Major depression is common in women, with 17% of women aged 18 years and older from a nationally representative US sample reporting a history of one or more major depressive episodes (Hasin et al., Reference Hasin, Goodwin, Stinson and Grant2005). Results from multiple population surveys have revealed that African-American (AA) women are less likely than European-American (EA) women to meet criteria for lifetime Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Edition (DSM-IV) major depressive disorder (MDD; e.g., Hasin et al., Reference Hasin, Goodwin, Stinson and Grant2005; Kessler et al., Reference Kessler, Berglund, Demler, Jin, Koretz, Merikangas and Wang2003; Williams et al., Reference Williams, Gonzalez, Neighbors, Nesse, Abelson, Sweetman and Jackson2007) — a finding that has been noted as paradoxical in light of the considerably higher disease burden from ‘physical’ illnesses and exposure to environmental stressors among AA women in the United States (Jackson et al., Reference Jackson, Knight and Rafferty2010; Keyes, Reference Keyes2009). Studies exploring reasons for the lower lifetime prevalence of MDD among AA women have often combined data across genders and/or age categories (Kessler et al., Reference Kessler, Berglund, Demler, Jin, Koretz, Merikangas and Wang2003; Keyes et al., Reference Keyes, Barnes and Bates2011; Williams et al., Reference Williams, Gonzalez, Neighbors, Nesse, Abelson, Sweetman and Jackson2007). The few studies that have examined racial differences in MDD prevalence and risk factors specifically in women have focused on middle- and older-aged women. As there is consistent evidence of birth cohort effects on the prevalence of MDD with individuals born more recently having greater cumulative lifetime prevalence of MDD than members of older age cohorts did at the same ages (Kessler et al., Reference Kessler, Berglund, Demler, Jin, Koretz, Merikangas and Wang2003; Wittchen & Uhmann, Reference Wittchen and Uhmann2010), it is possible that associations between and within racial categories observed in previous studies using older samples do not generalize to young adult women.
Using data from monozygotic (MZ) and dizygotic (DZ) twin pairs reared together (sharing 100% or an average of 50% of segregating genes respectively), it is possible to parse the variance in a phenotype into additive genetic sources (heritability), environmental sources shared by members of a twin pair (e.g., family socio-economic status, neighborhood, school), and environmental influences that contribute to within-pair differences. Classical twin studies have shown that genetic as well as environmental factors contribute to risk of MDD. In a meta-analysis of twin studies consisting almost entirely of men and women of European ancestry (Bierut et al., Reference Bierut, Heath, Bucholz, Dinwiddie, Madden, Statham and Martin1999; Kendler et al., Reference Kendler, Pedersen, Neale and Mathe1995a, Reference Kendler, Walters, Neale, Kessler, Heath and Eaves1995b; Kendler & Prescott, Reference Kendler and Prescott1999; Lyons et al., Reference Lyons, Eisen, Goldberg, True, Lin, Meyer, Joanne and Tsuang1998; McGuffin et al., Reference McGuffin, Katz, Watkins and Rutherford1996), 37% (95% confidence interval [CI] = 31–42%) of the variance in liability to MDD was estimated to be attributable to additive genetic effects, with the remaining variance due to non-shared environmental factors (Sullivan et al., Reference Sullivan, Neale and Kendler2000). Similar estimates were reported in a more recent study of the heritability of lifetime DSM-IV MDD using data collected at baseline from the same EA and AA female twin pairs used for the current analyses (Glowinski et al., Reference Glowinski, Madden, Bucholz, Lynskey and Heath2003). Given the relatively low prevalence of MDD due to the young age of the sample (median age: 15 years) at the baseline assessment, there was insufficient statistical power to permit contrasts of the heritability of lifetime MDD by race.
Environmental factors may affect heritability estimates through gene by shared environment interaction (G × SE); variance attributable to G × SE interactions, if present, is included in the heritability estimate, as heritability and variance due to G × SE interactions are confounded using the classical twin method (Heath & Martin, Reference Heath and Martin1993). Thus, it is possible that heritability estimates from European ancestry samples do not generalize to African-Americans due to differences in environmental exposures. To our knowledge, to date only one study has examined the heritability of depressive symptomatology among AA twin pairs, finding that both additive genetic (40%) and non-shared environmental (56%) effects influenced liability to past week depressive symptoms in AA male and female twin pairs aged 25–88 years (mean age: 47.1 years; Whitfield et al., Reference Whitfield, Edwards, Brandon and McDougald2008). While these estimates were similar to those from previous studies using European ancestry samples, conclusions regarding depression heritability differences by race cannot be drawn because the study used a non-diagnostic, state measure of past week depressive symptoms and did not include any European ancestry twin pairs for comparison (Suthers et al., Reference Suthers, Gatz and Fiske2004).
Given the paucity of information in the literature about potential racial differences in the heritability of major depression, the objectives of the current study were to explore racial differences in (1) MDD prevalence, symptomatology, and risk factors, and (2) latent genetic and/or environmental liability to DSM-IV MDD in a large, representative sample of AA and EA young adult female twins.
Materials and Methods
Sample
The Missouri Adolescent Female Twin Study (MOAFTS) is a study of female twin pairs identified from state birth records as born in Missouri between 1975 and 1985 to a mother who was a state resident. Participants included both AA (14.6%) and EA (85.4%) individuals (as reported by the mother at the time of birth), reflecting the racial distribution in the state during this time period. A baseline interview was conducted with the twins, beginning in 1995 (median age: 15 years; Glowinski et al., Reference Glowinski, Madden, Bucholz, Lynskey and Heath2003). When possible, interviews were also conducted with a parent (usually the mother) at the time the twins entered the study. Zygosity was assigned using an algorithm based on answers to standard questions (Nichols & Bilbro, Reference Nichols and Bilbro1966) included in the young adult follow-up assessment. This method has been shown to be 95% accurate in comparison to genotyping (Eaves et al., Reference Eaves, Eysenck and Martin1989). The first full-length young adult follow-up interview was conducted on an average of 6 years after the baseline assessment (median age: 22 years), as all members of the target cohort were ≥18 years of age and study participation was no longer contingent upon parental consent, all individuals from the original sampling frame were invited to participate, even if they had not participated at baseline, unless they or their families had previously refused consent. All protocols were approved by the institutional review board at Washington University School of Medicine. Additional details regarding the sample are available elsewhere (Glowinski et al., Reference Glowinski, Madden, Bucholz, Lynskey and Heath2003; Heath et al., Reference Heath, Madden, Grant, McLaughlin, Todorov and Bucholz1999, Reference Heath, Howells, Bucholz, Glowinski, Elliot and Madden2002; Waldron et al., Reference Waldron, Bucholz, Lynskey, Madden and Heath2013). There were 550 AA (254 complete pairs, 43.7% MZ) and 3226 EA (1514 complete pairs, 56.3% MZ) respondents with complete depression assessments at follow-up, out of a total of 370 AA and 1999 EA pairs originally identified from birth records.
Assessment
Twins were interviewed at baseline and follow-up by telephone using an adaptation of the Semi-Structured Assessment for the Genetics of Alcoholism (SSAGA), a comprehensive structured psychiatric diagnostic instrument that has been shown to be a reliable and valid diagnostic assessment of lifetime DSM-IV psychiatric disorders, including MDD (Bucholz et al., Reference Bucholz, Cadoret, Cloninger, Dinwiddie, Hesselbrock, Nurnberger and Schuckit1994; Hesselbrock et al., Reference Hesselbrock, Mesa, Bucholz, Schuckit and Hesselbrock1999). For the current analyses, information on lifetime MDD symptoms was obtained from the follow-up interview, with lifetime diagnosis coded by computer algorithm. In the depression section of the follow-up interview, respondents who reported ever experiencing dysphoria, anhedonia, and/or irritability (if aged <18 years at the time the symptom was experienced) for ≥2 weeks were asked to identify the most severe period of having such symptoms. A series of questions probing functional impairment during that period followed, including receipt of treatment, substantial work or educational difficulties, and serious relationship disturbances. Respondents indicating functional impairment were then asked about specific DSM-IV major depression symptoms during their most severe depressive episode and asked whether they had experienced five or more symptoms together during the same 2-week period. If fewer than five symptoms were endorsed or if five or more symptoms did not occur together in a 2-week period, respondents were asked to nominate another 2-week period when they experienced dysphoria, anhedonia, and/or irritability and routed through the full depression section again for this other episode. Those who reported experiencing five or more symptoms during a depressive episode were coded positive for lifetime MDD. At the end of the section, respondents were also asked if and when they had experienced other depressive episodes, and if so, brief characterizations of these were obtained.
Demographic and environmental variables identified from the literature as being associated with MDD that were assessed in one or more waves of MOAFTS data collection were included as covariates in logistic regression models. Age at interview was modeled as a binary variable using the median age of 22 years at interview as the cut-off age. Age at menarche was dichotomized into early (<12 years) versus average/late (≥12 years; Black & Klein, Reference Black and Klein2012; Joinson et al., Reference Joinson, Heron, Lewis, Croudace and Araya2011). Twin marital status (e.g., Hasin et al., Reference Hasin, Goodwin, Stinson and Grant2005; Kessler et al., Reference Kessler, Berglund, Demler, Jin, Koretz, Merikangas and Wang2003) at the time of follow-up interview was coded as married or living with someone as though married versus not married or living with someone as though married.
Trauma history (e.g., child abuse; Molnar et al., Reference Molnar, Buka and Kessler, Ronald2001; Nelson et al., Reference Nelson, Heath, Madden, Cooper, Lynne, Bucholz and Martin2002; Widom et al., Reference Widom, DuMont and Czaja2007) was assessed at baseline (twins age: 16 years and older only) and follow-up using a checklist of traumatic events adapted from the National Comorbidity Survey (see Table 2 for the list of traumas assessed; Kessler et al., Reference Kessler, Sonnega, Evelyn, Hughes and Nelson1995). Information on physical abuse from the checklist was combined with responses to additional questions regarding harsh physical punishment from the childhood rearing environment section to form a single physical abuse variable. Similarly, checklist responses regarding rape and sexual molestation were combined with responses to questions on forced sex and incest from other interview sections to form a single childhood sexual abuse variable. Child abuse variables were coded positive if a respondent reported having experienced the event at either baseline or follow-up and the event first happened before age 16 years. This age cutoff was chosen because we were specifically interested in events occurring in childhood and early adolescence (Sartor et al., Reference Sartor, Waldron, Duncan, Grant, McCutcheon, Nelson and Heath2013).
Maternal and paternal education levels (used as an indicator of family socio-economic status; e.g., Hasin et al., Reference Hasin, Goodwin, Stinson and Grant2005; Kessler et al., Reference Kessler, Berglund, Demler, Jin, Koretz, Merikangas and Wang2003) were obtained from parental self-report or, if only one parent completed an interview, from co-parent's report. If data were not available from either parent, twin report of parental education from Wave 5, the only twin interview to query all respondents in the cohort regarding parental education, was substituted for parent report if available. Parental education was categorized into the following: less than high school, high school or greater, and a third category for women with missing maternal (n = 93) or paternal (n = 159) education data and included in multivariable models as a set of indicator variables with parental education as high school or greater as the referent. History of parental separation (Amato & Keith, Reference Amato and Keith1991) for reasons of relationship dissolution before the twins reached age of 18 years was coded from items included in the parent and twin interviews, with twin interviews only used when parental interviews were not available. (Due to limitations of the interview data, it was not possible to date the separation more precisely than <18 years for a portion of the sample; see Waldron et al., Reference Waldron, Bucholz, Lynskey, Madden and Heath2013 for details.) Maternal and paternal alcohol use disorder (Anda et al., Reference Anda, Whitfield, Felitti, Chapman, Edwards, Dube and Williamson2002) was coded as a three-level variable. A parent was considered ‘definite’ for alcohol use disorder if (1) he or she met criteria for DSM-IV alcohol dependence through self-report, or (2) two or more informants indicated that the parent had three or more alcohol dependence symptoms (asked of the co-parent) or that drinking had ever caused the parent ‘problems with health, family job, or police, or other problems’ and that the parent was an ‘excessive drinker’ (asked of the twins; Waldron et al., Reference Waldron, Bucholz, Lynskey, Madden and Heath2013). Parents with only one positive informant report were grouped into a second, ‘probable’ category. Thus, maternal and paternal alcohol use disorder was each included in logistic regression models as a set of indicator variables (definite, probable, and no alcohol use disorder [referent]).
Phenotypic Analyses
Phenotypic statistical analyses were conducted using Stata Version 9 (StataCorp, 2005). Survey commands were used for the analysis of bivariate associations. Under the survey command, the Pearson χ2 statistic is corrected for the twin sampling design using the Rao and Scott (Reference Rao and Scott1984) second order correction, converting the Pearson χ2 into an F-statistic (Rao & Scott, Reference Rao and Scott1984). Racial differences in continuous and ordinal variables were evaluated with t-tests and Mann–Whitney U tests respectively. For logistic regression models, the Huber–White robust variance estimation was used to adjust standard errors for the non-independence of observations inherent in twin data (StataCorp, 2005).
Phenotypic analyses proceeded in several steps. First, we assessed bivariate associations between race and the prevalence of lifetime DSM-IV MDD, as well as endorsement of specific MDD symptoms during the most severe depressive episode among women with a history of a lifetime MDD diagnosis (see Table 1). Second, we compared AA and EA women on MDD risk factors, initially including all women in the analysis and then limiting analyses to women with a lifetime MDD diagnosis (see Table 2). Variables with p < .20 for contrasts in the entire sample were then used as covariates in a logistic regression model for the association between race and MDD. Third, we compared women with and without MDD on MDD risk factors separately by race (see Table 3). To identify independent risk factors for MDD in AA and EA women, variables with p < .20 in the stratified analyses were then entered into stratified logistic regression models. In the interest of parsimony, variables that were not statistically significant after adjusting for other variables in the full model were then removed, and a log-likelihood ratio test was performed to ensure that the reduced and full models were comparable in fit. Final stratified models included any independent variable that was retained in the reduced model for either AA or EA women to allow for comparability between groups.
TABLE 1 Depression Symptoms Among European-American (n = 606) and African-American (n = 136) Female Twins Meeting DSM-IV MDD
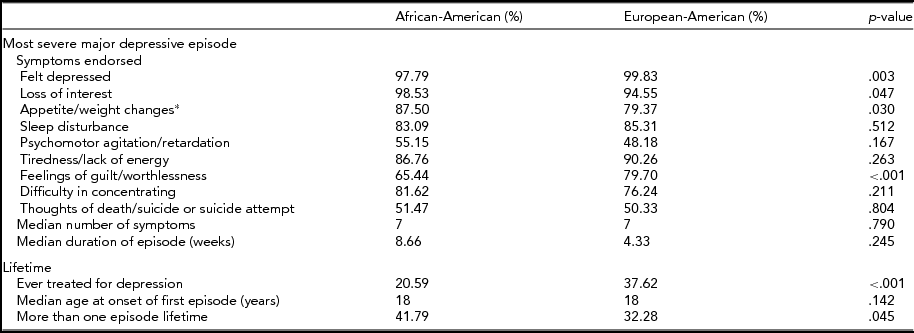
MDD = major depressive disorder.
*Increase or decrease.
p-values are from chi-square tests (dichotomous variables) or Mann–Whitney tests (ordinal variables).
TABLE 2 Sample Characteristics Among the Entire Sample and Among Women Meeting Criteria for DSM-IV Lifetime Major Depression
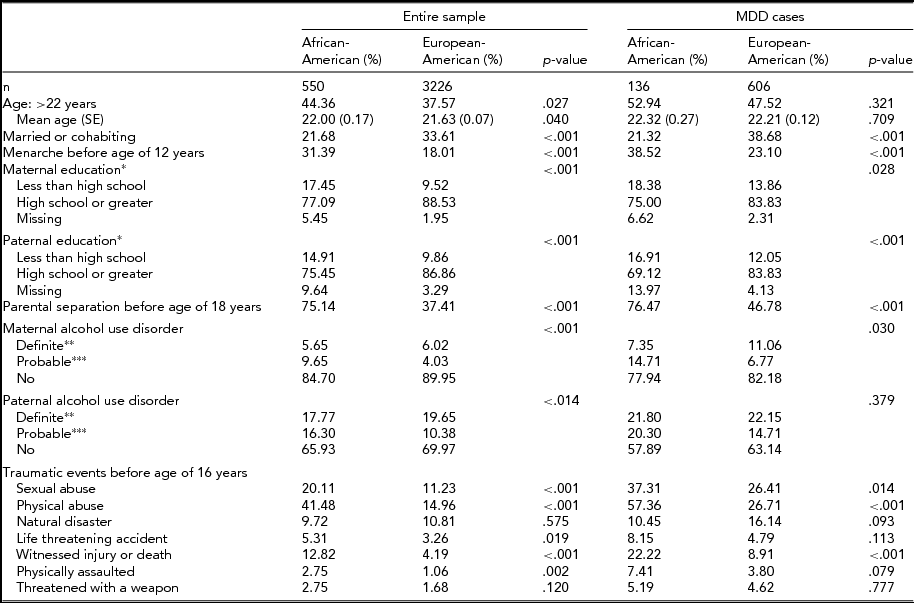
*Self-, co-parent-, or twin-report; **self-report or positive report from two or more informants; ***positive report from one informant.
TABLE 3 Sample Characteristics by Race and Lifetime DSM-IV Major Depressive Disorder Diagnosis
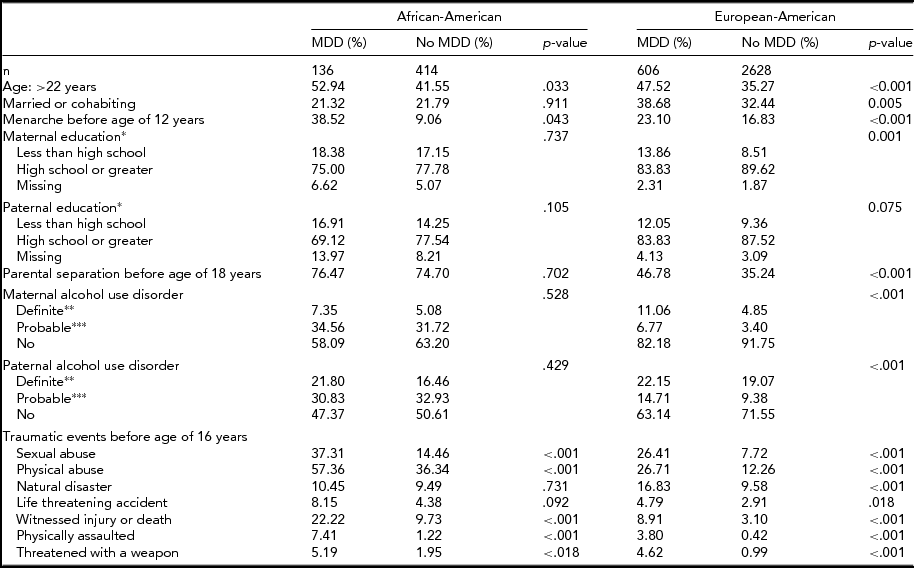
*Self-, co-parent-, or twin-report; **self-report or positive report from two or more informants; ***positive report from one informant.
Genetic Analyses
Data from MZ and DZ twin pairs can be used to estimate the liability to MDD that is due to additive genetic effects (A), shared environmental effects (C) or dominant genetic effects (D), and non-shared environmental effects (E), where: A is the sum of the individual effects of multiple genes on a given trait, C represents factors that make family members similar, D represents non-additive or genetic interaction effects, and E comprises factors that make family members dissimilar, as well as measurement error. In the classical twin design, members of MZ and DZ pairs are assumed to share 100% and 50% of additive genetic factors respectively. Shared environmental factors are assumed to be shared 100% across members of MZ and DZ pairs, and unique environmental influences are uncorrelated across twins (i.e., not shared by co-twins). Notably, in a classical twin design, the statistical power to detect dominant genetic effects is low, and it is not possible to examine these effects simultaneously with shared environmental effects due to confounding (Sham, Reference Sham1998).
Twin correlations and biometrical model-fitting were conducted in Mx (Neale & Cardon, Reference Neale and Cardon1992; Neale et al., Reference Neale, Boker, Xie and Maes2006). Lifetime MDD was modeled as a binary variable and variance components were adjusted for age at interview by controlling for the probit regression on age, which was included as a set of dummy variables reflecting age quartiles (age: 18–19, 20–22, and 23–24 years, with ≥25 years as the referent category). To determine the best fitting model, we first estimated the full univariate twin model separately among AA and EA women. Next, multiple sub-models of the full ACE or ADE model that constrained A, C, or D to zero were fitted to the data. Once the best fitting models for each racial group were selected, we then tested whether the specific parameter estimates could be equated across EA and AA groups. For all analyses, standard chi-square difference tests were used to compare the fit of nested models, with p < .05 an indication that the parameter(s) could not be dropped from the model without a significant decrement in model fit (Neale et al., Reference Neale, Boker, Xie and Maes2006). Akaike's Information Criterion (AIC) was used to compare non-nested models with lower AIC values indicating better-fitting and more parsimonious models.
Results
Phenotypic Analyses
The prevalence of lifetime MDD among AA women was significantly greater than that among EA women (24.73% vs. 18.78%, p = .003). As shown in Table 1, AA women with MDD were more likely to report recurrent episodes (41.79% vs. 32.23%; p < .001) but were less likely to have ever been treated for depression (20.59% vs. 37.62%, p < .001) compared with their EA counterparts. Rates of symptom endorsement for the most severe depressive episode were broadly comparable across groups, with the notable exception being the lower endorsement of feelings of guilt/worthlessness by AA women (65.44% vs. 79.70%, p < .001).
Risk factors for MDD were more commonly endorsed by AA women (Table 2, left half), with the most substantial differences observed for childhood sexual abuse (20.11% vs. 11.23%), childhood physical abuse (41.48% vs. 14.96%), parental separation (75.14% vs. 37.41%), and witnessing injury or death (12.82% vs. 4.19%). Similar differences in rates were seen even when comparisons were limited to MDD cases (Table 2, right half). Despite a higher overall prevalence of lifetime MDD, AA women had lower, but not statistically significant, odds of lifetime MDD than EA women after adjusting for risk factors that differed between AA and EA women (odds ratio [OR] = 0.88, 95% CI = 0.67–1.15).
Although many associations between MDD risk factors and diagnosis were similar for AA and EA women in bivariate analyses stratified by race, there were several risk factors that were only associated with MDD among EA women, such as parental separation and maternal and paternal education and alcohol use disorder (Table 3). Odds ratios in the final logistic regression models predicting MDD for AA and EA women tended to be similar; however, some ORs were only statistically significant among EA women (see Table 4). The only variables with substantial differences in effect size were definite maternal alcohol use disorder, which was positively associated with MDD solely in EA women (1.82 (1.25–2.64) vs. 0.90 (0.28–2.88) in AA women), and missing paternal education data (a function of paternal non-participation or lack of maternal or twin knowledge regarding paternal education level), which was associated with MDD only among AA women, 2.29 (1.14–4.63) versus 0.91 (0.54–1.54) in EA women.
TABLE 4 Odds Ratios and 95% Confidence Intervals for Variables Included in the Final Logistic Regression Models Predicting DSM-IV Major Depressive Disorder Among African-American and European-American Women
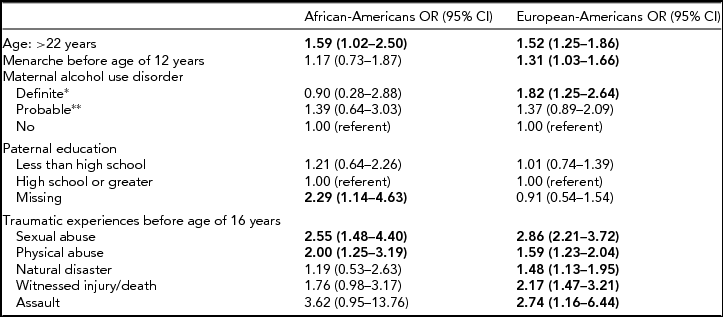
*Self-report or positive report from two or more informants; **positive report from one informant.
Bold type indicates statistical significance (p < .05).
Latent Genetic and Environmental Risk for Lifetime MDD
The MZ twin pair correlation was greater than the DZ twin pair correlation among AA (rMZ = 0.61, 95% CI = 0.31–0.82; rDZ = 0.16, 95% CI = 0.00–0.45) and EA (rMZ = 0.40, 95% CI = 0.27–0.51; rDZ = 0.19, 95% CI = 0.02–0.34) twins. In both AA and EA pairs, the best fitting model allowed for additive genetic and non-shared environmental, but not shared environmental, contributions to variation in MDD liability (see Table 5). Among AA women, 56% (95% CI: 29–78%) of the variance in MDD liability was attributable to additive genetic effects, with the remainder due to non-shared environment (44%, 95% CI = 22–72%; AIC = -464.29). In contrast, additive genetic and non-shared environmental effects accounted for 41% (29–52%) and 59% (48–71%) of the overall phenotypic variance in MDD respectively (AIC = -3228.87) among EA women. A model in which estimates were constrained to be equal across racial category, however, did not provide a statistically significantly worse fit to the data, and was thus chosen as the final model. In this model, additive genetic variance explained 43% (33–53%) of the variance in MDD, with the remainder attributable to non-shared environment (57%, 47–67%).
TABLE 5 Model-Fitting Results for Major Depressive Disorder

A = additive genetic effects; C = shared environmental effects; D = dominant genetic effects; E = non-shared environmental effects; a2 = proportion of variance in MDD due to additive genetic effects; c2 = proportion of variance in MDD due to shared environmental effects; d2 = proportion of variance in MDD due to dominant genetic effects; e2 = proportion of variance in MDD due to non-shared environmental effects; -2LL = -2 log likelihood; df = degrees of freedom; AIC = Akaike's Information Criterion; Δχ2 = chi-square difference test statistic; Δdf = change in degrees of freedom; Δp = p-value associated with Δχ2.
The best fitting models are indicated in bold type.
*This is a 1-df test because with two parameters, the second parameter by definition becomes fixed when the first parameter is equated across ethnicities.
Discussion
This study examined racial differences in MDD prevalence, symptomatology, and risk factors in a large, representative sample of AA and EA young adult female twins. Although the lifetime prevalence of MDD was higher in AA women, most of the assessed risk factors were more likely to be endorsed by AA than by EA women, and after adjusting for these factors AA women had lower, but not statistically significant, odds of meeting criteria for MDD than EA women. This finding is consistent with previous studies reporting no significant differences or lower prevalence of depression in AA women compared with EA women (Dunlop et al., Reference Dunlop, Song, Lyons, Manheim and Chang2003; Hasin et al., Reference Hasin, Goodwin, Stinson and Grant2005; Kessler et al., Reference Kessler, Berglund, Demler, Jin, Koretz, Merikangas and Wang2003; Riolo et al., Reference Riolo, Nguyen, Greden and King2004; Williams et al., Reference Williams, Gonzalez, Neighbors, Nesse, Abelson, Sweetman and Jackson2007). Results from latent genetic analyses provided some evidence for heterogeneity of effects by race, with higher heritability among AA women; however, the best fitting model was one in which additive genetic and non-shared environmental effects were constrained to be equal for AA and EA women. We obtained zero estimates for shared environmental contributions to variation in MDD risk, a pattern seen consistently in twin studies of MDD (cf. Sullivan et al., Reference Sullivan, Neale and Kendler2000). This pattern of consistent zero estimates across studies strongly implies negative confounding, that is, non-additive genetic contributions to risk are masking any shared environmental influences so that we are unable to precisely quantify the magnitude of the latter influences. It is sometimes misinterpreted as implying the absence of shared environmental effects (Sullivan et al., Reference Sullivan, Neale and Kendler2000): If the true value of a variance component were zero, in the absence of negative confounding we would expect to observe some studies reporting positive point estimates.
To our knowledge, this was the first study to examine racial differences in the heritability of MDD among AA and EA young women. Our combined heritability estimate was comparable with that reported in a previous meta-analysis of twin studies of the heritability of major depression conducted with predominantly European ancestry samples (37%, 31–42%; Sullivan et al., Reference Sullivan, Neale and Kendler2000), as well as more recent studies (Glowinski et al., Reference Glowinski, Madden, Bucholz, Lynskey and Heath2003; Kendler et al., Reference Kendler, Gatz, Gardner, Charles and Pedersen2006), including that from a previously published study that estimated the heritability of MDD to be 40.4% (23.9–55.1%) in the same cohort using combined data (i.e., no stratification by race) collected at the baseline interview, which was conducted at a median of 6 years prior to the data used for the current analyses (Glowinski et al., Reference Glowinski, Madden, Bucholz, Lynskey and Heath2003). Although the heritability estimate calculated separately among AA women in our study was greater than that reported in the only other published study of the heritability of depression in AA twins, that study used a state depression phenotype (CES-D score, which is a measure of past 7-day depressive symptoms), an older sample that included men and women, and did not include non-AA twins (Whitfield et al., Reference Whitfield, Edwards, Brandon and McDougald2008). Thus, one cannot draw meaningful comparisons to the results presented here.
It was possible to constrain the MDD heritability estimates to be equivalent between AA and EA women; however, it should be noted that the heritability estimate among AA women was 1.36 times higher than that among EA women and that, given the relatively small number of AA twin pairs, we were underpowered to detect a difference of this magnitude. Thus, further research with larger samples of AA female twin pairs is needed to more definitively answer the question of whether or not there are differences between AA and EA women in the heritability of MDD, particularly since there are multiple reasons why such differences in heritability might be observed. For example, a plausible explanation for the higher heritability of MDD among AA compared with EA women is that there is a stronger contribution of genotype by shared environment interaction effects in AA women, with increased opportunity for the realization of genetic risk in this group because of the high prevalence and familiarity of adverse environmental experiences. As the effects of G × SE interaction cannot be estimated separately in the classical twin study, variance attributable to G × SE interaction is included in the total heritability estimate (Heath & Martin, Reference Heath and Martin1993). Of note, multiple previous studies have reported evidence of specific gene-by-measured environment interaction in MDD (Caspi et al., Reference Caspi, Sugden, Moffitt, Terrie, Taylor, Craig, Harrington and Poulton2003; Karg et al., Reference Karg, Burmeister, Shedden and Sen2011; Munafo, Reference Munafo2012; Risch et al., Reference Risch, Herrell, Lehner, Liang, Eaves, Hoh and Merikangas2009). Given racial discrimination, residential segregation, and lower availability of socio-economic resources, AA women on average are more likely to be exposed to many stressors than EA women (Gee et al., Reference Gee, Walsemann and Brondolo2012; Shuey & Willson, Reference Shuey and Willson2008; Walsemann et al., Reference Walsemann, Geronimus and Gee2008, Reference Walsemann, Gee and Geronimus2009). In the current study, many of the risk factors significantly associated with MDD in multivariable models among AA women were also associated with MDD at similar magnitudes among EA women, but these risk factors were significantly more likely to be endorsed by AA women than by EA women. Another potential explanation is that heritability differences could be due to true or artifactual differences in the MDD phenotype between AA and EA women, although similar symptom endorsement probabilities by AA versus EA women with MDD histories make this explanation less likely.
Limitations
This study is subject to certain limitations. First, in addition to low power to detect differences in heritability by race/ethnicity, sample sizes also were not sufficiently large to permit disaggregation of the contributions of genotype by environmental risk factor associations for individual environmental risk-exposures such as those suggested above. Second, onset of MDD in women occurs throughout the lifespan (Kessler et al., Reference Kessler, Berglund, Demler, Jin and Walters2005); thus, it is likely that some women in the sample who were considered unaffected in these analyses will develop MDD in the future, particularly given the relatively young age of the sample (median age: 22 years). As such, it is possible that these results may not be generalizable to older cohorts. Third, some environmental risk factors and correlates of MDD that have been shown to differ between AA and EA women, such as neighborhood characteristics and availability of coping resources, were not assessed in this study. Further, we decided not to include parental depression in the phenotypic analyses because it was assessed only through parental self-report (report from the twins about parental depression was not elicited) and parental participation in this study was much less common in AA than in EA families (64.65% of AA families vs. 81.69% of EA families had maternal interviews and 28.75% of AA families vs. 61.08% of EA families had paternal interviews). Fourth, there may have been cultural differences in behavior or interpretation of interview questions that could have affected the results. Although it is possible that such cultural differences could explain the large difference between AA and EA women in prevalence of childhood physical abuse (41.87% vs. 15.06%), the fact that the association between childhood physical abuse and MDD was stronger in AA than in EA women suggests that the higher prevalence of childhood physical abuse among AA women may not be due to over-reporting. Fifth, due to the large difference in sample size between the AA and EA groups, there was substantially more statistical power to detect variables associated with MDD among EA women than among AA women. Finally, we employed a large number of statistical tests. As these tests were not independent of one another, there remains an increased possibility of type I error. Therefore, we have given the p-values for bivariate statistical tests out to the thousandth decimal place so that the reader may adopt a more stringent alpha level when considering the results.
Conclusions
Although AA young women had higher heritability of MDD than their EA counterparts, this difference was not statistically significant. The observed difference may be explained by the higher likelihood of environmental risk exposures among African-Americans. Environmental risk exposures associated with major depressive disorder were similar for AA and EA women; however, the prevalence of these exposures was greater among African-Americans. These findings underscore the necessity of conducting genetic research on samples that include enough participants of non-European ancestry to detect differential effects by race, as well as the need for comprehensive assessments of individual, family, and contextual environmental factors that have been shown to differ by race. More broadly, our results point to the need to develop more comprehensive etiologic models for psychiatric disorders that take minority sub-groups into account, rather than continued reliance on etiologic models developed on samples that consist largely or exclusively of white non-Hispanics, as findings may not generalize to members of other racial and ethnic groups.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (A.C.H., R01 AA009022, K05 AA017688, R37 AA007728, AA017915, AA021492, T32 AA007580 P60 AA011998; K.K.B., R01 AA012640; C.E.S., R01 K08 AA017921); the National Institute of Drug Abuse (A.A., K02 DA032573; P.A.F.M., R01 DA012854; M.W., K01 DA023696; K.K.B., R01 DA014363); and the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (A.C.H., R01 HD049024).







