Given a positive definite covariance matrix \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\widehat{\Sigma }$$\end{document}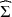 of dimension n, we approximate it with a covariance of the form \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$HH^\top +D$$\end{document}
of dimension n, we approximate it with a covariance of the form \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$HH^\top +D$$\end{document}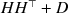 , where H has a prescribed number \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$k<n$$\end{document}
, where H has a prescribed number \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$k<n$$\end{document}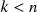 of columns and \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$D>0$$\end{document}
of columns and \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$D>0$$\end{document}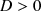 is diagonal. The quality of the approximation is gauged by the I-divergence between the zero mean normal laws with covariances \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\widehat{\Sigma }$$\end{document}
is diagonal. The quality of the approximation is gauged by the I-divergence between the zero mean normal laws with covariances \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\widehat{\Sigma }$$\end{document}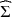 and \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$HH^\top +D$$\end{document}
and \documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$HH^\top +D$$\end{document}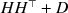 , respectively. To determine a pair (H, D) that minimizes the I-divergence we construct, by lifting the minimization into a larger space, an iterative alternating minimization algorithm (AML) à la Csiszár–Tusnády. As it turns out, the proper choice of the enlarged space is crucial for optimization. The convergence of the algorithm is studied, with special attention given to the case where D is singular. The theoretical properties of the AML are compared to those of the popular EM algorithm for exploratory factor analysis. Inspired by the ECME (a Newton–Raphson variation on EM), we develop a similar variant of AML, called ACML, and in a few numerical experiments, we compare the performances of the four algorithms.
, respectively. To determine a pair (H, D) that minimizes the I-divergence we construct, by lifting the minimization into a larger space, an iterative alternating minimization algorithm (AML) à la Csiszár–Tusnády. As it turns out, the proper choice of the enlarged space is crucial for optimization. The convergence of the algorithm is studied, with special attention given to the case where D is singular. The theoretical properties of the AML are compared to those of the popular EM algorithm for exploratory factor analysis. Inspired by the ECME (a Newton–Raphson variation on EM), we develop a similar variant of AML, called ACML, and in a few numerical experiments, we compare the performances of the four algorithms.