CVD is the leading cause of death globally( 1 ). Plasma HDL-cholesterol (HDL-C) concentrations are inversely associated with CVD risk and should be considered alongside LDL-cholesterol in the management of dyslipidaemic individuals( Reference Vergeer, Holleboom and Kastelein 2 , Reference Hansel, Kontush and Giral 3 ). Low HDL-C concentrations may reflect disturbances in TAG metabolism( Reference Vergeer, Holleboom and Kastelein 2 ). In conjunction with increased concentrations of TAG and small-dense LDL (sLDL) particles, they form the lipid triad or ‘atherogenic lipoprotein phenotype’ that is associated with obesity and insulin resistance (IR), the prevalence and subsequent contribution to CVD risk of which are steadily increasing( Reference Musunuru 4 ). Therefore, an understanding of the determinants of HDL-C concentrations is timely. Considerable variability in HDL-C concentrations exists within population groups( Reference Hansel, Kontush and Giral 3 , Reference Bove, Cicero and Manca 5 ). Heritability estimates for HDL-C concentrations range between 40 and 60 %. In addition, a range of environmental and metabolic factors, including TAG concentrations, waist circumference, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein concentrations, IR, alcohol consumption and smoking, have been shown to be associated with HDL-C concentrations( Reference Hansel, Kontush and Giral 3 , Reference Bove, Cicero and Manca 5 – Reference Peloso, Demissie and Collins 7 ).
Fruit and vegetables have long been identified as key elements of a cardioprotective diet. Yet, beyond the cholesterol-lowering properties of dietary fibres, conclusive benefits in relation to blood lipids remain largely unresolved. There are inconsistent findings, for example, as to the beneficial effects of flavonoid-rich fruit consumption on HDL-C concentrations( Reference Chong, Macdonald and Lovegrove 8 , Reference Dauchet, Amouyel and Dallongeville 9 ). Genetics, for example, differences in the prevalence of key gene variants, are likely to contribute to some of the variability in responses between populations. To our knowledge, however, no studies have investigated the variability in responsiveness of blood lipids to an intervention involving fruit.
In 2010, we conducted a randomised controlled trial in hypercholesterolaemic men, in which we assessed the impact of consuming two green kiwifruit a day alongside a healthy diet on plasma lipids. The primary results of this trial indicated that the consumption of two green kiwifruit every day for 4 weeks had favourable effects on plasma HDL-C concentrations and the total cholesterol (TC):HDL-C ratio compared with the consumption of a healthy control diet alone( Reference Gammon, Kruger and Minihane 10 ).
Based on the primary results, one of the secondary objectives of the above-mentioned trial was to select gene polymorphisms related to lipid metabolism that could explain the heterogeneity in response observed. For the present study, we selected four SNP related to HDL metabolism, and given the sample size, we focused on common variants with more than 20 % minor allele frequencies. The SNP chosen were the cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) Taq1B, APOA1 − 75G/A, hepatic lipase (LIPC) − 514C → T, and endothelial lipase (LIPG) I24582 (T+2864C/In8) variants.
CETP TaqIB is one of the most widely studied polymorphisms( Reference de Grooth, Klerkx and Stroes 11 ), and substantial evidence from meta-analyses shows an association with HDL-C concentrations( Reference Boekholdt, Sacks and Jukema 12 , Reference Thompson, Di Angelantonio and Sarwar 13 ). Evidence is more limited for the other three SNP, but all have been reported to be associated with either HDL-C concentrations( Reference Mank-Seymour, Durham and Thompson 14 – Reference Zhang, Lopez-Ridaura and Rimm 17 ) or related factors( Reference Juo, Wyszynski and Beaty 18 – Reference Souverein, Jukema and Boekholdt 20 ).
Therefore, the aim of the present study was to assess the effects of these selected HDL-C-related polymorphisms on the plasma lipid response to a kiwifruit intervention.
Subjects and methods
Subjects and study design
Data for the analyses reported herein were obtained as part of an 8-week randomised controlled cross-over trial conducted between May and September 2010. The details of study participant recruitment, flow diagram, participants and protocol have been described previously( Reference Gammon, Kruger and Minihane 10 ). Briefly, eighty-seven hypercholesterolaemic men with a LDL-cholesterol concentration >3·0 mmol/l and a plasma TAG concentration < 3·0 mmol/l but otherwise who were healthy, non-smokers and not taking any cholesterol-lowering medication were recruited from the Auckland region in New Zealand. The study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki, and all procedures involving human subjects were approved by the Massey University Human Ethics Committee: Southern A 09/76. Written informed consent was obtained from all the subjects. The trial was registered with the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (no. ACTRN12610000213044, http://www.ANZCTR.org.au).
The measurement of anthropometric parameters (height, waist circumference, weight and percentage body fat) and collection of blood samples for lipid analyses were carried out during the first visit (baseline 1) to the Massey University Human Nutrition Research Unit. The subjects had to complete a 3 d food record before attending a nutrition consultation with a nutritionist, during which details of the healthy diet that the subjects were required to follow for the 12 weeks of the study were outlined. The healthy diet was based on the Heart Foundation of New Zealand's ‘9 steps to Eating for a Healthy Heart’ and was also used to make recommendations to improve their current dietary habits (Gammon et al. ( Reference Gammon, Kruger and Minihane 10 ), Supplementary table (available online)) and included the requirement that they consume at least two servings of fruit (other than kiwifruit) per d. The nine steps are a series of guidelines to encourage individuals to make healthier choices focused on heart health, such as incorporating fruit and/or vegetables in every meal, choosing whole-grain breads and cereals instead of white and low-fibre varieties, and reducing salt, saturated fat and alcohol intakes. After completing their 4-week healthy diet run-in period, the subjects returned to the research unit and were randomly assigned, using computer-generated random numbers (http://www.randomization.com), to one of two 4-week intervention sequences: healthy diet alone (control intervention) or replacement of two of their normal fruit servings with two Zespri® Green kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa var. Hayward) per d (average weight without skin 176 g/d, which is approximately equivalent to 2 × 80 g standard fruit portions) plus a healthy diet (kiwifruit intervention). The collection of additional blood samples and measurement of anthropometric parameters and blood pressure were carried out, and a 24 h food record was completed by a nutritionist during this visit (baseline 2) and at the end of each intervention period, as detailed in Gammon et al. ( Reference Gammon, Kruger and Minihane 10 ). The subjects were requested to maintain their normal daily routine (including physical activity) for the duration of the study, and compliance was monitored by weekly self-completed diaries.
Laboratory measurements
Venous blood samples were collected into vacutainers buffered with EDTA or heparin or without an anticoagulant after an 8 h fast. Once processed, aliquots were stored at − 80°C for analysis in one batch at the end of the study. Buffy coat aliquots were stored in LoBind DNA-free Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf). Plasma lipid, serum apo, plasma glucose and insulin, and serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein analyses were conducted by Canterbury Health Laboratories, Christchurch, New Zealand (IANZ ISO 15 189)( Reference Gammon, Kruger and Minihane 10 ). SNP determination and sLDL analysis were conducted at the Biomedical Research Centre, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK. The homeostasis model assessment 2 model was used to calculate IR, based on fasting insulin and glucose concentrations( Reference Wallace, Levy and Matthews 21 ).
All the subjects (excluding one subject who requested not to be included in any gene analysis) were directly genotyped for four selected polymorphic sites: CETP Taq1B (rs708272); APOA1 − 75G/A (rs670); LIPC − 514C → T (rs1800588); LIPG I24582 (T+2864C/In8) (rs6507931). Genomic DNA was isolated from the buffy coat samples using the QIAamp DNA Mini Blood Kit (catalogue no. 51 104, QIAGEN Limited). Applied Biosystems 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System (software version 2.0.5; Applied Biosystems) and TaqMan® SNP genotyping assays (Applied Biosystems) were used to determine the allelic discrimination of the selected gene variants.
Statistical analyses
A power calculation was carried out to establish the sample size for the primary study, and it was based on detecting a difference of 0·5 mmol/l in TC and LDL-cholesterol concentrations between the interventions and on the prevalence of apo E4 allele carriers( Reference Gammon, Kruger and Minihane 10 ). The sample sizes of 51 and 31 in the Taq1B B2 carrier and B1/B1 groups, respectively, retrospectively provided 98 % power in the B2 carrier group and 87 % power in the B1/B1 group to detect a mean difference of 0·24 mmol/l in the TC:HDL-C ratio at an α-level of 0·05. This was based on the significant difference in the TC:HDL-C ratio of B1/B1 homozygotes during the kiwifruit and control intervention periods. This difference was related to about a 12 % reduction in CVD risk( Reference Stampfer, Sacks and Salvini 22 ). Additionally, the sample size provided 70 % power to detect a genotype × treatment interaction for the TC:HDL-C ratio.
Statistical analyses were carried out using IBM SPSS statistics version 20 (IBM Corporation). Normal distributions were tested using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov, Shapiro–Wilk tests and normality plots. Non-normally distributed data were transformed into approximately normal distributions, if possible, by logarithmic transformations. Normally distributed data are expressed as means and standard deviations or, when reporting inter-group differences, as mean difference with their standard errors. Non-normally distributed data are expressed as geometric means (95 % CI) if log-transformed (Table 1) or medians (25th and 75th percentiles) (Table 2).
Table 1 Positions and genotypic distributions of the selected SNP and HDL-cholesterol (HDL-C) concentrations in the study population at baseline (Mean values and standard deviations; geometric means and 95 % confidence intervals)
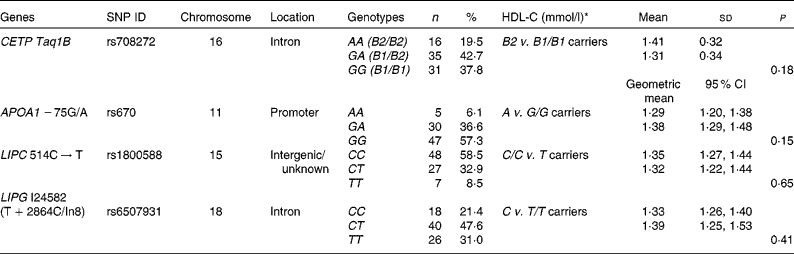
ID, identification; CETP, cholesteryl ester transfer protein; LIPC, hepatic lipase; LIPG, endothelial lipase.
* Mean values were significantly different between the genotype groups at baseline 1 (minor allele carriers v. major allele homozygotes) (P< 0·05; independent Student's t test).
Table 2 Baseline characteristics of the subjects by cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) Taq1B genotype group (Mean values and standard deviations at baseline 1, unless otherwise indicated; median values and 25th and 75th quartiles)
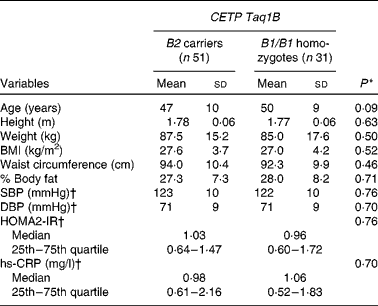
SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HOMA2-IR, homeostasis model assessment 2 model for insulin resistance; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
* Values were significantly different between B2 carriers and B1/B1 homozygotes (P< 0·05; independent Student's t test and Mann–Whitney test).
† Values obtained at baseline 2.
The data were examined for any interaction effects due to the sequence of interventions (kiwifruit followed by control and vice versa) using a two-way ANOVA. No interaction was observed, and so data collected during the two intervention periods were combined.
Multivariate ANOVA was used as an initial screen to investigate differences in the multivariate patterns of lipid variables between the genotype groups (major allele homozygotes v. minor allele carriers) to reduce the likelihood of chance findings from multiple comparisons.
Significant effects of CETP Taq1B on the multivariate pattern of lipid responses were observed, and this observation was backed by an assessment of assumptions and univariate patterns. Therefore, further analysis of this genotype was conducted. Repeated-measures ANOVA was used to examine genotype × treatment interactions. For ANOVA interactions where P< 0·05, a stratified analysis was carried out. Data were stratified by genotype group, and within-group comparisons between baseline 2 and end of the intervention periods (control and green kiwifruit interventions separately) and between the control intervention period and the kiwifruit intervention period for changes in each univariate lipid measure were made using dependent Student's t tests. Between-group comparisons for other variables were made using independent Student's t tests or Mann–Whitney test for non-normal data. Differences were considered significant at P< 0·05.
Results
As has been reported previously, eighty-five subjects completed the 12-week trial( Reference Gammon, Kruger and Minihane 10 ). Genotyping was completed for eighty-four subjects, although alleles for two subjects for three of the SNP could not be determined. Table 1 reports the positions and genotypic distributions for the four selected SNP. HDL-C concentrations at baseline 1, by genotype group (minor allele carriers v. major allele homozygotes), are also reported in Table 1. There was no significant difference in HDL-C concentrations between minor allele carriers and major allele homozygotes for any SNP at baseline 1.
Based on the results of the initial statistical screening using multivariate ANOVA, the CETP Taq1B SNP was found to affect the lipid profile at baseline 2 (F(10,71) = 3·561; P= 0·001). No significant results were obtained for any other SNP; therefore, further analysis was carried out only for the CETP Taq1B SNP.
Baseline characteristics of the subjects by cholesteryl ester transfer protein Taq1B genotype group
The baseline characteristics of the subjects stratified by CETP Taq1B genotype group are summarised in Table 2. There were no significant differences between the two groups for any anthropometric parameter, blood pressure, homeostasis model assessment 2-IR or high-sensitivity C-reactive protein concentrations.
Dietary intakes during the interventions by cholesteryl ester transfer protein Taq1B genotype group
Dietary intakes according to genotype group are summarised in Table 3. There was a small, but significant difference in energy intake between kiwifruit and control intervention periods in both groups. No significant differences in macronutrient intake were seen between kiwifruit and control intervention periods for either group. In both the groups, significantly higher intakes were observed for vitamins C and E during the kiwifruit intervention period than during the control intervention period.
Table 3 Dietary intakes during the interventions by cholesteryl ester transfer protein Taq1B genotype group (Mean values and standard deviations; median values and 25th and 75th quartiles, n 51 B2 carriers and n 31 B1/B1 homozygotes)

End-Kiwifruit, end of the kiwifruit intervention period; End-Control, end of the control intervention period.
* Values were significantly different between the green kiwifruit and control interventions (P< 0·05; dependent Student's t test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test).
† Mean values were significantly different from baseline 2 to the end of the intervention period (P< 0·05; dependent Student's t test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test).
When fruit servings per d were analysed by genotype, no significant differences were observed between the two groups for any period. At baseline 1, the median intake for both groups was 1·33 servings per d (below recommendations); this increased to two servings at baseline 2 and three servings during the two intervention periods.
Effects of diet run-in period and interventions on body weight by cholesteryl ester transfer protein Taq1B genotype group
During the 4-week healthy diet run-in period, there were small, but significant decreases in weight (mean difference − 0·39 (sd 1·33) kg, P= 0·04) and BMI (mean difference − 0·12 (sd 0·41) kg/m2, P= 0·05) in B2 carriers and in percentage body fat (mean difference − 0·60 (sd 1·35), P= 0·02) in B1/B1 homozygotes. From the end of this period (baseline 2) to the end of the 8-week intervention period, there were no changes in body weight in either group regardless of the intervention received by the groups (green kiwifruit or control) (Supplementary table, available online).
Effects of interventions on lipid concentrations by cholesteryl ester transfer protein Taq1B genotype group
The effects of interventions on plasma lipid concentrations by CETP Taq1B genotype group are summarised in Table 4. At baseline 2, B2 carriers had significantly lower TC:HDL-C ratio (mean difference − 0·39 (se 0·19) mmol/l, P =0·05), TAG:HDL-C ratio (mean difference − 0·31 (se 0·15) mmol/l, P =0·05), and apoB1:apoA1 ratio (mean difference − 0·10 (se 0·05) g/l, P =0·04) and sLDL concentrations (mean difference − 0·24 (se 0·12) mmol/l, P =0·05) than B1 homozygotes. The differences between B2 carriers and B1 homozygotes with regard to HDL-C and apoA1 concentrations were 0·14 (se 0·07) mmol/l, P= 0·07, and − 0·11 (se 0·05) g/l, P= 0·06, respectively.
Table 4 Changes in plasma lipid and apolipoprotein concentrations during the two intervention periods by cholesteryl ester transfer protein Taq1B genotype group∥ (Mean values and standard deviations)

TC, total cholesterol; LDL-C, LDL-cholesterol; HDL-C, HDL-cholesterol; sLDL, small-dense LDL.
* Mean values were significantly different from baseline 2 to the end of the intervention period (P< 0·05; dependent Student's t test).
† Mean values were significantly different between B2 carriers and B1/B1 homozygotes (P< 0·05; independent Student's t test).
‡ Values were significantly different between the genotype groups, treatment × gene interaction (P< 0·05; repeated-measures ANOVA).
§ Values were significantly different between the kiwifruit and control interventions (P< 0·05; dependent Student's t test). Only P values for variables with an ANOVA interaction (P< 0·05) are reported.
∥ Subjects followed a cross-over design protocol during the two intervention periods.
There was no genotype × treatment interaction for HDL-C concentrations. The kiwifruit intervention resulted in greater HDL-C concentrations than the control intervention in both the genotype groups. The mean difference between kiwifruit and control intervention periods for HDL-C was 0·06 (sd 0·10) mmol/l, P =0·002, for B1/B1 homozygotes and 0·05 (sd 0·15) mmol/l, P= 0·03, for B2 carriers, with this group (B2 carriers) during the control intervention period having a significant decrease from baseline − 0·05 (sd 0·15) mmol/l, P= 0·02.
There was a significant genotype × treatment interaction for the TAG:HDL-C ratio (P= 0·03). On stratification for this variable, the two genotype groups were found to differ in response to the interventions, with B1/B1 homozygotes responding favourably, with significant improvements being observed during the kiwifruit intervention period than during the control intervention period for the TAG:HDL ratio, − 0·23 (sd 0·58) mmol/l, P= 0·03. There were no significant treatment differences in B2 carriers. Since significant (P< 0·05) genotype × treatment interactions were not observed for any of the other lipid variables, results of stratified analysis for these are not reported.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first study to report a possible association between a polymorphism in the CETP gene and plasma lipid response to a fruit intervention. Since the results are based on one SNP and a relatively small cohort, the findings should be seen as explorative and will need to be confirmed in future research in a larger sample.
The genotype frequencies for all the four SNP investigated in the present study were in line with those reported by other studies in the literature( Reference Boekholdt, Sacks and Jukema 12 , Reference Mank-Seymour, Durham and Thompson 14 – Reference Zhang, Lopez-Ridaura and Rimm 17 , Reference Ruano, Seip and Windemuth 19 , Reference Do, Nazih and Luc 23 – Reference Ordovas, Corella and Cupples 25 ). However, there was a tendency towards a greater percentage of minor allele carriers for APOA1 − 75G/A (42·7 v. 28–29·6 %)( Reference Do, Nazih and Luc 23 , Reference Ordovas, Corella and Cupples 25 ) in the participants of the present study.
The CETP Taq1B genotype significantly modulated the TAG:HDL-C ratio in response to the kiwifruit intervention. Favourable effects of consuming two green kiwifruit a day against the background of a healthy diet were observed on the plasma TAG:HDL-C ratio, but only in B1/B1 homozygotes of the CETP Taq1B genotype. The HDL-C response was not modulated by the CETP Taq1B genotype, since improvements were observed in both the genotype groups. Although no genotype interactions were observed for the TC:HDL-C ratio or TAG concentrations, the lack of observed effects may have been due to insufficient power (70 % power to observe an interaction effect on the TC:HDL-C ratio), as there were trends of greater improvement in these variables in B1/B1 homozygotes, but not in B2 carriers.
The most established function of CETP is the mediation of the transfer of neutral lipids, cholesteryl esters (mainly from HDL-C) and TAG (found in TAG-rich lipoproteins, VLDL and chylomicrons) between plasma lipoproteins( Reference Barter, Brewer and Chapman 26 , Reference Chapman, Le Goff and Guerin 27 ). Elevated CETP activity results in enhanced TAG enrichment of both HDL and/or LDL, which are more readily remodelled by LIPC into smaller particles. This consequently leads to a decrease in plasma HDL-C and apoA1 concentrations as a result of increased removal of these HDL remnants from circulation by renal clearance and/or the hepatic holo-receptor and an increase in the number of atherogenic sLDL particles( Reference Chapman, Le Goff and Guerin 27 , Reference Charles and Kane 28 ).
The TaqIB polymorphism of the CETP gene is due to a base change from G to A at position 277 in intron 1. It is not readily apparent as to how this base change can modulate CETP expression. However, it has been suggested that while the SNP is not itself functional, it may act as a marker due to its linkage disequilibrium with a functional variant( Reference de Grooth, Klerkx and Stroes 11 , Reference Boekholdt and Thompson 29 ). Moderate inhibition of CETP activity and higher HDL-C and apoA1 and lower TAG concentrations have been observed in B2 carriers than in B1/B1 homozygotes( Reference Thompson, Di Angelantonio and Sarwar 13 ). Conversely, B1/B1 homozygotes tend to have a more atherogenic lipoprotein profile( Reference Dullaart and Sluiter 30 ).
In the present study, minor allele frequency for CETP Taq1B was 41 %, which compares closely with the value of 42 % calculated in healthy white individuals in a meta-analysis( Reference Thompson, Di Angelantonio and Sarwar 13 ). B2 carriers tended to have higher HDL-C and apoA1 and lower TAG concentrations than B1/B1 homozygotes at baseline 2, but the differences were not significant, possibly as a result of a lack of power. However, at baseline 2, TC:HDL-C, TAG:HDL-C and apoB:apoA1 ratios and sLDL concentrations were significantly lower in B2 carriers than in B1/B1 homozygotes. Overall, this is suggestive of a better CVD risk profile for B2 carriers, in line with the literature( Reference Thompson, Di Angelantonio and Sarwar 13 ).
The current increase in obesity rates and associated deleterious effects on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism, independent of LDL-cholesterol concentrations, have led to much research being focused on strategies to address these other lipoprotein abnormalities. Recent research suggests that lipid and lipoprotein ratios have a greater predictive value than isolated parameters, with regard to CVD risk, as they more accurately capture overall lipoprotein metabolism( Reference Musunuru 4 , Reference Millan, Pinto and Munoz 31 ). The TAG:HDL-C ratio has been suggested as a surrogate marker for IR, describing altered lipid and carbohydrate metabolism( Reference Cordero, Andres and Ordonez 32 ). Furthermore, the ratio is linked to the presence of atherogenic sLDL( Reference Miller, Stone and Ballantyne 33 ). With improvements being observed in the TAG:HDL-C ratio, the results of the present study indicate that B1/B1 homozygotes of the CETP Taq1B SNP (more than 30 % of the population) could particularly benefit from the regular daily consumption of green kiwifruit. Although modest, the reduction in the TAG:HDL-C ratio, if confirmed, could be expected to translate into CVD risk reduction in this group.
Although we did not measure CETP mass or activity, we hypothesise that the variance in responses to the kiwifruit intervention between B1/B1 homozygotes and B2 carriers observed in the present study may be mediated in part by a differential impact of kiwifruit bioactives on CETP activity, with a greater inhibition in B1/B1 homozygotes along with the net effect of increasing HDL-C and decreasing TAG concentrations. In a 6-week study in hamsters, the addition of apple polyphenols to a control diet has been found to lower CETP activity and result in higher HDL-C and lower TAG concentrations. The inhibition of CETP by apple polyphenols has also been confirmed in vitro ( Reference Lam, Zhang and Yu 34 ). Some of these apple polyphenols are also found in kiwifruit, with kiwifruit also containing a high percentage of additional unextractable (non-identified) phenolics( Reference Fiorentino, D'Abrosca and Pacifico 35 – Reference Tarascou, Souquet and Mazauric 37 ).
A strength of the present study was the randomly controlled cross-over design, as this is considered to be the most robust statistically to identify inter-individual variability in dietary responses, as subjects serve as their own controls( Reference Rideout 38 ). The SNP chosen were carefully considered with regard to factors such as the frequencies of the alleles and their relationship with HDL metabolism.
As a retrospective analysis, which is, therefore, exploratory by nature, the study does have some limitations. Importantly, mechanistic pathways could not be explored, including whether kiwifruit can inhibit CETP activity. The study was also conducted in a specific population group. Therefore, it will be important for future studies to not only confirm our findings, but also to test the effects in other populations, including women.
In conclusion, we report that the Taq1B polymorphism of the CETP gene could modulate the plasma lipid response to the consumption of green kiwifruit against an overall healthy diet background in hypercholesterolaemic males, with improvements in the TAG:HLD-C ratio of B1/B1 homozygotes, a group at a higher risk of an atherogenic lipoprotein profile. Although moderate, if confirmed, these effects could be expected to translate into an overall reduction of CVD risk in B1/B1 homozygotes and add to the accumulating evidence that this genotype may particularly benefit from targeted interventions.
These findings add to the body of evidence on diet–gene interactions, which may in future lead to a greater personalisation of dietary recommendations. However, this area of research is far more complex than first thought, and the challenge is to integrate multiple genetic, physiological and environmental interactions into stratified recommendations that will afford maximum benefit to individuals( Reference Rideout 38 , Reference Minihane 39 ).
Supplementary material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0007114513003437
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the participants of the study, the IFNHH research team and A. M. M.'s research team at the University of East Anglia and cordially thank the research team at the University of East Anglia, especially Kenna Slim and Dr David Vauzour.
The present study was funded by an unrestricted grant from Zespri International Limited, New Zealand. Zespri International Limited had no role in the design and analysis of the study or in the writing of this article.
The authors' contributions were as follows: W. S., R. K., C. A. C., P. R. v. H. and C. S. G. were involved in study design and data collection; C. S. G. carried out SNP determination and statistical analyses in collaboration with B. J.; A. M. M. gave significant advice regarding the analysis and interpretation of genotype data and conducted sLDL analysis; C. S. G. wrote the initial draft of the manuscript, which was modified after feedback from all the co-authors.
None of the authors has any conflicts of interest to declare.






