun; from the Institut Géographique National) and 18 variables for vegetative land cover, of which 14 concerned forest (Table 1). Vegetation data were for 1992–1994, from the Inventaire Forestier National. All maps have grid cells of 50 × 50 m, which matches the 50 m radius of a nest territory. We considered a study area of 80 × 80 km centred on the release site, although all nest records up to 2008 were located within a radius of 15 km of the release site.
Table 1 Description of the vegetation cover variables used to model the ecological features of nesting sites of black vultures Aegypius monachus reintroduced in the Grands Causses, France (Fig. 1).
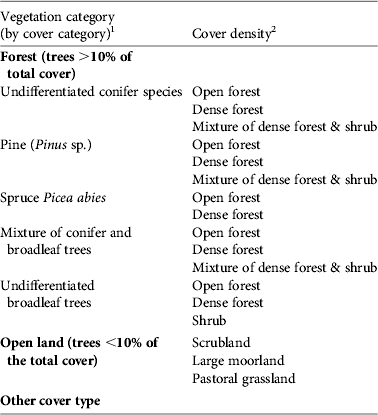
1 A dominant tree species or taxon was defined as one that constituted ⩾ 75% of canopy cover within a grid cell. A mixture of tree taxa indicates that all taxa constitute <75% of cover within a grid cell.
2 Open forest, tree cover is 10–40% of a grid cell; dense forest, tree cover ⩾ 40% of a grid cell; shrub, young trees 10–30 years old
Habitat suitability modelling
We built habitat suitability models based on presence-only data for black vulture nests, using Maxent (Phillips et al., Reference Phillips, Anderson and Schapire2006). To identify habitat suitability in presence-only habitat suitability models, environmental characteristics of species locations can be compared to those of locations where the species could really be absent (pseudo-absence data; Engler et al., Reference Engler, Guisan and Rechsteiner2004) or to the entire available area (Calenge et al., Reference Calenge, Dufour and Maillard2005). The degree of accuracy to which habitat suitability models predict species occurrence depends, for example, on the number of occurrence records (Pearson et al., Reference Pearson, Raxworthy, Nakamura and Peterson2007) or on the way pseudo-absences are selected (VanDerWal et al., Reference VanDerWal, Shoo, Graham and William2009). Rather than using pseudo-absences Maxent uses random points sampled from the whole background (Phillips et al., Reference Phillips, Anderson and Schapire2006). The algorithm used by Maxent predicts habitat suitability with a high degree of reliability, even from small data sets (Pearson et al., Reference Pearson, Raxworthy, Nakamura and Peterson2007).
The performance of habitat suitability modelling is commonly measured with validations made on independent locations using a part of the data (training points) to calibrate the model, which is then compared to the remaining data (test points). Validation is usually done with training points randomly extracted from the data set (Araujo & Pearson, Reference Araujo and Pearson2005) or spatially stratified subsamples (Peterson et al., Reference Peterson, Papes and Eaton2007). We performed temporal validation based on chronologically stratified subsamples. We split the data according to the chronological colonization of nest sites, to construct four different models. The first used the first 10 nests for 1996–2000 as training data and the 29 nests for 2001–2008 as test data. The second used the 21 nests for 1996–2004 as training data and the 18 nests for 2005–2008 as test data. The third model was built with the 33 nest sites for 1996–2006, with the six remaining nests for 2007–2008 as test data. The fourth model used all nest sites as training data to maximize the precision of the final predictions (validation was not possible with this model).
Predictions relying exclusively on temporal validation could potentially have problems with autocorrelation and therefore we performed spatial validation to ensure robustness. Similar to Peterson et al. (Reference Peterson, Papes and Eaton2007) we split the data set into four spatially stratified subsamples (corresponding to spatial quadrants), each containing a comparable number of nests. Spatial validations used nests of two quadrants as training data and nests of the two remaining quadrants as test data (Peterson et al., Reference Peterson, Papes and Eaton2007). We considered all combinations of paired quadrants as the training data set. Although a nest site could have been used for several years, its location was only used once in both temporal and spatial validation procedures.
We used the Maxent default values proposed by Phillips & Dudik (Reference Phillips and Dudik2008), except for the background points. A high number of background points compared to presence records can over-fit predictions (VanDerWal et al., Reference VanDerWal, Shoo, Graham and William2009) and therefore we used the 10,000 default value but also ran the validations with 1,000 and 100 background points (providing orders of magnitude closer to the number of nest locations). Model performances were evaluated using the area under the operating receiver curve (AUC) criterion. However, the AUC has been criticized (Lobo et al., Reference Lobo, Jiménez-Valverde and Real2008; Peterson et al., Reference Peterson, Papes and Eaton2007) and we resorted to additional criteria: the omission rate, the fractional predicted area and associated statistics (Anderson et al., Reference Anderson, Gomez-Laverde and Peterson2002). The omission rate measures the proportion of the test data not predicted by models parameterized with the training data. The fractional predicted area represents the proportion of the area predicted by models regarding the entire background. Statistics were based on the maximum sensitivity plus specificity approach (Liu et al., Reference Liu, Berry, Dawson and Pearson2005) and considered the null hypothesis that test points were predicted no better than random, using 1-sided probabilities. We also implemented jacknife validations to assess the contribution of each variable to predictions when the variable was considered alone (Phillips et al., Reference Phillips, Anderson and Schapire2006).
Results
Both temporal and spatially based habitat suitability models showed a good fit to the data (AUC scores were 0.97–0.99 and 0.96–0.99, respectively; Tables 2 & 3) and overall robust predictive performances whatever the number of presence and background points (Tables 2 & 3). Irrespective of the number of training and background points, environmental variables driving selection of nest site by black vultures were slope, vegetation cover and, to a lesser extent, elevation (Tables 2 & 3). The contributions of the environmental variables in the temporal validation were consistent with those of the spatial validation (Tables 2 & 3). Up to 80% of nest sites can be predicted when considering the contribution of both slope and vegetation (81.2–99.9%, Table 2). Undifferentiated conifer forests, dense forests of pine trees, and mixtures of dense forest and shrub composed of broadleaf trees and conifers offered suitable conditions (contribution of each variable to predictions when taken alone: open conifer forest = 0.9; dense conifer forest = 0.83; mixture of dense forest and shrub = 0.88; dense forests of pine trees = 0.89; mixture of dense forest and shrub of both broadleaf trees and conifers = 0.83). Other vegetation types, including spruce trees and broadleaf forests, were not chosen as nest sites. Black vultures preferentially selected steep slopes (increasing probabilities of presence with increasing slope, reaching a plateau at 30°; Fig. 2a) and altitudes of 750–800 m (Fig. 2b). Slope orientation and sunshine did not contribute more than 3.9 and 2.4%, respectively, to nest selection (Table 2).

Fig. 2 Response curves of black vulture nest site locations with (a) slope and (b) elevation (relative contribution of the variable to predictions when the variable is considered alone), from the habitat suitability model (see text for further details).
Table 2 Results of habitat suitability models for the nesting habitat of black vultures reintroduced in the Grands Causses (Fig. 1), constructed using Maxent with presence-only data for 10, 21, 33 or 39 nest site locations (i.e. so-called temporal validations that reflect the increase in the number of nests with time) and 100, 1,000 or 10,000 background points.
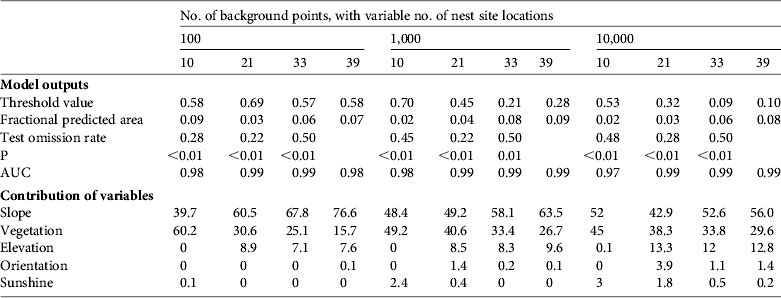
Table 3 Results of habitat suitability models for the nesting habitat of black vultures reintroduced in the Grands Causses (Fig. 1), constructed using Maxent with presence-only data for nest site locations in the four training areas considered (i.e. so-called spatial validations: north, n = 9; south, n = 10; east, n = 10; west, n = 10) and 100, 1,000 or 10,000 background points.
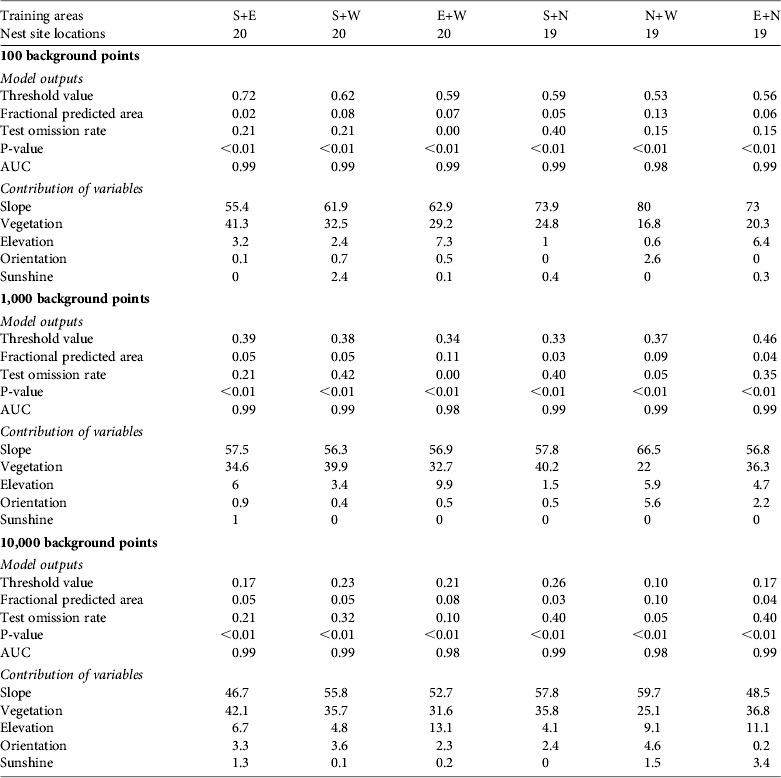
The accuracy of the predictions based on temporal validation varied with the number of presence points used as training data. The fractional predicted area indicated a slight increase with an increased number of nest sites while not being sensitive to the number of backgrounds points. The omission rate was not sensitive to the number of background points but there were contradictory patterns with the number of nest sites (decreasing from 10 to 21 nest sites and increasing from 21 to 33 nest sites; Table 2). Fractional predicted area and test omission rate of the spatial validation did not exhibit clear and consistent patterns but overall trends suggested that fractional predicted area decreased and omission rate increased as the number of background points increased.
Among temporal-based models with 100 background points the one based on 10 nest site locations seemed to strongly over-represent the contribution of vegetation cover, whereas models built with 21–39 nest sites overestimated the influence of slope. The spatial validation also indicated a high variance in omission rates (Table 3), partly because nests in the northern and southern quadrants poorly predicted nests in western and eastern quadrants, whereas nests in western and eastern quadrants showed low omission rates in northern and southern quadrants. We detected a decrease in the variance of the relative contribution of environmental variables when the number of nest locations and the number of background points increased. Using 2-dimensional aerial imagery the surface area of canyons with steep slopes is underrepresented compared to plateau areas, and therefore differences in slope or tree cover between a few presence locations can be buffered when a much higher number of random background points are sampled in plateau areas. We only present the habitat suitability map of black vulture nests from the most representative model, accounting for all presence locations (i.e. 39 nests) with 10,000 background points (Fig. 1).
Discussion
Features of nest sites
Defining all available suitable habitats for a species is not straightforward (Pearson et al., Reference Pearson, Raxworthy, Nakamura and Peterson2007), especially for small populations. Although interpolation generally facilitates good predictive power, extrapolation to predict species’ distributions in unsampled regions is difficult (Peterson et al., Reference Peterson, Papes and Eaton2007). Although habitat suitability models calibrated with presence–absence data usually give more robust information than those using presence-only data (Elith & Graham, Reference Elith and Graham2009), the assumption that absence data indicate unsuitable habitat may be partly incorrect; e.g. when the number of occurrences is low because of low detection probabilities (Pearson et al., Reference Pearson, Raxworthy, Nakamura and Peterson2007), low population density (Hirzel et al., Reference Hirzel, Posse, Oggier, Crettenands, Glenz and Arlettaz2004), high movement abilities in vagile species or extinction–colonization dynamic processes (Engler et al., Reference Engler, Guisan and Rechsteiner2004). In reintroductions population size is typically low and founders do not have experience of the local environmental conditions. The first founders released cannot copy the behaviour of wild congeners and reintroduced populations may face ecological traps if founders select sub-optimal habitats (Mihoub et al., Reference Mihoub, Le Gouar and Sarrazin2009). Therefore, absences may not reflect avoidance of unsuitable habitat and, conversely, presence may not indicate optimal habitat selection. Using presence-only data is more conservative in such situations.
Although initially founded by young birds without any breeding experience, the chosen nesting habitat of the reintroduced population of black vultures in the Grands Causses was similar to that of natural populations. In Europe, black vultures preferentially nest on large trees growing on steep slopes (Poirazidis et al., Reference Poirazidis, Goutner, Skartsi and Stamou2004; Gavashelishvili et al., Reference Gavashelishvili, McGrady and Javakhishvili2006; Moran-Lopez et al., Reference Moran-Lopez, Sanchez-Guzman, Costillo Borrego and Villegas Sanchez2006a). Slopes may be advantageous because of their updraughts (Cramp & Simmons, Reference Cramp and Simmons1980), and provide protection against predation or disturbances (Donázar et al., Reference Donázar, Blanco, Hiraldo, Soto-Largo and Oria2002; Moran-Lopez et al., Reference Moran-Lopez, Sanchez-Guzman, Costillo Borrego and Villegas Sanchez2006a). Every nest recorded in the Grands Causses was on Scots pine Pinus sylvestris, although forests of other pine tree species and broadleaf trees were available and could offer suitable nest support (e.g. Juniperus sp., Gavashelishvili et al., Reference Gavashelishvili, McGrady and Javakhishvili2006; Pinus sp., Poirazidis et al., Reference Poirazidis, Goutner, Skartsi and Stamou2004; Moran-Lopez et al., Reference Moran-Lopez, Sanchez-Guzman, Costillo Borrego and Villegas Sanchez2006a). Tree species and density appear to be of secondary importance if the size and height of trees are large enough (Fargallo et al., Reference Fargallo, Blanco and Soto-Largo1998; Poirazidis et al., Reference Poirazidis, Goutner, Skartsi and Stamou2004). Open lands such as pastoral grasslands or scrublands were not used for nesting. Preference for a particular tree species could be a result of selection of the topography where trees grow. Correlation between slope and vegetation cover could arise from the physical requirements of tree species, such as sunshine, soil composition or water retention. Spatial segregation of tree species with respect to topography could explain the attractiveness of junipers growing on steep slopes for nest sites in Georgia, where oaks available in flat areas were not used (Gavashelishvili et al., Reference Gavashelishvili, McGrady and Javakhishvili2006). In addition, black vulture pairs start constructing their nests in winter (i.e. early January in the Grands Causses, Eliotout et al., Reference Eliotout, Lécuyer and Duriez2007), when deciduous trees do not bear any leaves. Coniferous leaves can provide information on the vitality of trees and enhance selection of these species.
Elevations of 750–800 m were preferred in the Grands Causses but elevation is probably linked to local topography rather than to intrinsic species-specific requirements. Sunshine and slope orientation appeared to be of low importance. Black vultures mainly nested on slopes of the Jonte and Tarn canyons (Fig. 1), which have different orientations. In the study area, heterogeneity in elevation, air currents or sunshine exposure may hinder identification of preferences for selection patterns of these abiotic variables.
Slight changes in nesting habitat characteristics with time and/or population size may explain increased fractional predicted area and relatively high omission rates (see next section) and suggest (1) negative density-dependence, with sites of highest quality being selected first, (2) selection of alternative but equally suitable environmental conditions, or (3) shifts towards more suitable habitats as a result of increasing experience. Breeding success remained low from 1996 to 2006 (0.46 ± SD 0.29, n = 84, Eliotout et al., Reference Eliotout, Lécuyer and Duriez2007). Since 2005, however, 17 nests have been colonized and breeding success was 0.68 ± SD 0.22 (n = 63) during 2005–2009, which is comparable to natural Spanish populations (e.g. 0.68, n = 1,629, for the whole of Spain in 2006, De la Puente et al., Reference De la Puente, Moreno-Opo and Del Moral2007; 0.70 ± SD 0.14, n = 390, Moreno-Opo et al., Reference Moreno-Opo, Guil, El Khadir, Oria, Soria and Guzmán2012). Increasing breeding skills and selection of better habitats are undistinguishable, and therefore we are not able to distinguish between a progressive use of alternative but equally suitable habitat combined with increasing breeding skills and a shift towards better habitats. Nevertheless, the habitat suitability identified in this study represents reliable predictions.
Predictive reliability of habitat suitability models
Extrapolating suitable habitats from a small number of geographically localized occurrences is risky (Peterson et al., Reference Peterson, Papes and Eaton2007). Projections of black vulture nesting habitats from models based on chronological nest settlement were robust to the number of presence locations and provided a good fit to the data once 10 pairs had established following release. Nevertheless, the fractional area predicted as suitable increased with the number of nest sites, and omission rates were relatively high independent of the number of nest locations or background points, suggesting that old nests may differ slightly from newly colonized ones. Increasing the number of nests used as training points allowed us to describe the potential range of suitable conditions better, and increased the area predicted as suitable. However, the low sample size did not allow depiction of all the diversity in nest-site features and failed to decrease the omission rate for nests with new characteristics. Nevertheless, predictions obtained from a reduced number of training points were at worst conservative and were consistent with black vulture nest features. Increasing the number of background points could partly buffer this effect by increasing the relative marginality of the main contributing variables compared to the entire study area.
The low effect of the number of locations on predictive performance could result from artefacts from spatial autocorrelation or pseudo-replication. Black vultures are not strictly colonial but form loose-knit colonies (Poirazidis et al., Reference Poirazidis, Goutner, Skartsi and Stamou2004). Such conspecific attraction can generate problems of spatial autocorrelation if new nests are established close to old ones, which probably means in similar habitats. All nest records in the Grands Causses up to 2008 were located within a radius of 15 km of the release site; i.e. within a small area relative to the entire study area. Pseudo-replication may over-represent the habitat features of the nests of a few breeding pairs. As we used multi-year observations with no reliable individual identification of breeding birds, a pair nesting at different locations could be represented more than once in the data but these locations would be considered as independent. However, spatial validation indicated high omission rates, with high variance independent of the number of locations, suggesting heterogeneity among quadrants and corroborating the fact that habitat features show slight differences between nests. In addition, up to 18 different nests were used simultaneously and were thus occupied by different pairs; i.e. at least 46% of the nests used in the analysis were independent locations. If not avoided, problems associated with pseudo-replication were strongly reduced.
Management recommendations in the Grands Causses
The habitat suitability map indicated a large extent of areas suitable for nesting in the Grands Causses, mainly north and east of the current nesting area. To date, the availability of nesting sites is not a limiting factor for this population. The dependence of nest-site locations on feeding stations and foraging areas could restrict the extent of suitable habitat but this does not seem to be a major constraint; some black vultures have not been seen for a decade on feeding stations but have been identified from their individual rings as breeders, indicating that these individuals foraged and fed elsewhere in the region.
Predictions of areas suitable for nesting can guide landscape management for the species. In the Grands Causses most forested areas are dedicated to productive forestry, game hunting or outdoor leisure activities detrimental to the persistence of wildlife populations (Marshall et al., Reference Marshall, White and Anke2007). Although human disturbance is difficult to quantify, these factors negatively affect the breeding success of black vultures, particularly during pre-laying and laying periods (Donázar et al., Reference Donázar, Blanco, Hiraldo, Soto-Largo and Oria2002; Poirazidis et al., Reference Poirazidis, Goutner, Skartsi and Stamou2004; Gavashelishvili et al., Reference Gavashelishvili, McGrady and Javakhishvili2006; Moran-Lopez et al., Reference Moran-Lopez, Sanchez-Guzman, Costillo Borrego and Villegas Sanchez2006a). Despite the acceptance of vulture species in this region, resulting in low risks of hunting or poisoning, unintentional perturbations can still be a threat.
Divergence in the use of natural territories by humans and wildlife can be buffered by designing appropriate management strategies. Identifying suitable areas for black vulture nests can prevent negative effects of human activities. For example, tree felling can be timed to take place during periods that are less harmful for black vulture reproduction; i.e. during late autumn and winter. Similarly, encouraging selective logging rather than clear felling could help reconcile economic activities with the conservation of this raptor. Nest selection by black vultures occurs between January and February, when most human activities (tourism or outdoor sporting practices) are low (Eliotout et al., Reference Eliotout, Lécuyer and Duriez2007). Consequently, black vultures could establish their nests in places that will suffer from disturbance that is not perceptible when the nest site is selected. Dialogue and cooperation between conservationists, forestry managers and practitioners of outdoor leisure activities would provide opportunities for negotiating the use of unprotected areas in both time and space.
Acknowledgements
Population monitoring was carried out by the Ligue pour la Protection des Oiseaux (BirdLife France)–Mission Rapaces, the Parc National des Cévennes and volunteers. We particularly thank C. Boléat, T. David, B. Descaves, I. Malafosse and J.-L. Pinna for help with fieldwork. Financial support was provided by the National Restoration Plan for the black vulture and by the French Ministry of Research. We thank M. Duprez from the Inventaire Forestier National for facilitating data acquisition, and J.-P. Moussus for corrections and helpful comments. We dedicate this article to the memory of our friend and colleague Bertand Eliotout who died tragically in a car accident in 2009.
Biographical sketches
Jean-Baptiste Mihoub's research activities mainly focus on demography and animal behaviour with respect to translocations. Frederic Jiguet is an ornithologist. He has carried out research on many aspects of bird ecology, in particular on bird communities facing global change. Philippe Lécuyer and Bertrand Eliotout have played key roles in the reintroduction and monitoring of vultures in the Grands Causses. François Sarrazin carries out research on reintroduction biology and has been involved in the recovery of vultures in France for more than 20 years.







