Introduction
It is often taken for granted that glacial erosion was the main land-forming agent in formerly glaciated areas. However, in some cases when the large-scale forms of the bedrock are examined, it is impossible to see any patterns that relate to glacial-flow patterns, with the exception of some great lakes, fjords and lake basins along mountain fronts. If the landform categories are examined, with respect to saprolite remnants and cover rocks, another picture can emerge (Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergström, 1995a, Reference Lidmar-Bergströmb). Wherever the Precambrian basement emerges from below lower Paleozoic cover rocks on the Baltic and Canadian Shields, it is extremely flat. On the other hand, where it emerges from below Jurassic and Cretaceous cover rocks, it is hilly with a relative relief up to more than 200 m. Remnants of deep (<60 m thick) kaolinitic saprolites are abundant in close connection with the covers in southern Sweden. The relief is etched out along fractures and other zones easily affected by deep weathering; a structural and lithological control is obvious in these areas, which are labelled exhumed sub-Mesozoic etch surfaces (Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergström, 1988, Reference Lidmar-Bergström1989). A third type of relief exists, plains with residual hills which, as far as we know, have not been protected by any cover rocks or may have had a short-lived Eocene cover at certain elevations. The development of these three types of topographies seems to be related to uplift and exposure during specific Phanerozoic periods, interrupted by long intervals with subsidence and covering of the forms in the basement. The present distribution seems to be the result of Tertiary uplift events (Reference Lidmar-Bergström, Smith, Whalley and WarkeLidmar-Bergström, 1999).
In southeastern Sweden, an exhumed sub-Cambrian surface rises gently from near sea level, close to the coast, to 300 ma.s.l., 75 km inland, with a relative relief below 20 m within the intact parts. The exhumed sub-Cambrian peneplain also occupies large parts of central Sweden. It is more or less faulted (Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergström, 1996; Fig. 13) and some areas can therefore have moderate relief; but within the fault blocks, flat relief is maintained. The vertical throws are mainly only tens of metres, but can be up to 150 m. Glacial erosion has not obliterated these exhumed fault-line scarps. The sub-Cambrian peneplain occupies the Väner Basin (Fig. 1). In its southern parts, remnants of lower Paleozoic cover rocks are preserved as mesas and buttes below capping dolerite. The peneplain rises to the south and west. It is probably never very far from the summit surfaces, even along the west coast, as Cambrian fissure-fillings are present (Reference SamuelssonSamuelsson, 1975). The relief changes dramatically towards the coast, from a well-preserved featureless plain to a structurally and lithologically controlled landscape that disappears below Jurassic/lower-Cretaceous cover rocks in the Skagerrak. By its general relation to Mesozoic cover rocks, reports of kaolinized fractured zones and the type of relief similar to the well-dated exhumed sub-Cretaceous relief in southeastern Sweden (Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergstrom, 1988, 1989, 1995b; Reference Elvhage and Lidmar-BergströmElvhage and Lidmar-Bergström, 1987; Reference Lidmar-Bergström, Smith, Whalley and WarkeLidmar-Bergström and others, 1999), this higher-relief landscape is interpreted as an exhumed sub-Mesozoic etch surface. The total amount of erosion in southern Sweden, in basement areas with exhumed sub-Mesozoic relief, since the re-exposure of the sub- Cambrian pene plain in the Mesozoic, ranges from zero on some hill tops (later exhumation?) to about 200 m (Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergström, 1988, 1997). The erosion includes stripping of saprolites that may have been several tens of metres thick or more. The erosion occurred during three distinct intervals: before the sedimentation of the cover rocks, after a second re-exposure in the Late Tertiary and by glacial erosion during the Quaternary. How much of the Cretaceous cover was already gone in the Late Tertiary is difficult to judge, but exhumed sub-Cretaceous relief in southern Sweden, with weathered flints as the only remnant of the former Cretaceous cover (Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergström, 1982) and the occurrence of short transported silicified wood probably of Miocene age (Reference Kornfält and BergströmKornfält and Bergstrom, 1983), suggest erosion of the cover rocks here before the glaciations. A Late-Tertiary erosion of the covers along the northern part of the west coast is suggested due to the total loss of the Cretaceous cover here, despite the irregular topography, as well as the long distance to preserved cover rocks in the Skagerrak (Fig. 1)

Fig. 1. Map of palaeosurfaces in southern, Sweden with the study area indicated.
Bohus granite occupies the northern part of the Swedish west coast. The bedrock is exposed over large areas, which has given opportunities for detailed studies of glacial forms (Ljungner, 1930; Johnson, 1956) and, according to common text books, the landscape must be labelled “an areally scoured glacial terrain” (cf. Reference Sugden and JohnSugden and John, 1976; Reference SugdenSugden, 1978; Reference MenziesMenzies, 1996). However, the recognition of its character, mainly as an exhumed etch surface (Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergström, 1995b), gave rise to the question: what, in reality, is the glacial impact on the forms? If the bedrock surfaces are examined in detail in the field, is it then possible to judge which processes have been involved in the ultimate shaping of the forms and the relative importance of the processes involved?
The occurrence of a kaolinized fracture zone (Reference Lidmar-Bergström, Smith, Whalley and WarkeLidmar-Bergström and others, 1999) and the existence of large clefts with weathered walls within a rock hill at Hunnebostrand, Bohuslän (Fig. 1), made this area suitable for a detailed study. The purpose was to examine meso- and micro- forms in the field to ascertain what processes and structures were responsible for the relief, and to get a perspective on the effect of glacial erosion on the exhumed sub-Mesozoic granite surface. For interpretations of glacial geomorphology, it is important to be able to ascertain what is glacial and what is non-glacial relief.
Geology and Topography
In the northernmost part of the Swedish west coast, the bedrock is predominately 920 Myr old Bohus granite (Lundq-Reference Lundqvist and Fredénvist and Bygghammar, 1994). Several textural and colour varieties occur, but the dominant type is greyish-red, medium-grained and massive (Reference AsklundAsklund, 1947). The bedrock relief is characterized by sets of straight valleys, lake basins and other depressions, interrupted by well-defined square-, lozenge- or irregularly shaped rock hills forming steep-sloped plateaux or domes. The straight outline of the landscape expresses structural contrasts within the basement rocks, revealed by exogenic processes. The relief amplitude is normally between 20 and 100 m, however, in some extreme cases it is close to 150 m and even 200 m from the fresh bedrock in a fjord bottom to the nearby hilltops (Flodén, 1973; p. 98). The hills mainly lack cover of Quaternary deposits and bedrock is exposed. The small- to medium-sized bedrock forms are characterized by massive glacial scouring from the northeast, and roche moutonnées are the dominant medium-scale landforms. Large valleys are frequently flat-floored, due to thick infill of glaciomarine clays deposited during the late Weichselian deglaciation (about 13 000-12 400 BP). The highest late-glacial shoreline ranges from 110ma.s.l. in southern Bohuslän to above 170 m a.s.l. in the north (Lundq-Reference Lundqvist and Fredénvist, 1994).
Study Area
Hunnebo is situated within the Bohus granite on the Sotenäs peninsula (Fig. 1). Three sets of fractures north—south, northeast—southwest and west-northwest—east-southeast have been mapped from air photos (Fig. 2). Valleys have developed along these fractures and, between the clay-filled valleys, rock hills with exposed bedrock occur. There are several isolated hills in the area, and south of Hunnebostrand, two larger circular, steep-sided, plateau-crested granite hills rise to about 65 m above the adjacent sea level (Fig. 2). The round shapes of the hills is a result of the fracture patterns. The northern hill (Fig. 3, inset map) has a system of joints in the west, where large clefts have developed. This part was chosen for detailed study.

Fig. 2. Joint-aligned valleys and circular rock hills in the granitic region of Bohuslän at Hunnebostrand. Inset box refers to inset map in the upper right corner of Figure 3.
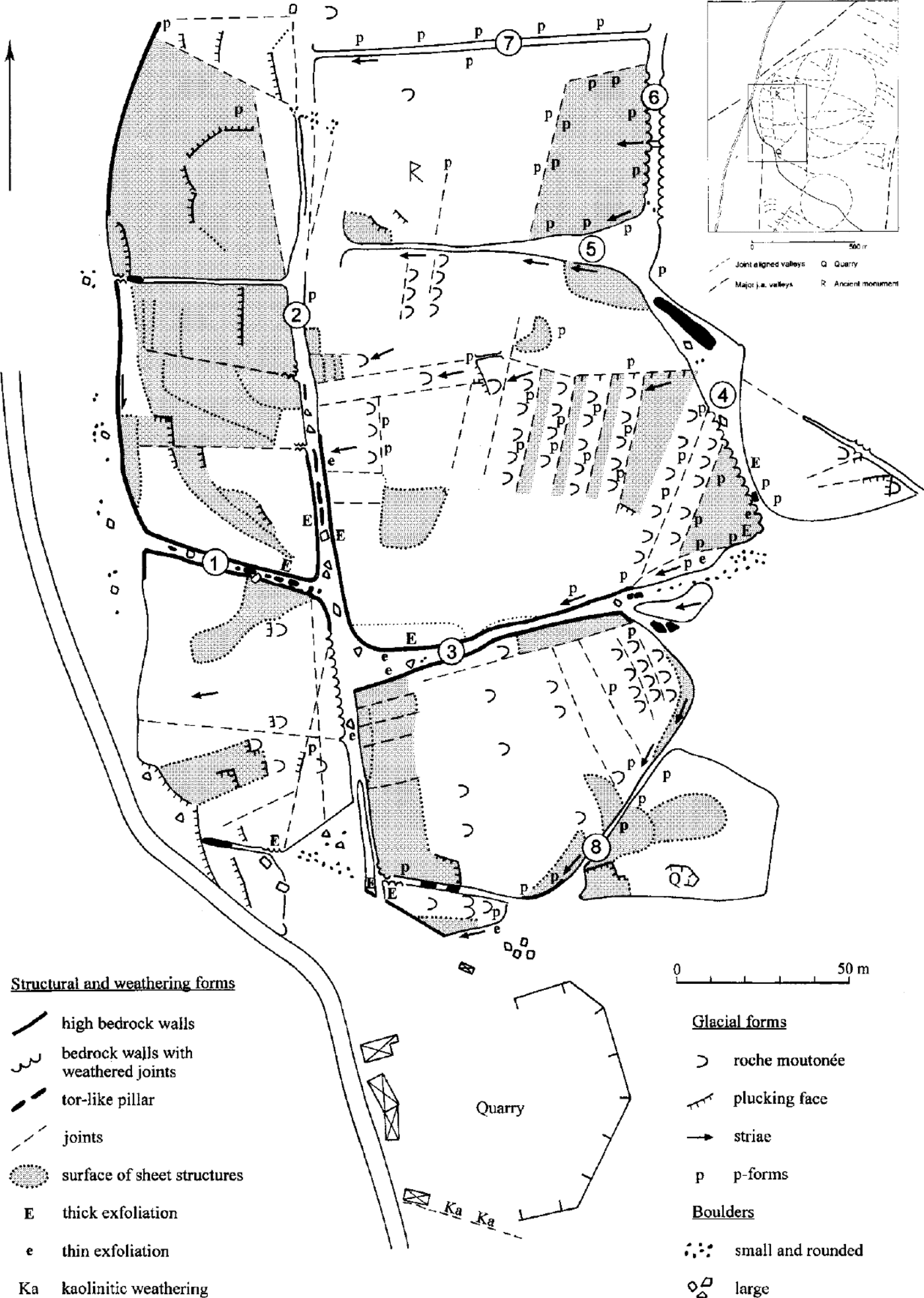
Fig. 3. The Hunnebo clefts mapped by Göran Lindberg, Kama Lidmar-Bergström, Jan Bergström and Mats Olvmo. Inset map: Bedrock structures mapped from air photos within and around the study area south of Hunnebostrand. The clefts are numbered (l)—(8).
Methods
Small-to medium-scale bedrock forms were mapped, described and classified either as glacial or non-glacial. The non-glacial forms were further subdivided according to process of formation. The glacial surfaces were used as a relative time reference for interpretation of the geomorphological evolution. The other forms were determined to be either older or younger than the glacial surfaces.
Form-process considerations
Bedrock forms related to weathering processes
In most rocks, deep weathering (that is sub-surface weathering) works preferentially along joints or other types of partings. In rocks such as granite, this effect is significant due to the marked contrast in permeability between fractured and intact rock blocks (Reference TwidaleTwidale, 1982; Reference Twidale and CampbellTwidale and Campbell, 1993). This favours the movement of meteoric water along such partings, which thus forms the initial loci of decomposition. Weathering will start at the original joint surface and the zone of decomposed rock will progressively grow laterally and parallel with this surface. As a consequence, straight joint-controlled bedrock surfaces, clefts and widely opened joints will appear after stripping of the weathering products. Fresh cores of the rock with rounded edges (tors) as well as residual boulders, once corestones in the weathered rock, will also be left after stripping.
The transition from fresh to friable weathered rock is often separated by a zone consisting of laminated masses of less-altered rock, which extends conformably around boulders or runs parallel with joint surfaces (Reference TwidaleTwidale, 1982). The resulting spalls or flakes, produced by exfoliation, are known to develop by surface and sub-surface weathering. We have noted this type of weathering both on corestones within saprolites in southern Sweden (Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergstöm and others, 1997) and on glaciated surfaces in Bohuslän and other parts of Sweden. Differential weathering at a mineralogical scale will produce rough rock surfaces which also form in both subsurface and surface environments (Reference Twidale and BourneTwidale and Bourne, 1976; Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergström, 1989; Reference SwantessonSwantesson, 1989).
Forms related to erosion by ice sheets and subglacial meltwater
Glacial erosion in hard rock is a result of abrasion, plucking, subglacial water erosion and subglacial dissolution (Reference DrewryDrewry, 1986). The most conclusive evidence of glacial abrasion is striae or grooves. Plucking is the effect of fracturing, loosening and evacuation of rock fragments by different subglacial processes (Reference DrewryDrewry, 1986). This leads to the formation of freshly broken rock surfaces with sharp edges, and a jagged and sometimes stepped outline. Abrasion and plucking lead to the evolution of the classic roche moutonnées. However, the actual bedrock form produced is highly variable and dependent on rock structure (Ljungner, 1930; Reference Rastas and SeppäläRastas and Seppälä, 1981; Reference Laitakari and AroLaitakari and Aro, 1985).
Subglacial meltwater erosion may erode the bedrock surface and produce a variety of forms at different scales. In the study area, most typical subglacial meltwater forms are potholes and variously shaped longitudinal furrows, cavettos and flutes with typically concave or trough-shaped cross-sections.
Forms related to wave abrasion
Some examples of vertical joints, exploited by shore processes during isostatic uplift, occur along the Swedish west coast (Reference SjöbergSjöberg, 1986). These so-called tunnel caves have a form that resembles a wine glass turned upside-down. The caves can form in areas open to the sea, where concentrations of beach shingle occur. The position of the tunnel, the widened joint, is a function of its relation to sea level during a stage when the fetch and the availability of abrading material were optimal. The abraded tunnel walls are smoothly rounded or flared and notably well-polished. These wave-abraded surfaces are easy to distinguish from glacially abraded surfaces. It is, however, difficult to distinguish between marine abrasion and abrasion by subglacial meltwater, but the local conditions often clarify the situation. Still there is some uncertainty in this case.
Results
The mapped area includes seven rock blocks and eight intervening clefts (Fig. 3). The two northernmost and centrally situated blocks exceed 65 m a.s.l. The block to the south of cleft (3) is 50–55 m a.s.l., and the two northernmost of the westerly blocks are 40–50 m a.s.l. The southwestern block only reaches 35 m a.s.l. The mapped features of clefts and summits are presented in Fig. 3 and divided into three groups: (1) structural and weathering forms; (2) glacial forms; and (3) boulders. Some comments on the vertical distribution of forms and other features not easily read from the map will follow.
Clefts
Non-glacial features: joint-controlled clefts and weathering
The clefts have vertical joint-controlled walls, which range in height from a few metres to about 15 m. The floor at the mouth of cleft (1) is about 25 m a.s.l. The rock walls are parted by horizontal sheeting joints and, particularly in the inner part of cleft (1), are separated by many vertical joints resulting in the formation of rock blocks. Weathering occurs along the joints and has caused rounded edges on the blocks. Cleft (1) is occupied by tor-like pillars of granite, with rounded edges. The pillars increase in height in the inner part, where granite boulders are perched on each other, in situ (Fig. 4). Exfoliation sheets, 0.05–0.1 m thick occur along the northern wall, on the pillars and also on some of the boulders strewn on the floor. On the rock walls, as well as on the boulders, there is a typical rough surface caused by differential mineral weathering. A 0.2–0.3 m wide vertical zone in the easternmost part of the cleft is weathered in situ to gruss. The weathering emanates from a central joint. There is also a high amount of fine angular quartz and alkali feldspar gravel on the cleft floor. These features are characteristic for most of the clefts. Cleft (3) is the deepest cleft. Tor- like pillars are present only in the eastern part. Thick exfoliation occurs along the northern wall, and in the western end, large exfoliated blocks rest as boulders on the ground. Otherwise, this cleft is mainly devoid of boulders.

Fig. 4. Tor-like pillars, Hunnebo, the eastern part of cleft (1)(see Fig. 3 for location). View towards the west. The pillars in the centre are about 3 and 4 m high, respectively. Note also the boulders with rounded edges in the lower left corner. (Photo by M. Johansson).
In most of the clefts, weathering has acted extensively along sheeting joints in the walls and well-rounded surfaces have formed between the joints. Good examples are exposed in clefts (4) and (6) (Fig. 5). As a result of this weathering, the edges of the sheeting structures have distinct convex profiles (cf. Fig. 7).

Fig. 5. Sheets of granite weathered to convex forms at the intersection between clefts (3) and (4) (Fig 3). A thick exfoliated granite slab can be seen on the lowermost sheet structure. The exposed rock wall on the photo is approximately 4 m high. Photo towards west-southwest.
Evidence of kaolinitic deep weathering is documented in the abandoned quarry in the southernmost part of the area. Here, the granite is weathered to a soft and friable saprolite within about a 0.5 m wide vertical fracture zone (Fig. 3). The clay fraction consists of kaolinite and smectite, the same minerals as within the basal parts of Mesozoic saprolites in southern Sweden (Reference Lidmar-Bergström, Smith, Whalley and WarkeLidmar-Bergström and others, 1999).
Effects of glacial erosion and erosion by subglacial meltwater
In general, the cleft walls have no traces of glacial abrasion and are unaffected by glacial erosion. However, erosion by subglacial meltwater has exploited the weathered sheeting structures along the upper part of the steep wall facing southwards at the eastern end of cleft (3). Furrows with concave cross profiles have been formed (Fig. 6). These forms are normally referred to as p forms (Reference DahlDahl, 1965; Reference Benn and EvansBenn and Evans, 1998), or sometimes s forms (Reference Kor, Shaw and SharpeKor and others, 1991). They have been incised into the original convex weathering forms (Fig. 7). This type of reshaping by subglacial meltwater is frequent and it demonstrates that the convex weathering forms predate the concave glacial forms. Such p forms are common and well- developed along the upper parts of clefts (3), (5), (7) and (8), but are also developed to some extent along cleft (6).

Fig. 7. Principal sketch of vertical zonation of forms within the clefts.
Marine abrasion of cleft walls
The pillars in the centre of cleft (1) are polished on the sides exposed to the western (seaward) entrance, while east-facing surfaces are rough. The winding cleft (3) has slightly curved overhanging walls in the centre. Beach pebbles partly cover the floor and the lower parts of the rock walls are occasionally nicely polished. Marine abrasion may have contributed to the shape of the walls.
Zonation of forms
Observations of the vertical distribution of forms caused by weathering and by erosion of glaciofluvial meltwater can be summarized as follows (Fig. 7). Weathering features predominate in the lower part of the cleft walls, however some are remodelled by wave action. In the uppermost parts, the weathering forms have been remodelled by glacial erosion, mainly by subglacial meltwater, and many weathering forms have been converted to ρ forms.
Forms outside the clefts
The plateau-like summit
In contrast to the clefts, the plateau-like summit (between clefts (2), (7), (6), (4), and (8)) of the hill is highly affected by glacial abrasion. Roche moutonnées, indicating ice flow from the northeast, occur in abundance. The structural influence is prominent since the sheeting has a major influence both on the plateau form and on the stoss- and lee-side topography (cf. Ljungner, 1930). The sheeting joints dip gently away from the ice-flow direction. Steep and short stoss sides are developed on the outcropping edges of the sheet structures (Fig. 8). The lee sides are often conformable with gently dipping sheeting joints due to joint-controlled glacial plucking.

Fig. 8. Top surfaces of plateaux between clefts (3) and (8) (foreground) and (2)-(5) (background). Cleft (3) cuts through the centre. Note the influence of sheeting on the stoss- and lee-side topography. Steep stoss sides have normally developed on the outcropping edges of bedrock sheets, while plucking has occurred preferentially along southwest-dipping sheeting joints. Photo towards north.
Selective erosion, by subglacial meltwater of the top surface, is shown by more or less continuous plastically sculptured furrows. The p forms commonly follow structures running parallel to the ice-flow direction, but the systems are sometimes dislocated by cross joints.
The glacially eroded summit surface at Hunnebo is also characterized by different types of small-scale glacial forms. Striae are ubiquitous, but often partly remodelled and sometimes completely obliterated by postglacial weathering. Other small-scale features, such as friction cracks and chattermarks, are widely distributed, but are normally reshaped by postglacial weathering. Postglacial weathering has been most effective in small glacial troughs (Sichelwannen), where moisture retention has promoted weathering. The initial pits have often developed further by a thin flaking. It is, however, important to note that postglacial weathering has been incapable of significantly rounding glacially broken edges.
The top surfaces of the low-rock compartments
The surfaces of the westerly low-rock compartments (west of cleft (2)) follow the sheeting of the granite and are glacially plucked surfaces. The two compartments in the northwest are in the lee of ice from the northeast and no roche moutonnées have developed
The hill sides
The northeastern part, outside the mapped area, is heavily glacially abraded and the sides are less steep. The steep western walls of the hill have slightly flared slopes, the origin of which are obscure. They are either weathering forms (cf. Reference TwidaleTwidale, 1982) or glacial forms developed by ice flow from the north, as these walls have preserved north—south striae.
Evaluation and Timing of Land-Forming Processes
An evaluation of the importance of different processes for the bedrock forms in the study area is presented in Table 1. The landforms of the granite are controlled by well-developed vertical and horizontal joint systems, just as in areas not affected by glaciations (Reference TwidaleTwidale, 1982; Reference Twidale and CampbellTwidale and Campbell, 1993; Reference Twidale, Vidal Romani, Campbell and CentenoTwidale and others, 1996).
Table 1. Relative importance of different processes.

Origin of the clefts
The forms of the clefts and the saprolite remnants suggest that weathering processes were important for their formation. The weathering forms are particularly well-preserved in clefts protected from glacial erosion and erosion by subglacial meltwater, particularly in those running north— south. Weathering along joints is clearly older than the p forms exploiting them.
A map of the clefts (incorrect concerning their width, length and orientation) was presented by Reference Mahaney and SjöbergMahaney and Sjöberg (1993). They argued for a Pliocene age for etching of the clefts, referring to the dissolution of quartz grains. The preserved kaolinitic saprolite in the fracture in the quarry suggests that the original deep weathering responsible for the cleft formation is Mesozoic. As no remnants of cover rocks are preserved within Bohuslän and the area has experienced a (Late) Tertiary uplift (Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergström, 1996; cf. Reference JapsenJapsen, 1998), it is probable that the Mesozoic cover was already gone in the Neogene. It is possible that the clefts have been affected by repeated events of etching, stripping and burial. Due to the occurrence of beach pebbles and wave-abraded surfaces, it is suggested that marine erosion is responsible for the latest stripping event in the lower parts of the clefts. Erosion by subglacial meltwater has mainly affected the upper parts of the clefts, except for cleft (3), where it might have influenced the whole cleft.
Structural importance for glacial shaping and reshaping of forms
It is quite obvious that sub-horizontal sheeting governs the plateau-like top surfaces and has also strongly influenced the shape of the medium-scale glacial forms (cf. Ljungner, 1927, 1930). Reshaping of the upper parts of the clefts by subglacial meltwater led to the transformation of the convex edges of the rock sheets to concave ρ forms along the preglacially weathered sheeting joints. Glacial plucking along sheeting joints has contributed to a stepped appearance of the west-facing slope. The lee-side compartments have been lowered about 20–30 m by glacial plucking, which gives the hill an asymmetrical form.
Postglacial shaping
Postglacial thick exfoliation occurs in positions sheltered from glacial erosion. The absence of thick exfoliation sheets on glacially abraded surfaces suggests that the present exfoliation results from reactivation of preglacially weathered cleft walls.Postglacial differential weathering and thin exfoliation have affected all kinds of surfaces, both inside the clefts and on the summits, but their morphological effects are only marginal.
The Glacial Impact: A Discussion
The general forms of the landscape in Bohuslän and around Hunnebostrand, controlled by lithology and structures, are typical of etched terrains throughout the world (Reference TwidaleTwidale, 1982; Reference OllierOllier, 1984; Reference ThomasThomas, 1994). The difference is that, compared to nonglaciated areas, little is left of the original saprolites. Compared to central and northeastern Skåne and southernmost Sweden, with many thick saprolite remnants, Bohuslän is almost stripped of its saprolites and remnants only occur within narrow fracture zones or clefts. The area gives the impression of a scoured glacial terrain.
How much fresh bedrock has the ice eroded? It is difficult to judge, but the direct abrasion is limited to decimetres or metres on the stoss sides and the main erosive effect has been achieved by plucking, which amounts to at least 20— 30 m on the lee side. It is probable that whole sheets of bedrock have also been plucked from the high summits. The available relief in the Precambrian bedrock from the position of the sub-Cambrian peneplain can be estimated to be about 100 m (Reference Lidmar-BergströmLidmar-Bergström, 1988; Fig. 3h). As the whole appearance of the landscape is of etch character, it is probable that part of this amount was denuded in preglacial times (Mesozoic and Late Tertiary) so we end up with the conclusion that some tens of metres may have been removed from the high summits by glacial erosion.
Glacial erosion has not obliterated the bedrock hills that are characteristic of an etch surface, but many hills are asymmetric due to glacial plucking. In protected positions, even non-glacial medium-scale weathering forms are preserved. The latest stripping event might be postglacial, caused by marine abrasion. Glacially formed features in the bedrock are of meso- and microscale and occur on hilltops and stoss sides. Glacial scouring does not mean a total obliterating of preglacial landscapes and residual hills are definitely not destroyed by glacial erosion, as is suggested by Reference SelbySelby (1982; p. 191). It is, however, only in areas with extensively preserved saprolites and limited glacial reshaping of forms that we can talk about weak glacial erosion.
Conclusions
It is important to establish the inherited character of a landscape before the impact of glacial erosion is evaluated. The granite forms in Bohuslän mainly exhibit the same basic shape as granites in nonglaciated areas, but with some very specific alterations. The most notable difference from nonglaciated terrain is the absence of the weathered mantle. Landscapes labelled “areally scoured glacial terrain” can, at least in some locations, also be described as totally stripped and slightly incised etch surfaces. This study has further emphasized the importance of detailed field mapping of bedrock surfaces and saprolite remnants for sorting out the processes involved in the ultimate shaping of the relief.












